High Blood Sugar Symptoms

The Connection Between Carbs and High Blood Sugar
Carbs and High Blood Sugar
High blood sugar can be a serious problem, and not just for those with diabetes. Eating too much of the wrong type of carbs can affect your blood sugar levels, whether you’re diabetic or not. Learn how the two are connected, and how you can make simple dietary and lifestyle changes to help keep your blood sugar in check.
High Blood Sugar and the Connection to Carbohydrates
Understanding the link between carbohydrates and high blood sugar is crucial for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
Here, we will delve into the brief explanation of high blood sugar and its effects, emphasizing the importance of comprehending the connection between carbs and elevated blood sugar levels.
High Blood Sugar: A Brief Explanation:
When we consume food, especially those rich in carbohydrates, our bodies break down these complex sugars into glucose, the primary source of energy for our cells. As glucose enters the bloodstream, our pancreas releases the hormone insulin, which enables glucose to enter the cells and provide them with energy.
However, in individuals with diabetes, a disruption occurs in this balance, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Effects of High Blood Sugar
- Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels can cause excessive thirst, leading individuals to consume more fluids and subsequently urinate more frequently. This occurrence is due to the kidneys working harder to eliminate the excess glucose from the body through urine.
- Fatigue and Lack of Energy: When cells are unable to efficiently absorb glucose due to insufficient insulin or insulin resistance, the body is deprived of its main energy source. Consequently, this can lead to constant fatigue, decreased productivity, and an overall lack of energy.
- Blurred Vision and Slow Healing: Prolonged periods of elevated blood sugar levels can affect various parts of the body, including the eyes. Blurred vision may occur due to the swelling of the lens caused by changes in fluid balance. Additionally, high blood sugar impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds, increasing the risk of infections and delaying the healing process.
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease: Persistently high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and lead to the development of cardiovascular conditions. Over time, the excess glucose in the bloodstream can cause inflammation and atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart-related complications.
Understanding the Connection: Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar:
- Carbohydrates: The Primary Culprit
Carbohydrates play a significant role in raising blood sugar levels as they are broken down into glucose during digestion. It is essential to distinguish between different types of carbohydrates, such as simple carbohydrates found in sugary foods and refined grains, and complex carbohydrates present in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables.
- Counting Carbohydrates for Blood Sugar Control
Carbohydrate counting is a valuable strategy for individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. By monitoring and balancing their carbohydrate intake throughout the day, individuals can optimize their insulin dosage and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Understanding Carbohydrates
Here, we will delve into the fascinating world of carbohydrates – the essential nutrients that fuel our bodies and provide us with the energy we need to go about our day. We will explore the definition and types of carbohydrates, understand their role as a primary source of energy, and uncover the impact they have on our blood sugar levels. So, let’s begin our journey of understanding carbohydrates!
Definition and Types of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients, alongside proteins and fats, that are vital for maintaining a healthy and balanced diet. They are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and they can be classified into two main types: simple and complex carbohydrates.
Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, consist of one or two sugar molecules and are easier for the body to break down and absorb. They are commonly found in fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and refined sugars. Examples of simple carbohydrates include glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
On the other hand, complex carbohydrates are made up of longer chains of sugar molecules, making them more complex for the body to digest. They are found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables like potatoes. Complex carbohydrates provide a slower and more sustained release of energy compared to simple carbohydrates.
Role of Carbohydrates as a Primary Source of Energy
Carbohydrates play a vital role as the primary source of energy for our bodies. When we consume carbohydrates, our digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which is then transported through the bloodstream to cells throughout the body. Our body’s cells use glucose as fuel to perform various functions, including physical activity, brain function, and everyday tasks.
Additionally, carbohydrates provide quick energy. Simple carbohydrates, due to their shorter chains of sugar molecules, are rapidly absorbed by the body, leading to a quick burst of energy. This is particularly beneficial during intense physical activities or when immediate energy is needed.
Impact of Carbohydrates on Blood Sugar Levels
One crucial aspect of understanding carbohydrates is their impact on blood sugar levels. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which enters our bloodstream. As a result, the level of glucose in our blood rises.
For individuals with diabetes or those concerned about blood sugar management, monitoring carbohydrate intake becomes essential. Simple carbohydrates, due to their ease of digestion, can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, provide a slower and steadier release of glucose, promoting more stable blood sugar levels.
It is essential to strike a balance when consuming carbohydrates, especially for individuals with diabetes, to ensure proper blood sugar control. Understanding the types and effects of carbohydrates can aid in making informed dietary choices and managing overall health.
How Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbohydrates are a crucial source of energy for our bodies. They are found in various foods like grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. When carbohydrates are consumed, they undergo a digestion process in our bodies, ultimately affecting our blood sugar levels. Understanding how carbohydrates impact blood sugar is vital for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
- Digestion Process of Carbohydrates in the Body
The digestion of carbohydrates begins in our mouths, where enzymes break down complex carbohydrates into smaller molecules. As we chew and swallow, these carbohydrates pass through our digestive system and into our stomachs. Here, the stomach acid further breaks them down.
Next, the carbohydrates enter the small intestine, where they are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and galactose. These sugars are then absorbed into the bloodstream, causing a rise in blood sugar levels.
- Conversion of Carbohydrates to Glucose
Glucose, the primary sugar molecule derived from carbohydrates, plays a vital role in keeping our bodies functioning optimally. Once carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, it is transported via the bloodstream to our cells, providing them with the energy they need.
However, it is crucial to note that not all carbohydrates are equal. Different types of carbohydrates, such as complex and simple carbohydrates, affect our blood sugar levels differently.
Simple carbohydrates, found in foods like soda, candy, and sugary sweets, are rapidly converted into glucose, causing a sharp increase in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, are digested more slowly, leading to a gradual and steady release of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Release of Insulin to Regulate Blood Sugar Levels
To maintain stable blood sugar levels, our bodies rely on insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. When blood sugar levels rise after consuming carbohydrates, the pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream.
Insulin acts as a key that unlocks the cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy. It signals to the cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream, consequently lowering blood sugar levels. This intricate process helps prevent blood sugar levels from reaching dangerously high levels.
However, in individuals with diabetes, the production or effectiveness of insulin is impaired. This can result in high blood sugar levels because the cells are unable to effectively utilize glucose.
Consequently, people with diabetes need to manage their carbohydrate intake, medication, and lifestyle choices to regulate their blood sugar levels effectively.
The Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a measurement that ranks carbohydrates based on their effect on blood sugar levels. It provides valuable insights into how different foods can affect our bodies and is a valuable tool for managing blood sugar levels and overall health.
- Definition and Significance of the Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index is a numerical scale that measures how quickly and how much a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels compared to pure glucose, which has a GI value of 100. The GI scale ranges from to 100, with higher values indicating a faster and larger rise in blood sugar levels. This index is particularly relevant for individuals with diabetes, as it helps them make informed food choices that can aid in managing their condition.
The significance of the glycemic index lies in understanding how different carbohydrates affect our bodies. Foods with a high GI value are rapidly digested and absorbed, causing a sharp increase in blood sugar levels.
On the other hand, low-GI foods are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual and more sustained rise in blood sugar levels. By incorporating low-GI foods into our diets, we can promote stable blood sugar levels, increase satiety, and potentially reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
- Explanation of Low-GI and High-GI Foods
Low-GI foods are those that have a GI value of 55 or less. These foods are usually rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, which slow down digestion and absorption, leading to a gentle and steady increase in blood sugar levels.
Examples of low-GI foods include whole grains like quinoa and oatmeal, legumes such as lentils and chickpeas, most fruits and vegetables, and nuts and seeds. Incorporating these foods into our meals can provide sustained energy, promote weight management, and support overall well-being.
On the other hand, high-GI foods are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. These foods have a GI value of 70 or higher and are often low in fiber and nutrients. Examples of high-GI foods include sugary snacks and beverages, white bread and rice, potatoes, and processed breakfast cereals.
Consuming too many high-GI foods can result in blood sugar fluctuations, increased hunger, and a higher risk of chronic diseases. However, it’s important to note that not all high-GI foods are unhealthy, as some nutritious fruits and vegetables can have a high GI value due to their natural sugars.
- Influence of GI on Blood Sugar Levels
The glycemic index plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. When we consume high-GI foods, our blood sugar levels rise rapidly, triggering the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin helps transport glucose from the blood into the cells for energy or storage. However, this sudden surge in blood sugar followed by a rapid drop can leave us feeling tired, hungry, and craving more high-GI foods.
In contrast, low-GI foods promote a slower and more steady increase in blood sugar levels, resulting in a gradual release of insulin. This helps maintain stable energy levels, keeps us feeling fuller for longer, and reduces the likelihood of overeating or experiencing intense sugar cravings. For individuals with diabetes, understanding the GI of various foods can assist in managing insulin levels and achieving better glycemic control.
The Impact of Carbohydrate Consumption on High Blood Sugar
Now, it is time to explore how excessive carbohydrate intake can lead to blood sugar spikes, the effects of refined and processed carbohydrates on blood sugar, and the crucial role of portion control in managing blood sugar levels.
Excessive Carbohydrate Intake and Blood Sugar Spikes
- Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar: Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is a primary source of energy for our bodies. When we consume excessive amounts of carbohydrates, our blood sugar levels can soar, leading to a condition known as hyperglycemia.
- Glycemic Index: Different carbohydrates have varying effects on blood sugar levels. High glycemic index foods, such as white bread and sugary drinks, cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, while low glycemic index foods, like whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, result in a slower rise in blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Resistance: Chronically high blood sugar levels due to excessive carbohydrate consumption can contribute to insulin resistance. This condition makes it difficult for the body to properly regulate blood sugar, leading to a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Effects of Refined and Processed Carbohydrates on Blood Sugar
- Definition of Refined and Processed Carbohydrates: Refined and processed carbohydrates refer to foods that have been stripped of their natural fiber and nutrients during processing. These include white bread, pasta, sugary cereals, and processed snacks.
- Rapid Blood Sugar Spikes: Refined and processed carbohydrates are quickly broken down into glucose, causing a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This sudden surge is followed by a sharp drop, leaving individuals feeling fatigued and hungry, which can lead to overeating.
- Lack of Satiety: Foods high in refined carbohydrates often lack fiber and protein, which are essential for feeling full and satisfied. As a result, individuals may consume larger portions, leading to continued blood sugar spikes and weight gain.
Role of Portion Control in Managing Blood Sugar Levels
- Understanding Portion Sizes: Portion control involves being mindful of the quantity of food we consume. It is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. It allows for a more balanced and controlled intake of carbohydrates, preventing blood sugar spikes.
- Balancing Macronutrients: By managing portion sizes, we can ensure that our meals consist of a proper balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This helps slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to more stable blood sugar levels.
- The Plate Method: A useful tool for portion control is the plate method. This involves dividing your plate into sections for specific food groups, such as dedicating half the plate to non-starchy vegetables, a quarter to lean protein, and a quarter to whole grains or starchy vegetables.
Managing High Blood Sugar through Carbohydrate Choices
High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, is a common concern for individuals living with diabetes or anyone seeking to maintain optimal blood sugar levels. One effective way to manage this condition is by making mindful carbohydrate choices. In this chapter, we will explore the importance of selecting complex carbohydrates over simple ones, incorporating fiber-rich foods, and finding the right balance with proteins and fats to minimize blood sugar spikes.
- Opting for Complex Carbohydrates over Simple Carbohydrates
When it comes to managing blood sugar levels, the type of carbohydrates we consume plays a crucial role. Complex carbohydrates are a healthier choice compared to simple carbohydrates, as they are digested and absorbed more slowly by the body. This slow breakdown reduces the sudden increase in blood glucose levels.
The list of complex carbohydrates includes nutrient-rich whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread. Unlike refined grains, which have been stripped of most of their nutritional value, whole grains offer essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. By replacing white bread, white rice, and processed cereals with their whole grain counterparts, you can provide your body with a steady release of energy and better blood sugar regulation.
- Incorporating Fiber-Rich Foods to Slow Down Carbohydrate Digestion
Another effective way to manage high blood sugar is by incorporating fiber-rich foods into your daily diet. Dietary fiber is the indigestible part of plant-based foods that adds bulk to your meals, promoting feelings of fullness and aiding in digestion. More importantly, fiber helps slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Fruits and vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are excellent sources of dietary fiber. By including a variety of these foods in your meals, you not only enhance nutritional intake but also contribute to better blood sugar control. Aim for at least 25 to 30 grams of fiber per day, gradually increasing your intake to allow your body to adapt.
- Balancing Carbohydrate Intake with Proteins and Fats to Minimize Blood Sugar Spikes
While the focus of blood sugar management lies in carbohydrate choices, it’s crucial to strike a balance between carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Combining these macronutrients can help slow down digestion and minimize blood sugar spikes after meals.
Adding lean protein sources like poultry, fish, tofu, or beans to your meals helps regulate blood sugar levels. Protein takes longer to digest, preventing the rapid release of glucose into the bloodstream. Additionally, incorporating healthy fats from sources such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil can further slowdown digestion, providing a more sustained release of glucose.
By creating balanced meals that include a healthy mix of complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, you can effectively manage your blood sugar levels and maintain greater control over your health.
Monitoring Carbohydrate Intake for Better Blood Sugar Management
Here, we will discuss the importance of carbohydrate counting or tracking, the utilization of technology and tools to aid in carbohydrate monitoring, and the significance of consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance. By understanding these aspects, you can take control of your blood sugar levels and promote better overall health.
Importance of Carbohydrate Counting or Tracking
Carbohydrates are the main macronutrient that significantly affects blood sugar levels. Monitoring carbohydrate intake allows individuals to have better control over their blood sugar levels. Here’s why carbohydrate counting or tracking is crucial:
- Blood Sugar Management: By knowing the amount of carbohydrates consumed in each meal and snack, individuals can adjust their insulin doses or medications accordingly, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Individualized Approach: Different individuals may have different sensitivities to carbohydrates. Monitoring carbohydrate intake enables individuals to personalize their diet plans based on their unique needs, optimizing blood sugar management.
- Balanced Nutrition: Carbohydrate counting promotes a well-rounded and balanced diet. This approach emphasizes portion control and awareness of overall nutrient intake, ensuring that other essential nutrients, such as proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, are adequately included in meals.
Utilizing Technology and Tools to Aid in Carbohydrate Monitoring
With advancements in technology, various tools and applications have been developed to assist in carbohydrate monitoring. These technological aids offer convenience, accuracy, and real-time data, making blood sugar management easier for individuals. Here are some key tools and technologies:
- Carbohydrate Counting Apps: These smartphone applications allow users to track their carbohydrate intake by simply entering the food they consume. These apps often provide a database of foods and their corresponding carbohydrate content, simplifying the process of tracking and monitoring carbohydrate intake.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: CGM systems provide real-time blood sugar readings, helping individuals understand the impact of their carbohydrate intake on their blood sugar levels. By monitoring trends and patterns, individuals can make informed decisions about their food choices and insulin dosing.
- Insulin Pumps: Insulin pumps deliver a constant flow of insulin throughout the day, with the ability to customize insulin boluses based on carbohydrate intake. Some newer models even have built-in carbohydrate databases, allowing users to calculate and administer insulin doses more accurately.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional for Personalized Guidance
While technology and tools can greatly assist in carbohydrate monitoring, it is vital to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance. These professionals, including doctors, dietitians, and diabetes educators, can provide tailored advice and support based on an individual’s specific needs. Here’s why consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial:
- Individualized Recommendations: Healthcare professionals consider various factors such as age, weight, physical activity level, and overall health status to provide personalized recommendations regarding carbohydrate intake. This ensures that individuals receive the most appropriate guidance for their specific circumstances.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adjustments: Healthcare professionals can help individuals set goals and regularly monitor their progress. They can make adjustments to the carbohydrate intake plan as needed, considering changes in health or lifestyle that may impact blood sugar management.
- Education and Support: Diabetes management encompasses more than just monitoring carbohydrate intake. Healthcare professionals offer essential education on food choices, portion sizes, reading nutrition labels, and other aspects crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. They also provide the necessary support, answering questions and addressing concerns individuals may have along their diabetes journey.
Conclusion
High blood sugar is a problem that can have serious health implications. Eating too many of the wrong kinds of carbs can make it harder to manage your blood sugar, so it’s important to be aware of the connection between carbs and high blood sugar. Making small changes like eating more whole grains, eating smaller portions, reducing sugar intake and getting active can help you stay healthy and keep your blood sugar levels in check.
FAQs about the Connection Between Carbs and High Blood Sugar
Can all carbohydrates cause high blood sugar?
- While all carbohydrates can affect blood sugar levels, some have a greater impact than others. Refined carbs, processed foods, and sugary beverages tend to cause a more rapid and significant increase in blood sugar compared to whole foods that contain natural sugars and fiber.
Is it necessary to avoid carbohydrates completely to maintain normal blood sugar levels?
- It is not necessary to eliminate carbohydrates entirely from your diet. However, individuals with high blood sugar or diabetes should be mindful of their carbohydrate intake and make healthier choices by opting for complex carbs, fiber-rich foods, and controlling portion sizes.
Can low-carb diets help manage high blood sugar?
- Low-carb diets, such as the ketogenic or Atkins diet, have shown positive effects in managing high blood sugar. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the body relies on alternative fuel sources, such as fats, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
What are some healthier carbohydrate options to help control blood sugar?
- Opt for whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread instead of refined grains. Include plenty of non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and cauliflower. Additionally, legumes like lentils and chickpeas are excellent sources of complex carbs and fiber.
Are there any specific carbs that can help stabilize blood sugar levels?
- Foods rich in fiber, such as oats, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, can help slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, resulting in a slower and more controlled release of glucose into the bloodstream. Incorporate these foods within a balanced diet to promote stable blood sugar levels.
Should I monitor my carbohydrate intake if I have prediabetes or diabetes?
- If you have prediabetes or diabetes, monitoring carbohydrate intake is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. It is recommended to work with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to determine a suitable carbohydrate intake based on individual needs and medication.
Can lifestyle factors besides carbohydrates impact high blood sugar levels?
- Yes, lifestyle factors like physical activity, stress levels, and the overall balance of your diet can have an impact on blood sugar levels. Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and a well-rounded diet can contribute to better blood sugar control alongside carbohydrate management.

Can Blood Sugar Affect Blood Pressure?
Yes! Most definitely.
To understand the entire process and the associated traits, we must first understand what blood sugars are in the human body and their functions.
Also referred to as blood glucose, these constitute the significant sugars found in the bloodstream. They are usually the major energy sources within the human cells, among other sugars and molecules like ketone bodies.
Blood sugar levels are usually of utmost significance to individuals, given that too low levels could prompt varied health conditions, including hypoglycemia. At the same time, too high levels could lead to hyperglycemia and associated symptoms.
The human body is thus equipped with sensory cells all over capable of detecting changes in blood glucose levels and effecting subsequent changes. For instance, if the blood glucose level goes above the optimal levels, the condition will be detected in the pancreas prompting the release of insulin hormone, which, in conjunction with other hormones, rectifies the surge.
Similarly, pancreatic cells will also detect low blood glucose levels, prompting the release of glucagon and even catecholamine hormones that collectively work to fix the condition by increasing blood glucose levels. The healthy average blood glucose level thus typically ranges between 70 and 120 mg/dL.
Extreme blood glucose levels are usually associated with the different types of diabetes. However, to advance to the diabetes stage must imply that the blood glucose level detection system, the alpha and beta cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans, and the associated hormones are functionally impaired.
Hence, individuals with diabetes don’t often lose the ability to regulate blood sugar levels but rather the cells and systems involved.
How Your Body Regulates Blood Pressure
Despite near similar processes exploited in maintaining blood glucose and blood pressure levels, regulating blood pressure is often more complicated and critical. For instance, the body usually regulates blood glucose levels by making more blood sugars or exploiting alternative energy sources.
However, there is no way of making more or breaking down blood instantly within the body to regulate blood pressure. In fact, the body cannot make more or less ‘blood pressure’ like it does blood glucose. As such, blood glucose regulation is often much simple and achievable, unlike blood pressure regulation for the human body.
Take, for example, an individual with low blood pressure from low blood volume cannot instantly rectify their condition as more blood would be needed, something the body can’t manage to manufacture fast enough as it is with blood glucose. These individuals can suffer massive health implications like incapacitation and long-term brain and body harm. This hints at the severity and dangers associated with blood pressure imbalances.
Therefore, due to the limited blood pressure regulation options, the body often utilizes the hormones used in blood sugar regulation, catecholamine/adrenalin, and other hormones to facilitate the process. As such, if you have low blood pressure, the body detects this and releases catecholamines. These subsequently tighten up the blood vessels through vasoconstriction, making them narrower and thus more challenging for the heart to pump blood through the arteries, ultimately raising the blood pressure levels.
On the other hand, high blood pressure usually warrants reducing the arterial pressure build-up by lowering the overall blood volume in the vessels. This is often achieved through several avenues.
First, some of the blood glucose regulating hormones like insulin stimulate nitric oxide production by the endothelial cells, which initiates the vasodilation/expansion of the blood vessels. This subsequently reduces the arterial pressure and the pressure against the heart.
Expanded vessels also release water through diuresis in the kidneys, further lowering blood volume and thus blood pressure. These are just some of the few standard blood pressure regulation processes.
Similar to diabetics, imbalance in blood pressure prompts conditions like hypertension and hypotension. These individuals often can regulate their blood pressure but have impaired sensors and body systems responsible for controlling blood pressure levels.
How Blood Sugar Affects Blood Pressure
The blood sugar and blood pressure regulation systems are all interconnected, given that they depend on similar body hormones to affect changes in the body. For instance, as indicated above, insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose, is also associated with stimulating nitric oxide production in blood vessels.
It usually blocks the body’s ability to make nitric oxide which is significant for vasodilation of blood vessels and decrease in blood pressure. As such, if an individual with diabetes is utilizing insulin doses to facilitate blood glucose regulation, they should be aware of the underlying risks of high blood pressure, given that the body’s ability to lower blood pressure via nitric oxide production would be severely impaired.
Catecholamine hormones that regulate low blood pressure would also impact blood sugars by immensely raising the levels given the interconnected responses.
The same goes for low blood sugar individuals whose body systems utilize catecholamines to regulate the levels, subsequently prompting high blood pressure levels. This is a clear indication of how low blood sugar or low blood pressure could influence the rise/decline of the other.
It is also important to note that some blood pressure and blood glucose regulation medications may override the body’s natural protection systems and trigger these processes.
Can Diabetes Cause High Blood Pressure?
Diabetes and high blood pressure (hypertension) often go hand in hand as individuals suffering from one are often likely to suffer from the other. An individual with diabetes is thus often twice as likely to have high blood pressure as opposed to healthy folks.
The high blood sugar levels among diabetes patients can also often damage blood vessels and nerves of the heart, and these, when coupled with high blood pressure and associated symptoms, often result in increased strain on the heart muscles and blood vessels. This further increases the risk of heart/cardiovascular disease and even stroke.

As such, diabetes and hypertension often occur comorbidly, either at the same time or simultaneously. This is usually evident among populations as nearly one in every three American adults have hypertension.
Subsequently, two out of every three patients with diabetes usually have high blood pressure or take respective blood pressure regulating prescription medications. Further reports also indicate that diabetes often doubles one’s likelihood of dying from stroke or heart disease compared to those without diabetes.
Experts in the field also believe that both the conditions, diabetes and high blood pressure, often have common potential causes and risk factors. They have thus been linked to;
- Oxidative stress
- Insulin resistance
- Inflammation
- Obesity
Essentially, diabetes is associated with elevated blood sugar levels. High glucose levels often stress the vessels causing damage, narrowing, and accumulation of plaque such as cholesterol and fats within the vessel walls. These plaques further narrow the vessels making it difficult to pass adequate blood through. As such, the heart has to pump even harder to compensate for the narrowing leading to high blood pressure throughout the body.
Subsequently, the plaque formation and build-up due to the blood sugar levels further causes atherosclerosis, a condition which, when coupled with the high blood pressure, increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease for the associated individual.
Does Sugar Raise Blood Pressure Quickly?
People commonly associate salt with high blood pressure despite sugar also often playing a crucial role in blood pressure regulation. For instance, eating too much sugar may often inhibit nitric oxide production, eliminating vasodilation. This leaves an opportunity for vasoconstriction, which can result in high blood pressure. As such, sugar, just like salt, is also among the leading causes of high blood pressure.
Take fructose, for example, a simple sugar, which, upon ingestion, raises uric acid levels in the blood. High uric acid concentrations often inhibit nitric oxide production, which further eliminates flexibility and vasodilation capabilities of the blood vessels, prompting a rise in blood pressure.
Subsequently, excessive sugar consumption often leads to weight gain, and continued weight gain results in obesity. Since obesity is a major contributing factor to high blood pressure, increased sugar consumption thus raises blood pressure above optimal levels.
Sugars, more so added sugars, like table sugar and syrup, used in food preparation and processing have also been realized to contribute significantly to hypertension. This is because they are usually more harmful to human bodies, unlike the naturally occurring sugars in fruits and milk. Therefore, increased amounts above recommended range could result in high blood pressure.
Furthermore, hyperinsulinemia, a condition depicted by higher-than-normal levels of insulin in the blood, also contributes to high blood pressure if left untreated. Studies have actually shown that nearly half of high blood pressure patients often suffer from hyperinsulinemia or glucose intolerance.
The body often uses glucose for energy. However, with insulin resistance, associated individual systems often fail to respond to insulin as they should, prompting overproduction of the hormone to compensate for the high blood glucose and low energy levels. High insulin is usually associated with hypertension and together greatly increases the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Bottom line
Diabetes and high blood pressure are among some of the diseases claiming many lives globally. As such, individuals should always endorse frequent health checkups to determine their status with regard to the conditions. Subsequently, those living with either or both conditions should also invest in a close monitoring program to prevent treatment challenges and prevent unnecessary health complications.

Fasting Blood Sugar and Chart
Fasting Blood Sugar and Chart – There are different tests for testing Blood glucose – Random or Fasting Tests.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
Fasting Blood Sugar test means that no food or drinks (except for water) be consumed eight hours before the actual test. It is better to schedule the fasting test in daytime or first thing in the morning so that fasting won’t be hard since you were already in a fasting state when you were asleep.
Random Blood Sugar Test
Unlike the fasting test, this test allows you to eat and drink even right before the glucose test.
More Common: Fasting Blood Sugar Test
The fasting test is more common since this test is said to get much more accurate results compared to the random glucose test. In addition, fasting glucose test is easier to interpret. Fasting Blood Sugar and Chart
It is important that before the test starts, inform your doctor about all the medications you have been taking, both prescription drugs, over-the-counter-drugs, and even supplements whether herbal or not. Your doctor might ask to pause from taking your medications or just to change the dose before the blood glucose test. This is important to get accurate results since there are medications that may affect the body’s blood glucose levels.
Here are certain Medications that may affect blood sugar levels:
- corticosteroids
- diuretics
- birth control pills
- hormone therapy
- aspirin (Bufferin)
- antipsychotics
- lithium
- epinephrine (Adrenalin)
- tricyclic antidepressants
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- ·phenytoin
- sulfonylurea medications
Blood sugar levels increases when a person gets stress from certain circumstances such as:
- surgery
- trauma
- stroke
- heart attack
You should tell your doctor if you’ve recently had any of these.
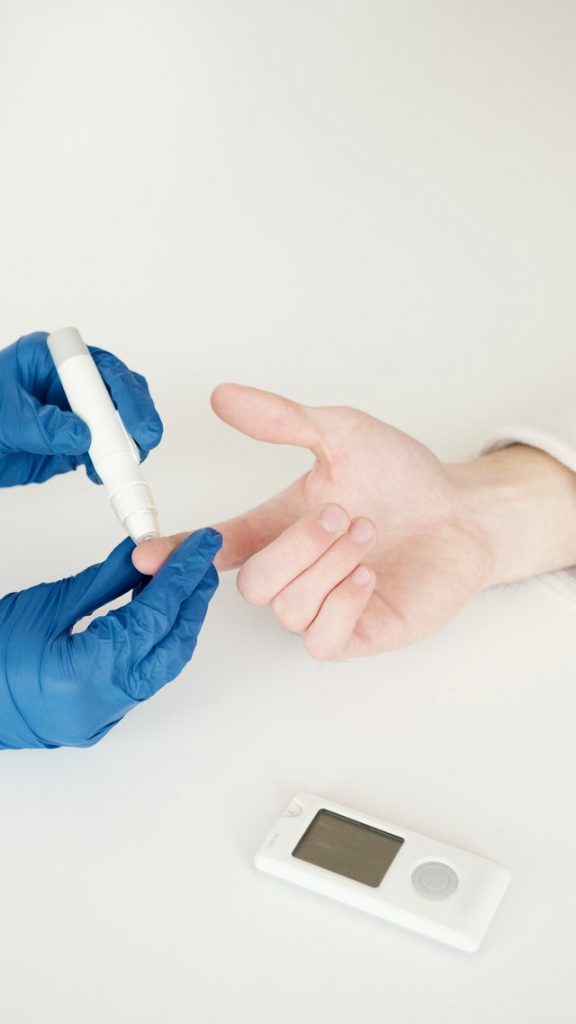
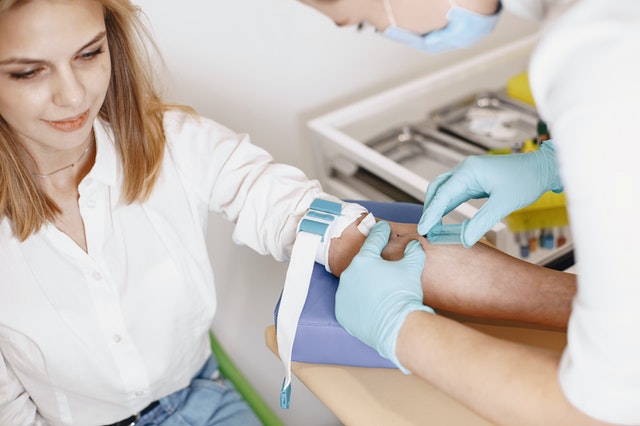
What happens during a Blood Sugar Test?
Blood sample is taken by using a device that merely pricks a finger to get that small blood sample. In other tests, blood from a mere prick is not enough that is why doctors would collect blood directly from a vein.
1. Before collecting the blood sample, the nurse/healthworker in charge would first clean the area where the blood is taken from, usually by wiping the area with cotton with alcohol to kill germs.
2. Second step uses a method that makes a vein visible. Usually, this method uses an elastic band to wrap around the upper arm. Once the vein is visible enough, a sterile needle will be inserted to collect the blood. It is important to relax your arm to reduce the moderate pain from the needle.
3. After collecting the blood, the nurse/healthworker removes the needle and covers up the skin with a band-aid.
4. The blood sample is then transferred to the laboratory to be tested. Fasting Blood Sugar and Chart
5. When the results are ready, the doctor will then discuss what’s in the result.
What are the Possible risks associated with a blood sugar test?
There is very little chance that people who get their blood tested develop health problems. Although the chances are very little, it is not definitely zero percent. Fasting Blood Sugar and Chart There are possible risks such as:
- multiple puncture wounds if it’s difficult to find a vein
- excessive bleeding
- lightheadedness or fainting
- hematoma, or blood collecting under your skin
- infection
Results of Blood Glucose tests
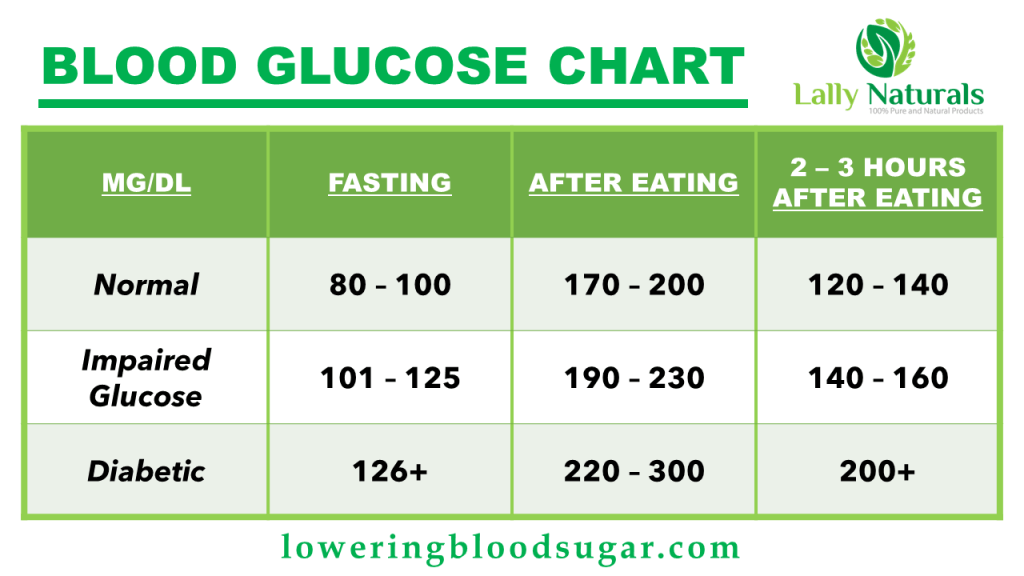
Normal Blood Test Results
The results depend on whether the test was the Fasting Blood Sugar test or the Random Blood Glucose Test. For the fasting blood sugar test, normal levels is between 70mg per deciliter and 100 mg per deciliter (mg/dL). On the other hand, the random blood sugar test levels are usually under 125mg per deciliter. However, the exact levels will still depend on what you ate last. Fasting Blood Sugar and Chart
Abnormal Blood Test Results
Again, the results depend on whether the test was the Fasting Blood Sugar test or the Random Blood Glucose Test. For the fasting blood sugar test, the results listed below will indicate whether there are signs of prediabetes or diabetes:
- A blood glucose level of 100–125 mg/dL indicates that you have prediabetes.
- A blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL and higher indicates that you have diabetes.
On the other hand, the random blood sugar test levels the results listed below will indicate whether there are signs of prediabetes or diabetes:
- A blood glucose level of 140–199 mg/dL indicates that you may have prediabetes.
- A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL and higher indicates that you likely have diabetes.
If your random blood glucose test results are abnormal, your doctor will probably order a fasting blood glucose test to confirm the diagnosis or another test such as an Hgba1c.

High Blood Sugar Symptoms

High Blood Sugar Symptoms – Naturally, human beings have sugar (also known as glucose) in the blood. Normal levels of blood sugar gives energy for the cells and organs in the body to function. However, having too much is bad.
Blood sugar is naturally produced from the liver and from the muscles in the body, however, most human beings get too much from food and drinks containing carbohydrates. Hyperglycemia is a condition wherein it means that there is way too much sugar in the blood. Having too much blood sugar (or having high blood glucose) means that the body lacks enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels at a normal state.
What is insulin?
Generally, insulin is a hormone that helps the body transform the foods or drinks we consume into energy. Insulin also helps directs blood sugar to be stored in the liver, muscles, and in fat.
Without enough insulin, blood sugar will not be stored or converted to energy, and instead, it will dangerously build-up which will cause serious health problems such as diabetes.
Hyperglycemia
What is hyperglycemia? What causes hyperglycemia?
Right amounts of blood sugar is fuel for the body. However, too much does not equate to more energy… in fact, too much blood sugar causes the opposite of having a boost in energy.
| High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia) What is hyperglycemia? What causes hyperglycemia? Right amounts of blood sugar is fuel for the body. However, too much does not equate to more energy… in fact, too much blood sugar causes the opposite of having a boost in energy. |
High Blood Sugar Symptoms
What does it feel like to have high blood sugar?
A number of high blood sugar symptoms can happen, such as:
– Drowsiness especially right after eating
– Have headaches or other aches in the body
– Thirsty or hungry all the time
– Difficulty in concentrating
– Blurry vision
– Feels bloated
– Urinates more often
– Wounds or skin injuries might take more time to heal

Caution: Low insulin and having high blood sugar levels can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which is a serious complication that will need urgent medical attention.
Common symptoms may occur, such as:
– Shortness of breath
– Rapid beating of the heart
– Breath might smell fruity
– Disorientation
– Vomiting
– Dehydration
– Comatose
Blood sugar levels may reach over 250ml/dL. High blood sugar symptoms may be experienced at any time of the day, even in the morning for those who are suffering from diabetes.
What are the effects of high blood sugar in the body?
High blood sugar can lead to various symptoms and complications in the body. The following are examples of high blood sugar symptoms:
1. Frequent Urination – High blood sugar goes into the kidneys and urine which makes you more thirsty even when drinking lots of water.
2. Causes Unexplained Weight Loss – Even when there is high blood sugar in the body, high levels will cause the body’s cells to not get the glucose they actually need for burning fat and muscle.
3. Feeling Numb and Feels Tingling – High blood sugar can cause numbness, burning sensation, or tingling in the parts of the body such as the hands, legs, and even the feet. This complication of diabetes happens because of the diabetic neuropathy that happens after many years of having high blood sugar levels in the body.
High blood sugar symptoms cause harm to the body which will lead to long term complications:
1. May cause Heart Attack or Stroke
2. May cause damage or loss of eyesight.
3 May cause Kidney Problems
4. May cause skin problems such as slow healing of wounds or infections
Prevention of Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar)
Here are the different ways or strategies to prevent Hyperglycemia:
– Regularly check blood sugar levels, especially when it is advised by the doctor
– Take insulin, again, when advised by the doctor
– Ask for dietary help from licensed dietitians or nutritionists to ask help what your best diet would be.
– Always be mindful and take precautions to avoid any infections or certain diseases
– Get regular exercise. Home exercise or go to the gym, either way.
– Get enough sleep and avoid way too much stress as much as possible by engaging in stress-reducing activities.
Fortunately, at this day and age, testing kits for checking blood sugar levels are readily available in the market and may be purchased and used at home. For a more accurate reading, it is best to check with your doctor.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
When does low blood sugar occur? Some of the factors that increases the risk of low blood sugar includes:
a. Being diagnosed with certain medical conditions
b. Taking certain medicationsExercising too much
c. Skipping meals or eats way too little
d. Taking too much insulin can also be one that causes low blood sugar.
Low blood sugar symptoms are:
– Feels weak
– Feeling hungry
– Feeling nervous or anxious
– Feeling the chills
– Feeling irritable
– Experiencing fast heartbeat
– Palpitations
To help with hypoglycemia, fruit juice or eating something sweet will help with the symptoms. For more information about your health, it’s best to consult with your doctor.
Type 1 Diabetes
As researched by the American Diabetes Association, 5% of the population which already has diabetes suffer from the type 1 diabetes.

When the body lacks insulin, high blood sugar levels occur. Unfortunately, this happens because the immune system somehow attacks the cells in the body that produces insulin/ The cells in the pancreas produces the insulin we need in the body. If the body cannot naturally produce insulin, people, especially those with diabetes, would resort to take insulin through the methods medically available such as taking it via needle, a pen, or insulin pump. Insulin is vital in the body to keep blood sugar levels in the normal condition.
What causes Type 1 Diabetes?
In recent studies, researchers believe that people with a family history of type 1 diabetes is more likely to also be passed on to next generations. However, certain environmental factors such as viruses and infections may also cause the same.
Unfortunately, once diagnose with type 1 diabetes, there is no turning back. Dietary changes, regular exercise, or other healthy lifestyle choices will not undo it. It can happen at any time in our lives even during childhood.
Type 2 Diabetes
In this type, the body produces insulin but the problem is that the body is not able to utilize it. Yes, the pancreas makes insulin but cannot make enough to make sure the blood sugar level is at a stable or normal state. This effect is also known as “insulin resistance.” How should people take care of themselves when they have type 2 diabetes?
Taking insulin, proper medical pills, proper diet and exercise will definitely increase the chances to help manage blood sugar levels.
What causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Certain factors may cause to develop type 2 diabetes, such as the following:
- Certain genetics, especially when having a parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes
- Being overweight and being inactive most of the time
- Certain ethnicities are more prone to develop type 2 diabetes such as the African-American, Alaska Native, American Indian, Asian-American, Hispanic, or Pacific Islander ethnicity
- People who are over the age of 45 years
- People who have a blood pressure of 140/90 or higher
- Those who have low levels of good cholesterol or those who have high levels of triglycerides
Gestational Diabetes

What is gestational diabetes? This occurs when, during pregnancy, the body is experiencing insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. It is most vital to constantly monitor pregnant women’s blood sugar levels, as it can lead to lots of health complications for both the mother and the child. After delivery, this type of diabetes usually goes away.
People who have high blood sugar or experiencing high blood sugar symptoms should visit their doctor. Each person is different and therefore have different reactions and experiences.
What is Hyperglycemia?
Natural Blood Sugar Supplements. Hyperglycemia is the increased glucose level or sugar in our blood. The food we ate are broken down into glucose which are carried into our blood to all the cells in our body and are converted into energy with the help of insulin hormone produced by our pancreas. Insulin helps move glucose into the cells.  The body at times stop producing insulin as in the case for type 1 diabetes or the insulin produced does not work properly as in the case of type 2 diabetes. When glucose stay in the blood and is not carried into the cells of the body, this result in development of high blood sugar levels. Uncontrolled high sugar level may lead to dehydration and more serious complications may develop.
The body at times stop producing insulin as in the case for type 1 diabetes or the insulin produced does not work properly as in the case of type 2 diabetes. When glucose stay in the blood and is not carried into the cells of the body, this result in development of high blood sugar levels. Uncontrolled high sugar level may lead to dehydration and more serious complications may develop.
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus causes high blood sugar or hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia maybe caused by too much intake of carbohydrates which the body of a diabetic person is unable to convert into energy fast enough and so resulting to high blood sugar levels.
Another cause of hyperglycemia is when insulin production is not controlled either thru injection or taking medicines for insulin production. Diabetic people has to balance diet, medication and physical activity to prevent increased blood sugar levels.
Other possible causes of hyperglycemia or high blood sugar levels are stress, no exercise or minimal exercise, illness, surgery or infections and certain drugs like steroids can also affect blood sugar levels..
Common symptoms of hyperglycemia includes dry mouth, thirst, frequent urination and night urination, dry and itchy skin, blurry vision, weight loss, increased appetite and fatigue or drowsiness.
If hyperglycemia persists for hours and dehydration results, other symptoms include difficulty in breathing, rapid weight loss, dizziness when standing, increased confusion and drowsiness and even unconsciousness or coma.
Home remedies or self-care
Home remedies or self-care for hyperglycemia or high blood sugar is regular check of blood glucose meter if it is higher than normal. Regular meals and scheduled medication should be observed. Sugar-free and caffeine-free liquids must only be taken. In addition, check your urine for ketones and take blood sugar readings until it is back to normal.
 Ways to lower blood sugar level includes regular exercise, dietary regime solely for diabetics should be followed, and Natural Blood Sugar Supplements recommended by your doctor.
Ways to lower blood sugar level includes regular exercise, dietary regime solely for diabetics should be followed, and Natural Blood Sugar Supplements recommended by your doctor.
When hyperglycemia persists for more than three days or when ketones appear in your urine, you should immediately call your doctor to prevent complications.
Diabetics should follow their recommended dietary regimes, check their blood sugar regularly, do the recommended exercise daily and take the medicines as prescribed. A planned daily activities with a planned diet and Natural Blood Sugar Supplements will balance and manage blood sugar levels.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

Warning Signs and Symptoms Common to both Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition wherein a person has higher blood sugar levels than the normal. It is a metabolic disease that is caused by inadequate production of insulin or the cells of the body do not properly respond to insulin, or both.
Warning signs of diabetes are so mild that they are not noticeable especially in the case of type 2 diabetes. Only until they feel the long-term damage caused by diabetes do some people find out that they have the disease. In type 1 diabetes, the symptoms are quick and are much more severe. The common symptom of diabetes is increased levels of glucose or blood sugar in your blood.
Warning Signs and Symptoms Common to both Types of Diabetes
Fatigue and hunger. The food you eat is converted into glucose by your body for the cells to use for energy. Insulin helps bring the glucose in. If your produce inadequate insulin or when the cells rejects the insulin your body produce, glucose cannot get in and you will have no energy and thus feel tired and hungry more than the usual.
Frequent Urination. When diabetes raised up your blood sugar, your kidney cannot take all the glucose that is reabsorbed by the body land so excretes the excess ink the urine. The average rate of urination is between four and seven times. Diabetes may go for more than usual times.
Dry mouth and Itchy skin. Due to your frequent urination, you loss lots of fluids. You get dehydrated, your mouth feel dry and you feel itchiness in your skin.
Blurred vision. The changes in the fluid level in your body causes your lenses to swell up and changes its shape, making it lose the ability to focus.
 Weight Loss. When you have diabetes, your body cannot anymore get energy from the food you eat. It derives energy by burning fat and muscles instead, making your loss weight.
Weight Loss. When you have diabetes, your body cannot anymore get energy from the food you eat. It derives energy by burning fat and muscles instead, making your loss weight.
Nerve damage. Diabetes makes you feel pain and numbness in your feet or legs as a result of nerve damage. Another nerve damage results to slow-healing sores or cuts because it affects your blood flow.
Nausea and vomiting. The burning of fats for energy instead of getting it from food you eat results to production of ketones. Ketones in diabetic ketoacidosis makes your stomach feel sick.
The moment you start feeling these warning signs, it is time to go to the doctor and have a scheduled diabetic test. With proper diabetes diet coupled with regular exercise and recommended medications, diabetic persons may live an active and productive long life.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

How Do You Know You Have Diabetes?
Diabetes is disease that involves the inability of the pancreas to produce insulin or produces very minimal insulin that helps the body to store and use sugar and fat from the food we eat. The body is unable to use and store glucose.
is disease that involves the inability of the pancreas to produce insulin or produces very minimal insulin that helps the body to store and use sugar and fat from the food we eat. The body is unable to use and store glucose.
Two Types of Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the insulin is no longer produced by the body. to survive, diabetics needs to take insulin injections daily. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children or young adult or it can occur at any age.
Type 2 diabetes is a result of inability of the body to properly use insulin also known as insulin resistance or when the body does not produce enough insulin. This usually affects people over 40 years old, due to family history or overweight.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Fatigue and hunger. The body is unable to use glucose for energy because there is not enough insulin to bring glucose in.
Frequent urination. Diabetes pushes your blood sugar up causing the kidney to make more urine and when you pee a lot, you get thirsty a lot also.
 Dry mouth and itchy skin results because you pee a lot, the fluid is diminished and will make you dehydrated and dries your skin which in turn makes it itchy.
Dry mouth and itchy skin results because you pee a lot, the fluid is diminished and will make you dehydrated and dries your skin which in turn makes it itchy.
Numbness in the legs and feet and pain may be felt because nerve is damaged.
Slow-healing sores or cuts results because high blood sugar alters your body ability to heal wounds.
Weight loss. The body burns muscle and fat to get energy instead of deriving it from your food.
Nausea and vomiting. When your body burns fats, ketones is produced which can make you feel sick to the stomach.
Yeast infections between fingers and toes, under the breast and in or around your organs.
When you have any of these symptoms or you are over 40 years old, early detection is very crucial to avoid possible complications or nerve damage and heart trouble. Switch to a healthy lifestyle by adding more nutritious foods in your diet, natural supplements, and some exercise to avoid any health problems.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

Effects of High Blood Sugar and Ways to Maintain its Normal Level
Blood sugar level is raised by glucose, the main sugar found in the blood. This sugar is from the different types of food we eat that contain carbohydrates. However, other factors such as stress and the timing of the mealtime can also affect how the blood sugar is regulated.
also affect how the blood sugar is regulated.
When cells are not absorbing glucose, high blood sugar results which damages nerves, blood vessels and organs that would ultimately result to dangerous complications. Excess glucose in the bloodstream or hyperglycemia is a sign of diabetes.
Diabetes is either type 1 wherein the person with this type don’t make insulin. Or type 2 diabetes wherein the body does not use insulin properly. It is therefore important to regularly check blood sugar level and to watch out for symptoms that would indicate high sugar level.
Signs And Symptoms Of High Blood Sugar
- You pee a lot and drink a lot. Too much sugar in the blood which spills into urine. Making you pee a lot and thirsty. You also lose weight.
- You are tired all the time. This happens when the cells don’t have enough glucose and so has low energy.
- Thicker blood sugar making it difficult to get to small blood vessels.
- Vision loss. Blood sugar that is high can cause blurry vision and can harm eye health.
- Peripheral neuropathy. Prolonged high blood sugar level can lead to numbed toes and tingling fingers.
- Feet infection. High blood sugar can result to lose sensitivity in the feet.
- Loss of libido. Excess sugar in the blood results in erectile dysfunction and vaginal dryness.
- Constipation or frequent diarrhea. The nerves that control the internal body functions are affected by the high sugar level.
- Kidney problems. Increased level of blood sugar in the tiny vessels of the kidney damages its normal function which would eventually require dialysis or transplantation.
- Stroke and heart attack. Diabetes can elevate the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Alzheimer’s disease. Blood vessel damage due to high blood sugar level can affect your brain and impair thinking and memory.
- Tooth decay. Sugar in the saliva can leave plaque on the teeth. High blood sugar causes also painful gums and bleeding.
- Urinary tract infection. Diabetes can also damage the nerves that control the bladder function. There is difficulty in emptying the bladder or in retaining and releasing urine.
- Dry skin. There is body fluid loss and skin becomes cracked, dry and itchy.
- Risk factor. People who are overweight, have high blood pressure, physically inactive and have a family history are at risk for diabetes. It is therefore advisable to check blood sugar level repeatedly to have it get treated early land avoid possible complications.
How To Maintain Normal Blood Sugar
- Eat a healthy diet. Balance carbohydrates and sugar with protein and fats, Fiber and healthy fat can help s
 tabilize blood sugar.
tabilize blood sugar. - Natural Supplements. Take in natural supplements to help regulate your blood sugar.
- Switch carbs and sweeteners. Avoid refined sugar and use instead natural sweeteners.
- Get regular exercise. Exercise helps your muscles to take up more glucose and use it for energy and tissue repair. This process lowers blood sugar.
- Manage stress. Manage your stress because high stress can raise blood sugar and increase the level of stress hormone cortisol. Stress relievers like yoga, meditation and exercise can be relaxing and helps diabetes with insulin resistance.
- Enough rest. Lack of sleep can elevate stress and appetite hormones. Too little sleep, poor quality and wrong times when sleeping can impair insulin secretion. Stick to a schedule of sleep and aim to have longer sleeping hours

What is Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar is also known as blood glucose. It the main sugar found in the blood. Glucose is a simple sugar that is the primary source of energy and is important for the normal function of some tissues. Glucose is carried by your blood to all the cells in your body to use for energy. It is particularly needed by the normal function of the human brain. It is stored in the skeletal muscles and liver cells in the form of glycogen.
The body regulates blood sugar levels to maintain metabolic homeostasis. It is transported via the bloodstream to the other tissues in the body from the intestines or liver. Glucose in the cell tissues is regulated by a hormone produced by the pancreas called insulin.
Effects of High and Low Blood Glucose Level
- Hyperglycemia. When glucose levels are higher than normal, it causes inflammation in the blood vessels and nerves and causes diabetes. The normal function of insulin in keeping sugar in normal range is damaged when you have diabetes.
- Hypoglycemia. Low blood sugar level also causes potential health problem. It can cause dizziness, confusion or fainting.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
- Fasting. Under the official ADA recommendation, the normal level for a person without diabetes is 70-99 mg/dl (3.9-5.5 mmol/L). Person with diabetes is 80-130 mg/dl (4.4-7.2 mmol/L)

- 2 Hours after meals. Normal for person without diabetes is Less than 140 mg/dl (7.8 mmol/L) and the official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes is Less than 10 mg/dl (10.0 mmol/L)
Blood sugar level is usually lowest in the morning and before the first meal in a day. It rises in an hour or two after taking your meals. Blood sugar levels beyond the normal range indicates medical condition.
Having too much glucose in your blood may result to serious problems. Too high blood sugar levels results to diabetes. But even person without diabetes may have serious problems when their blood sugar levels are too high or too low. Regular exercise, maintaining a regular schedule of eating and taking the recommended medicine may help regulate your blood sugar.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()