Archive for February 2023

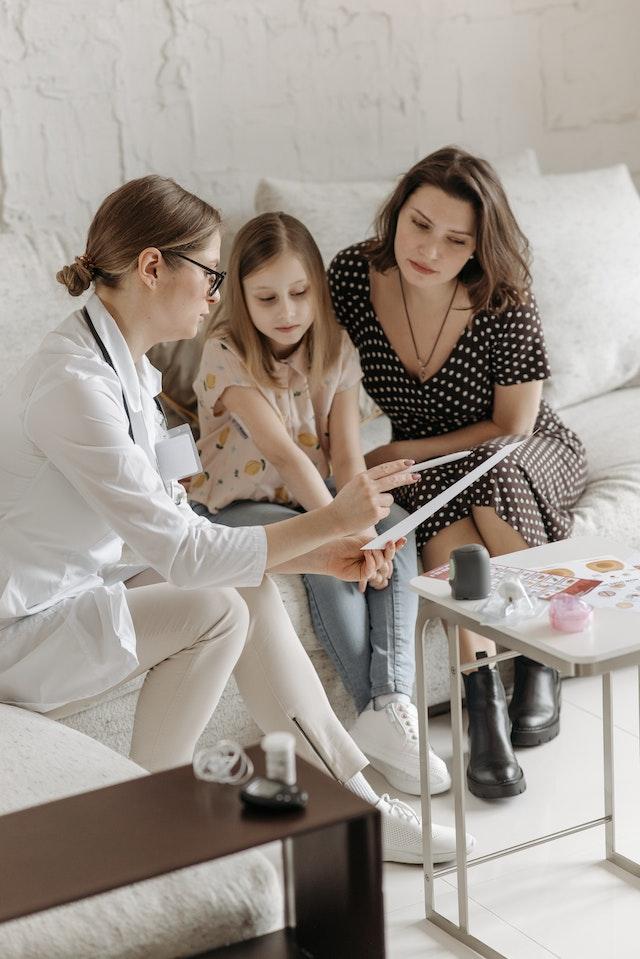
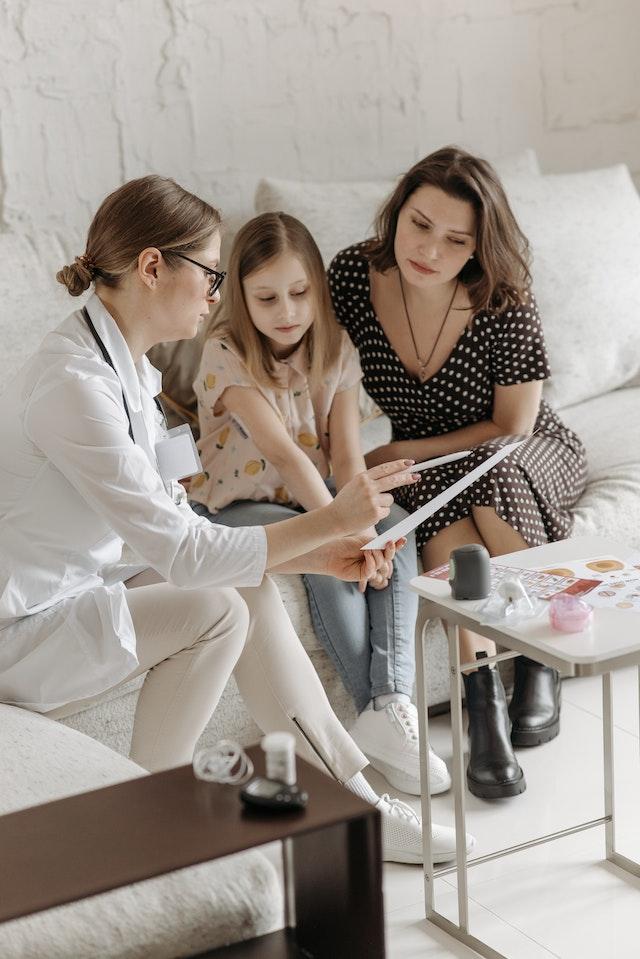
Diabetes and Sleep
Diabetes and sleep
Many benefits may be gained from a sufficient amount of sleep. Many complications may arise from having diabetes. Discover the role sleep plays in the control of your diabetes.
The ability to get a decent night’s sleep is a privilege. It’s common for people to go to bed later than they’d like because they’re trying to juggle too many things at once, such as school, job, exercise, and family. One-third of individuals in the United States are chronically sleep-deprived, which has been linked to an increase in the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, obesity, and depression.
Not getting enough sleep has detrimental effects on all aspects of diabetes treatment, including food intake: insulin sensitivity, state of mind, and the foods you choose to consume.
A well-maintained home may do wonders for your attitude and energy levels in addition to helping you better control your diabetes.
Just how much sleep do you require?
In order to maintain excellent health, getting enough sleep is crucial at any age. The optimal amount of sleep you need shifts as you become older. It has been suggested that individuals need at least 7 hours of sleep every night by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society. Youths and younger children need more.
Neglecting Your Sleep May Have Consequences
Your diabetes will be more difficult to control if you consistently obtain fewer than 7 hours of sleep every night.
Lack of sleep may:
- Decrease insulin resistance.
- Cause you feel less full after eating and hungry the next day.
- Cause you to want unhealthy, high-carb, high-sugar meals.
- Increase the difficulty of losing weight
- Cause a spike in blood pressure and a significant increase in the probability of cardiac arrest.
- Decrease your body’s resistance to illness.
- Raise the odds of experiencing emotional distress.
The Best Ways to Sleep More
Sleep Well.
You should focus less on the quantity and more on the quality of your sleep. Some indicators of poor sleep quality include:
- After getting enough shut-eye, you still don’t feel refreshed.
- Maintaining a pattern of waking up many times over the night.
- Experiencing sleep disorder symptoms (such as snoring or gasping for air).
Night owls are typical, as are those who rise early throughout the week but sleep in on the weekends.
Although it would be nice to make up for lost time, your brain cannot benefit from the additional sleep.
Making sure you receive adequate quality sleep on a constant basis requires maintaining a regular sleep schedule (waking up and going to bed at around the same time each day, including on weekends).
You may benefit from the following suggestions:
- Maintain a calm and restful atmosphere in your bedroom by keeping the lights off and the temperature down. The optimal temperature for sleeping, according to experts, is 65 degrees.
- Get the TV, computer, and phone out of bed.
- Try to get some exercise into your day.
- Before turning in for the night, let your mind decompress.
- Set a regimen that helps you wind down before night, such as a pre-shower shower, light reading, or journaling.
- Just go to sleep when you feel like it.
Furthermore, here are some things to keep in mind to avoid:
- Caffeine in the late afternoon and evening. The effects might last for as long as 8 hours.
- When consumed in the evening, alcohol might disrupt sleep breathing. It may also disrupt your sleep and make it less restful.
- Dinners that go till the wee hours of the morning. In addition to raising overnight blood sugar and bloating, eating late at night is also associated with gastrointestinal distress.
- It’s OK to nap after 2 o’clock. Because of this, you may feel less exhausted when it’s time for bed.
- Nicotine has similar effects as caffeine.
Get in touch with your doctor if you’re still having trouble sleeping.
FAQ
- Does diabetes impact your ability to get to sleep?
To compensate for elevated blood sugar, the kidneys increase the frequency of urination. In the middle of the night, you get up to go to the toilet, which disrupts your sleep. Sleep problems are yet another side effect of high blood sugar, headaches, thirst, and fatigue.
- Why do diabetics wake up in the middle of the night?
Nocturnal hypoglycemia occurs when a person’s blood glucose level drops below 70 mg/dl while they sleep. According to studies, almost half of all bouts of low blood glucose, including more than half of all severe episodes, are thought to occur at night when people are sleeping.
- What happens if a diabetic sleeps too much?
Besides hemoglobin A1c, sleep duration was shown to be associated with additional diabetes risk variables. For instance, those who slept for more than 8 hours each night tended to have higher fasting blood sugar levels.
- What can diabetics take to help them sleep?
According to anecdotal information gathered from several diabetic message boards, melatonin and antihistamines are the most often used treatments for sleeplessness. You won’t be so knocked out by these drugs that you won’t wake up in an emergency or from low blood sugar if you take them as directed.
- Why do diabetics wake up at 3 am?
A person with diabetes won’t see an increase in insulin production to counteract the spike in blood sugar levels that occurs first thing in the morning. The name “dawn phenomena” comes from the fact that it often occurs between 3 and 8 in the morning. Almost all diabetics experience the dawn effect at some point.
- Is napping healthy for people with diabetes?
The chance of getting type 2 diabetes is increased by taking naps throughout the day. Also, research seems to show that the capacity of people with type 2 diabetes to regulate their blood sugar is influenced by short and lengthy sleep duration and midday naps.
- Does sleep affect your A1C?
People who reported sleeping less than 5 hours per night or more than 8 hours per night had significantly higher levels of hemoglobin ATC in their blood, indicative of poor blood sugar control over the previous 2–3 months, compared to those who reported sleeping the recommended 7–8 hours per night on the questionnaires.
- Why do diabetics wake up tired?
Both high and low blood sugar levels are major causes of fatigue. Fatigue may occur from either an inadequate quantity of circulating insulin or an excessive amount of blood glucose.
- Why does a diabetic get sleepy after eating?
Feeling sleepy after eating may be a sign of hypoglycemia in people with prediabetes, Type 1, or Type 2 diabetes. Consuming an excessive amount of sugar might lead to hyperglycemia.
- Can high blood sugar levels be caused by not getting enough sleep?
Repeated nighttime awakenings, inadequate sleep, excessive sleep, and irregular sleep schedules have all been linked to an increased risk of developing glucose intolerance in a variety of studies. If a person has prediabetes or diabetes, they will have a more challenging time getting a good night’s rest.
- Do people with diabetes tire easily?
Research shows that persons with type 2 diabetes often struggle with acute weariness, making daily tasks difficult. It has such a profound effect that medical professionals often talk about “diabetes weariness.”
- How can one get over the exhaustion brought on by diabetes?
A few pointers are as follows:
- You should get between 7 and 9 hours of sleep nightly.
- Consistent physical activity is highly recommended.
- Cut off all the sugary and processed meals.
- If you’re an alcoholic, cut back.
- Caffeine is OK, but only in moderation.
- Instead of stressing out, try yoga or meditation.
- Why does my blood sugar go so high when I sleep?
Too little insulin with supper or a substantial meal or snack before bed may lead to overnight highs in blood sugar. Changing your diet or the timing of your medications would be beneficial. If your numbers seem OK before night, then you’re taking too little medicine.
- What is the recommended amount of sleep time for someone with high blood sugar or diabetes?
Your blood sugar will be more difficult to control if you consistently obtain fewer than 7 hours of sleep every night.

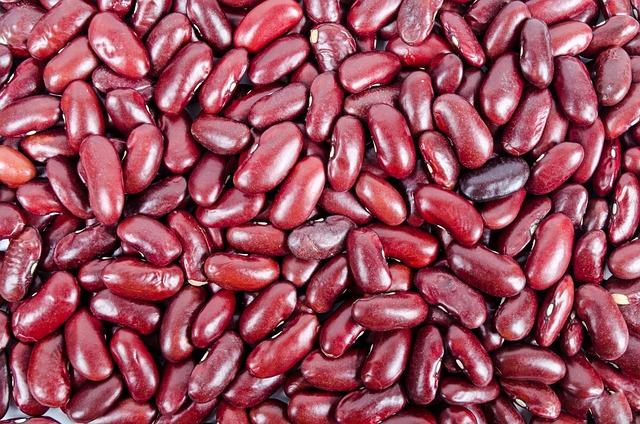
Are Beans Good For Diabetics?
Compared to other foods, beans are a food that normally does not receive a lot of appreciation. But because of their nutrient profile, low price, and positive environmental impact, they have quietly attained the title of superfood.
Additionally, a ton of research has shown how beneficial beans are for a variety of health conditions. But if you have diabetes, you might be asking if and how beans can be a part of your diet. Are beans healthy or bad for blood sugar levels? Now let us look.
What are beans?
Look in your pantry or cupboard; you may have some cans of chickpeas or kidney beans hidden there. Beans have a reputation for being a bit lower on the food chain and are frequently seen as a staple of the lower classes. They have been utilized as food since 9,000 years ago.
However, beans have always been thought to have unique abilities. Beans were placed in tombs by the ancient Egyptians as food for the dead as well as their spirits in the hereafter.
The United States is the “world leader in dry bean production,” according to The Bean Institute, and beans are now present in every culture. Every year, between 1.5 million and 1. 7 million acres of dry beans are planted by American farmers.
Beans are a member of the legume family, which also includes peas and lentils. According to the website aptly named Pulses, they are also known as “pulses,” the “edible seeds of plants in the legume family.” The seeds of several plant species are what we call beans.
Is it true that green beans, like black beans and kidney beans, are considered “beans”? No, as a matter of definition. Since green beans come in a pod, they are legumes rather than beans. We acknowledge that this is somewhat perplexing. But for this essay, the emphasis is on beans that are legumes and are not in a pod.
Types of beans
There are too many bean kinds to count, numbering in the hundreds. In different parts of the world, some varieties are more prevalent or well-liked. Here are some examples:
- Adzuki
A little, spherical, red bean with a seam down one side that is white. All around Asia are grown.
- Black bean
With a creamy texture, it is South and Central American native.
- Cannellini (white kidney bean)
Argentina-born, but highly well-liked in Italy. The beans feature a nutty flavor and a creamy texture.
- Fava bean (broad bean)
This bean, which is native to the Mediterranean region, grows in pods and can be consumed either fresh or cooked. They have a moderate, nutty flavor and are green in appearance.
- Garbanzo (chickpea)
The Middle East is the region of origin for this round, tan bean. The has a delicate nutty flavor.
- Kidney bean
A bean with the shape of a kidney and a moderate flavor.
- Mung
A little, round, green bean with a white stripe that is indigenous to India and Pakistan.
- Pinto
Originating in South America, this native has a moderate, slightly sweet flavor and is pink and brown.
Popular bean dishes
Despite the fact that you might not be enthusiastic about eating beans, it’s likely that you’ve already tried (and liked) foods that do, such as the following:
- Black bean soup
- Boston baked beans
- Hummus
- Refried beans
- Tuscan bean soup
- Navy bean soup
- Minestrone soup
- Red beans and rice
- Chili
- Cassoulet
A mainstay of vegetarian and vegan diets, beans have increased in popularity. There are recipes that employ beans in less “conventional” ways as well; some examples are black bean brownies, tortilla chips, bean smoothies, and Bolognese sauce made with beans rather than ground beef.
Do not be surprised if you browse the cereal section of your local grocery shop and discover that some cereals are manufactured with, you got it, beans!
Bean nutrition
Beans have a very amazing flavor, but their nutritional value is where they truly shine. Now let us examine what these legumes have to offer in more detail: –
Complex carbohydrate
Before you start to worry that beans are off-limits for people with diabetes, understand that the type of carbs present in beans are a combination of starch, resistant starch, nonstarch polysaccharides, and complex sugars known as oligosaccharides. These diverse carbohydrates are good for gut health and have low glycemic indexes, which means they are less likely to result in blood sugar increases.
Dietary fiber
Soluble and insoluble fibers can be found in beans. Blood cholesterol and blood sugar levels are reduced by soluble fiber. Colon cancer, diarrhea, and other digestive issues can all be avoided with insoluble fiber.
Protein
Since it can help you feel fuller for longer and may slow the digestion of carbohydrates, protein is a hot issue for people with diabetes. According to The Bean Institute, beans have a protein content of between 21% and 25% by weight. They are frequently utilized as a meat substitute because of this.
Vitamins and minerals
The majority of beans also contain magnesium, copper, iron, vitamin B6, riboflavin, thiamin, and folic acid in addition to potassium, which supports normal blood pressure.
Here is a breakdown of some of the most popular beans we typically consume in terms of their nutritional composition, displayed as a range.
Per 1 /2 cup serving:
- Calories: 110-125
- Carb: 19-24 grams
- Fiber: 5-1 O grams
- Protein: 6-9 grams
- Fat: 0.2-0.6 grams
- Sodium: 0-5 milligrams•
- Potassium: 305-502 milligrams
Beans and Diabetes
Beans are a healthy option for those who have diabetes, as was already mentioned. Beans’ soluble fiber is one of its main advantages. According to studies, consuming soluble fiber-rich foods in your diet will help reduce blood sugar and A1C levels.
Those with type 2 diabetes who consumed a cup of beans or lentils daily as part of a low-glycemic index diet were the focus of a study published in the Archives of Internal Medicine on October 22, 2012. Their A1C levels had decreased by 0.5 percentage points after three months.
According to a different study published in the journal Diabetes Care, soluble fiber reduces A1 C levels by roughly 0.6%.
What exactly is the mechanism of soluble fiber? In the digestive system, soluble fiber, commonly referred to as viscous fiber, gels up. Carbohydrate digestion is then slowed by the gel, which also inhibits glucose absorption. The outcome? decreases in A1C levels and blood sugars! Additionally, oats, apples, carrots, and barley are foods that are high in soluble fiber.
Speaking of soluble fiber, incorporating beans in your diet can also help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. To stop cholesterol from being taken into the bloodstream, soluble fiber binds to it in the small intestine. Following that, the cholesterol is eliminated.
Beans can assist you in achieving your weight loss objectives, which can also benefit your blood sugar levels and cardiovascular health. As a result, you eat less because of their high fiber and protein content, which also helps to control your appetite.
You might be wondering, though, what about all those carbohydrates in beans? It is a good question, and the answer is that beans do contain carbohydrates. For the purpose of calculating carbs, a serving of beans is defined as 1/2 cup (or 1/3 cup for baked beans), which is “counted” as one carb choice and one lean protein choice.
The American Diabetes Association points out that 1/2 cup of beans “provides as much protein as an ounce of meat without the saturated fat.”
You can understand how beans and other meals affect your glucose levels by utilizing a blood sugar meter or CGM (continuous glucose monitoring).
Tips
- If all of this conversation about beans has made your mouth swim, fantastic! Here are some pointers to bear in mind:
- Take it easy on the beans if you aren’t used to consuming a lot of fiber. To reduce gassiness and bloating, increase your intake gradually.
- Beans in cans are quite cost-effective and convenient. They sometimes contain a lot of sodium, which is a drawback. Before eating the beans, either look for ones that have no salt added or give them a good rinse.
- Beans that have been dried can also be used. They must soak for at least eight hours or overnight. After that, you’ll have to cook them for 45 to 2 hours. View the directions here.
- When chopping, cooking, and prepping beans, an Instant Pot will save you a ton of time. It is possible to cook them after a quick soak in the saucepan for one minute (the time will vary based on the type of bean you use). Find out here how.
- To replace eggs in baked items if you do not consume them, use aquafaba, the liquid found in canned beans: Equivalent to one egg is three tablespoons of aquafaba. You can make meringue without using egg whites if you whisk aquafaba into firm peaks, too.
- There are numerous strategies to increase the amount of beans in your diet. Include them in any soups or stews you prepare. They can be added to salads as a garnish. When preparing meatballs or hamburgers, mix cooked beans with ground beef.
FAQs
Do beans raise your blood sugar?
Beans are a wonderful source of protein and fiber. Although beans include carbohydrates, they have a low glycemic index (GI) and do not significantly raise a person’s blood sugar levels. Beans are a type of complex carbohydrate.
Can diabetics eat beans and rice?
As long as it has been combined with beans, diabetic rice lovers can now savor white rice without concern. In a recent study, which was partially financed by the USDBC, researchers discovered that rice can cause blood sugar levels to rise, but beans, a healthy part of any diet, can prevent this from happening.
Can diabetics eat beans every day?
The final line is that, especially if you have diabetes, beans should be a staple in your diet. According to research in the journal JAMA, increasing one’s intake of beans, lentils, and other legumes can assist patients with type 2 diabetes to improve their glycemic control and reduce their risk of developing heart disease.
Are beans better than rice for diabetics?
Rice causes a substantially higher insulin response than beans, which are high in fiber and protein.

Do You Have Cloudy Urine?
If your pee is not a typical, clear, light-yellow hue and instead appears milky or murky, you have cloudy urine. Although murky urine is typically not harmful, it may be an indication of a medical concern if it occurs frequently and repeatedly.
What is cloudy urine?
When your urine is milky in color and not clear, it is said to have cloudy urine. Cloudy urine is usually not harmful, but it can be a sign of a medical disease if it occurs frequently and repeatedly.
What does cloudy urine look like?
The color of typical urine is a translucent light yellow. As opposed to the typical straw yellow color, the color of cloudy urine ranges from foggy white to light yellow.
What causes cloudy urine?
The presence of alkaline is the most frequent reason for cloudy urine. Water, salts, and waste products from the kidneys make up urine; the ratio of these elements determines whether the urine is alkaline or acidic (pH). pH values for normal urine range from 4.5 to 8 in terms of acidity to alkalinity.
Pee that measures 8 pH or higher is alkaline, whereas urine that measures 5 pH or lower is considered acidic (basic). Urine that is murky is due to high alkalinity.
The following are additional potential reasons for cloudy urine:
- Dehydration.
- Kidney leakage (chyluria).
- Infection.
- High fruit and vegetable diet.
- Vaginal discharge.
What if I have cloudy urine during pregnancy?
Frequent urination is typical throughout pregnancy. As a result, you could occasionally notice that the color of your urine changes. Pregnancy-related reasons for cloudy urine include:
- Vaginal discharge.
- Dehydration (from morning sickness). Infection.
- Preeclampsia.
Visit your healthcare practitioner for a more thorough evaluation if you frequently have cloudy or discolored urine, or if you develop any symptoms like a headache, blurred vision, abdominal pain, or swelling.
What foods cause cloudy urine?
Some foods might increase your level of alkalinity, which can result in hazy urine. You are more likely to have greater levels of alkalinity, which can result in cloudy urine if you consume a diet high in fruits and vegetables and low in meats, grains, and cheeses (low-PRAL).
Urine changes to look for
Your urine’s qualities can vary from day to day based on a number of factors, but in general, healthy urine is light yellow and has a faint odor.
What diseases/disorders have cloudy urine as a side effect?
Cloudy urine is a symptom of a number of illnesses or conditions, including the following:
- Diabetes.
- Chyluria.
- Infection (urinary tract infection,).
- Preeclampsia.
- Kidney disease or kidney stones.
Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic, progressive condition that causes a lengthy range of symptoms, including nerve damage, eye issues, and frequent urination. It develops when your body is unable to balance the amount of sugar in your blood. Urine that is hazy can also result from it.
The color and scent of your blood alter when you have a lot of sugar and protein in it. Urine that is cloudy and has a sweet scent is a typical sign of type 2 diabetes.
Dehydration
When you do not drink enough, your pee may become hazy. Urine becomes more concentrated when there is a fluid deficit. The hue will also darken.
The solution to this issue is to increase your daily water intake. Your urine will be clear and light yellow after you have had enough fluids.
Urinary tract infection
Bacteria that enter your bladder, kidneys, or urethra can cause a urinary tract infection (UTI). Urine leaks from the location. You will have the following signs in addition to hazy urine:
- The burning or agony when urinating
- An increased urge to use the restroom pee leaks
- Odorous or bloody urine
- Lower abdominal pain
Most likely, your doctor would advise taking antibiotics to get rid of the infection. To ensure that all of the bacteria are killed, take all of the medications that have been prescribed.
Kidney Stones
The minerals and salts in your urine cause crystals called kidney stones to grow in your kidneys. Urine can become backed up in your bladder or another area of your urinary tract if there are large stones present. Sometimes they can result in really painful pain. Your lower back, side, or even when you urinate, could pain.
You run the risk of having blood or murky urine. Moreover, it could smell bad or have a red, pink, or brown appearance.
You can also experience the following symptoms:
• Fever and chills
• vomit and feel sick
In your urine, some kidney stones may naturally dissolve. Large stones that cannot be broken up by urination can be divided up by doctors using a noninvasive method. Stone removal surgery is occasionally required.
Does cloudy urine mean that I have a sexually transmitted disease (STD) or a sexually transmitted infection (STI)?
Urine that is cloudy is a symptom of some STDs and STLs. Although cloudy urine is not the only sign of many STDs or STls, it may help your doctor make a diagnosis. Cloudy urine is a sign of a number of ailments or infections, including
• Chlamydia.
• Gonorrhea.
• Vaginitis.
How is cloudy urine treated?
The following steps can be taken to treat hazy urine:
• Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated.
• Taking vitamin C to lower alkaline levels.
• Using antibiotics to treat any infections.
• Eating a healthy diet.
How can I prevent cloudy urine?
By leading a healthy lifestyle that includes drinking plenty of water and eating a diet that is balanced, you can avoid having hazy urine. You can also go see your doctor to get infections treated right away before they become more dangerous to your health.
FAQs
Is foamy urine the same as cloudy urine?
Urination occurs quickly, which results in air pockets forming in the urine and giving it a frothy quality, which is the source of foamy urine. In contrast to the typical, light-yellow tone, cloudy urine is not clear and appears to have a milky hue.
You should get evaluated by your doctor if you notice that your urine is continuously frothy as this could be an indication of kidney issues.
Is cloudy urine serious?
An issue in your urinary tract could be the cause of hazy urine. It can be a sign of a major medical issue even though it normally doesn’t suggest a medical emergency. Dehydration is one factor that might contribute to cloudy urine.
Is cloudy urine smelly?
The smell of urine can alter, although it often is not harmful and only lasts a short while. Your diet and any vitamins or minerals you are taking can alter the smell of your urine. For instance, vitamin B-6 pills and asparagus both leave a noticeable odor in the urine.
Keeping hydrated can help prevent occasional hazy urine as well as a strong odor. Contact your healthcare physician if the smell of your urine lasts more than a few days.
Can urine be cloudy without infection?
Can urine be cloudy without an infection? Other than diseases, urine can become hazy for a variety of reasons. Cloudy urine can be brought on by dehydration, diabetes, diet, kidney stones, and more.
What does protein in urine look like?
Urine that is foamy or bubbly. Your hands, feet, tummy, and face swelling (edema). urinating more frequently. breathing difficulty.
When should I see my healthcare provider for cloudy urine?
Urine that is occasionally cloudy is typical. Get in touch with your doctor if you have persistently hazy urine that doesn’t clear up in a few days.

Propolis Benefits for Diabetes
Propolis Benefits for Diabetes
Honeybees produce propolis, a resinous or waxy compound. Multiple hues, including white, red, brown, and black, may be found in propolis. Because bees use it to construct their hives, it is often called “bee glue.” Similarly, bees utilize propolis to ward against parasites.
Beeswax and tree exudates are blended with the bees’ saliva. Propolis is made from the resin of various plants, flowers, and trees; thus, its exact makeup, color, and qualities will change depending on where you live. However, propolis’s health advantages are shared by all of its varieties.
The Greeks, Egyptians, and Assyrians used propolis for various medical treatments. Wounds, stomachaches, and sore throats are just a few conditions it may treat.
Furthermore, it has potential pharmaceutical use due to its anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer characteristics. Propolis is effective against several microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. Propolis may be applied to the skin, taken orally, or used as a mouthwash.
Propolis composition:
- Resin 50g
- Wax 30g
- Essential oils 10g
- Organic compounds 10g
Amino acids, carbohydrates, minerals, vitamins, antioxidants, and bioactive chemicals are all examples of the organic substances found in propolis. Vitamins B1, B2, B6, C, and E may be found in this.
This includes bioactive chemicals, including flavonoids, polyphenols, and organic acids. Magnesium, copper, zinc, manganese, and iron may all be found here.
Propolis Health Benefits for Blood Glucose Control
Keeping your blood sugar in check is crucial to your overall health. Diseases like diabetes, however, make it impossible to regulate blood sugar. The damage from free radicals, or oxidative stress, worsens these problems.
It has been shown that consuming propolis may help control blood sugar levels and lessen oxidative stress’s negative effects on various body systems. This is due to the high levels of antioxidants (including vitamin C) found in propolis.
Antioxidants neutralize harmful free radicals and considerably mitigate oxidative stress. As a result, it prevents harm to the internal organs. Also, it helps avoid the onset of several persistent diseases, including diabetes.
Propolis has been shown to improve diabetes in a scientific investigation. Propolis consumption for 90 days resulted in lower blood sugar and higher insulin. Our bodies manufacture the hormone insulin to help control blood sugar levels. Many people with diabetes suffer from a lack of control over insulin production. Giving them a daily dose of propolis may help.
Intestinal absorption of sugars and starches is reduced by propolis. This has the effect of lowering blood sugar levels rather than raising them. Hence, it may help those with diabetes and high blood sugar levels.
As a bonus, propolis improves the organs’ ability to absorb glucose from the blood. It lowers blood sugar levels and nourishes and energizes organs simultaneously.
Propolis Health Benefits for the Lungs and Kidneys
The use of propolis has been linked to enhanced lung function and health. Antioxidants are plentiful in propolis, as was previously noted. They protect various tissues and organs from damage caused by free radicals. As a bonus, it helps keep lung cells healthy and reduces inflammation.
The amount of inflammatory cells in the lung alveoli is reduced by propolis, too. The protective effects of propolis against tobacco smoke and related lung illnesses have been the subject of at least one investigation.
The kidneys are also targets of propolis’s same mechanism—this aids in protecting the kidney from oxidative damage and inflammation. According to recent research results, it may help stave against chronic kidney disease. The flavonoid chrysin in propolis also protects the kidney’s structures from damage and aids in reducing renal injury.
Podocytes, kidney cells, are other cells that propolis helps shield against apoptosis. High blood glucose levels may prevent kidney cells from filtering out the sugar. Instead, it causes injury and, in some cases, death.
Benefits Cardiovascular Health
A study at the University of Plymouth found that propolis effectively lowered blood pressure. This is due to the fact that propolis has been shown to increase levels of beneficial bacteria in the oral cavity.
These microorganisms aid in the conversion of dietary nitrates to nitrite. As a chemical, nitrite can dilate blood arteries, allowing more room for blood to circulate and thereby reducing blood pressure. Those with hypertension (high blood pressure) may benefit from taking propolis.
Cholesterol levels may be lowered with the aid of propolis as well. The heart may be made healthy by reducing blood pressure and cholesterol levels. In addition, it helps protect against atherosclerosis, congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, and other chronic heart conditions.
Propolis Controls Cholesterol
Antioxidants in propolis protect tissues and organs from damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants may help lower total cholesterol and “bad” LDL cholesterol levels.
The levels of both “bad” (LDL) and “good” (HDL) cholesterol may be lowered and raised, respectively, by taking propolis extracts, as shown in recent research. They help keep the arteries free of cholesterol buildup and plaque.
Thus, it aids in warding off various cardiovascular conditions, including atherosclerosis, hypertension, and even heart attacks. Consuming regularly may help ward against a wide range of potentially fatal illnesses.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
There is evidence that propolis may help reduce inflammation in the body. Diseases including diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis have all been inflammation-related. It also aids with wound healing, which is a nice bonus. That’s why eating propolis is a great way to lessen general inflammation:
Propolis flavonoids can control inflammatory enzymes. Reduced levels of these enzymes and factors lead to less inflammation. Another mechanism by which propolis inhibits inflammation is by blocking macrophages’ synthesis of nitric oxide and cytokinin.
Inflammation is a common side effect of macrophages. Therefore, propolis decreases inflammation in the body by hindering the efficiency of macrophages.
Commercially accessible propolis nasal sprays are out there. The use of these sprays may mitigate sinus irritation. Additionally, they help alleviate the signs of a cold or flu.
Capacity to Heal Wounds
To speed up the recovery process, propolis is applied to the wound. Antioxidants in propolis, such as polyphenols, can mitigate the harm from free radicals. Therefore, it protects cells in various bodily systems from injury.
This quality also aids in wound healing and hastens the process. For instance, many over-the-counter cold sore treatments include propolis at a concentration of 3% to speed healing and forestall further outbreaks.
Researchers have found that propolis may help burns recover. Numerous bioactive chemicals found in propolis aid in cell division. In other words, it promotes the production of new cells and tissues. As a result, it may hasten the process of healing cuts and scrapes.
The anti-inflammatory qualities of propolis also help wounds heal more quickly. The body’s inflammatory reaction to wounds and germs. It has the potential to impede healing and aggravate wounds, though. The healing process for wounds is aided by decreasing inflammation.
In addition, propolis’s antimicrobial characteristics hasten the recovery from wounds. Bacteria and fungi are the most common infectious microorganisms. Therefore, decreasing the number of organisms in the wounds helps hasten their healing.
Antimicrobial Properties
The antibacterial qualities of propolis have made it famous. Properties against bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa are included. According to single research, Propolis has been shown to be effective against various bacteria, including Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, and Helicobacter pylori.
Infections caused by these bacteria range from those that manifest on the skin to those in the intestines. In particular, Helicobacter pylori may lead to infections and ulcers in the stomach.
Bioactive chemicals, such as flavonoids, propolis its antibacterial capabilities. Pinocembrin, a flavonoid, has been shown to inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis and disrupt bacterial energy metabolism. So it may put a halt to their development and offspring creation.
Evidence shows they are effective against other viruses, such as the Herpes virus, HIV, influenza, and COVID-19. Chrysin is a flavonoid that inhibits viral replication or virus generation.
Possible Propolis Adverse Effects
People sensitive to bee products may have adverse responses when exposed to propolis. Knowing what triggers an allergic reaction is, thus, essential. Consuming an excessive amount of propolis may cause oral irritation and ulcers. Propolis contains chemical ingredients that may prevent excessive blood clotting. People with bleeding disorders or who have recently had surgery should not use it. And it’s best to see a doctor before consuming propolis.
How to Use Propolis Most Effectively
A daily dose of 400–500 mg of propolis is suggested. Propolis may be taken orally as a dietary supplement or diluted with water. Propolis is also used in several topical treatments, such as cosmetics, mouthwashes, and ointments.
Final Thoughts
Bees produce a natural substance known as propolis. Propolis contains beneficial nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and bioactive substances. Propolis also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
This has the potential to improve the condition of the heart, lungs, and kidneys. Also, it can reduce our blood pressure and cholesterol levels, two risk factors for many types of chronic illnesses. More study is needed to understand its mechanism and efficacy.
FAQ
Is propolis good for diabetes?
Recently, studies have shown that propolis results in a lowering of blood glucose levels, serum insulin levels, serum glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, with improvement, for type 2 diabetics of insulin resistance
Can diabetics eat propolis?
Yes, in very limited amounts.
Can propolis cause a rise in blood pressure?
Extracts of propolis and pollen, made by bees, effectively control hypertension when taken in ethanolic form. It has been hypothesized that propolis and pollen may assist in controlling reproductive function by blocking the inflammatory processes that cause hypertension.
Can propolis assist in losing weight?
One of the primary components of propolis, caffeic acid phenethyl ester, prevents high-fat diet-induced adipogenesis through modulating cyclin D. Researchers have shown that the composition of human gut microbiota changes in response to food types and calories consumed.
Can we call propolis a “probiotic?”
Propolis may serve as a prebiotic at low quantities, but at greater concentrations, it may impair the probiotics’ planktonic development and biofilm-forming abilities.
Is there a need to keep propolis in the fridge?
Propolis can be kept at room temperature, but if you only need a small quantity, you can keep it in the fridge or freezer and break it up into tiny pieces on a cutting board or with a big spoon to use.
Are there those who shouldn’t take propolis?
Those with a bleeding issue may be at a higher risk of bleeding if they take propolis. Sensitivity: Bee venom has the potential to taint several propolis products. If you have an allergy to bee stings or other bee-related items, use care while using propolis. Surgery. Propolis contains a substance that may prevent blood clots from forming.

Medicinal Uses of Amla (Indian Gooseberry) for Diabetics
Medicinal Uses of Amla (Indian Gooseberry) for Diabetics
Phyllanthus Emblica, often known as Amla or Indian gooseberry, is a medium-sized tree native to India that bears a firm, spherical, greenish-yellow fruit. Indians use Amla extensively in the kitchen, and it also has several Ayurvedic applications.
However, does Amla help with diabetes?
Amla has well recognized as an excellent cure for diabetes thanks to its capacity to strengthen the immune system. With this essay, we are closer to answering the question of whether or not Amla is beneficial for diabetics. I
n people with diabetes, the B cells in the Isle of Langerhans in the pancreas produce inadequate amounts of the hormone insulin, leading to dangerously high blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the digestion of sugar and glucose absorption by cells from the blood.
Type 2 diabetes, or Diabetes Mellitus, is a metabolic condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to insulin resistance. People with diabetes must watch their caloric intake, and meals rich in fructose or starch are harmful to their condition.
However, numerous foods, including Amla, have been shown to aid with diabetic management. Amin is beneficial for those with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Amla has several health benefits.
Amla is a popular plant in traditional Ayurvedic medicine because of its powerful anti-aging, anti-diabetic, and kidney-protecting properties.
Heartburn caused by indigestion may be alleviated by using Amla juice or extracts. Because it aids in digestion and lessens gastrointestinal troubles caused by indigestion, dried Amia makes for a great snack after a big meal.
It has been shown via scientific research that amla has anti-aging properties that are advantageous. Amla promotes the regeneration of cells and aids in the healing of wounds. Amla prevents collagen, the protein matrix of the skin, from degrading, which helps to maintain the skin’s youthful appearance and elasticity. Because it strengthens the follicles of the hair, amla is also good for the eyes and the hair.
A high concentration of antioxidants may be found in Amla. When it comes to curing malignant cells, antioxidants are crucial. It has been shown that Amla extracts aid in the recovery of malignant cells.
Antioxidants like Vitamin C also aid in lowering blood pressure, which is beneficial for your heart. It reduces triglyceride, total cholesterol, and LDL (bad) cholesterol while raising HDL (good) cholesterol levels, which aids in normalizing fat and blood glucose levels. Diabetics may benefit from drinking amla juice.
Amla prevents blood from clotting and the buildup of plaque in arteries by reducing blood viscosity. Because of this, there is a decreased possibility of having a heart attack caused by the obstruction of arteries.
The use of amla juice may be beneficial for diabetics. Amla juice is a delicious and healthy option for diabetics because to the high level of antioxidants it contains.
Amla’s Diabetes-Friendly Benefits
Amis promotes insulin secretion and speeds recovery from pancreatitis. The advantages of Amla may also be extracted from Amla candies; however, fresh Amlas are always preferable. Reduces the concentration of sorbitol, a harmful sugar that contributes to an already high risk of diabetes sequelae, including retinopathy and neuropathy.
- Improves insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
- It betters the body’s ability to handle glucose.
- Reduces HbA1c in those with Type 2 Diabetes.
- The control of glucose metabolism
- It enhances how the body responds to insulin.
- The involvement of Amla in enzyme activity is substantial.
- Lowering triglyceride levels in the blood
- Elevate both HDL and LDL Synthesis
To what extent does Amla aid in glycemic management?
Amla promotes pancreatic repair, boosts insulin release, and improves cell sensitivity to insulin absorption.
Type 2 diabetics may benefit from the antioxidant qualities of Amla since it aids in glucose metabolism and lowers the body’s blood glucose levels.
Amla helps persons with type II diabetes because it reduces the buildup of toxins in the body.
In addition to its other benefits, Amis aids in reducing body fat and restoring a healthy fat-to-blood ratio.
Amla with Diabetes: Several Dosages and Preparations
You may drink amla juice or consume raw fruit. Although raw Amla is ideal, its strong sourness may put off certain consumers.
To make a delicious snack, cut open a raw amla, remove the seeds, and sprinkle with rock salt. However, those who already have hypertension should limit their salt consumption.
You may get Amla in powder or pure juice and drink it daily with water. Amla juice or raw amlas, used regularly, has been shown to reduce fluctuations in blood sugar levels significantly. Amla candy is beneficial for persons with diabetes since it maintains steady blood sugar levels without sacrificing taste.
Because it has a high concentration of antioxidants and vitamin C, amla murabba may be helpful in regulating blood sugar levels. In addition to this, taking amla murabba might cause an increase in the acidity of the stomach; as a result, there are some unexpected effects.
Because Amla murabba has not been the subject of substantial research, it is suggested that you see a nutritionist prior to purchasing any of it.
Conclusion
Amla has been revered in Ayurveda for its many uses since ancient times. Everyone, particularly diabetics, may benefit from adding more fresh Amla to their diet. The article explains how Amla may help with anything from weight loss to strengthening your immune system. Amla contains anti-diabetic qualities, including the ability to lower high blood glucose levels and the prevention of toxic buildup in the body.
Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics may benefit from Amla’s use since the herb has been shown to have several positive effects on both conditions.
FAQ
Does Amla lower blood sugar levels?
Amla is a traditional medicine that has been shown to reduce post-meal blood sugar crashes. Amla, also known as Indian gooseberry, is often advised by medical professionals as a general tonic and topical therapy for skin, hair, and other disorders.
Does Amla have a lot of sugar?
Amla, on the contrary, has no sugar and boasts a whopping 500–800 milligrams (mg) of vitamin C per Amla. Amla has many health benefits for everyone, but those with diabetes will see the most dramatic changes from eating it.
At what dose should A diabetic take amla?
Depending on how severe their diabetes is, an individual may consume either one or two Amla daily. Raw or juiced, the fruit is delicious. Amla is a fantastic natural alternative to insulin for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Amla for diabetes: how to use it?
If you find the sourness of a single Amla a day too much to bear, you may always chase it with a glass of water. This is the most effective approach to utilizing Amla for diabetes management. Amla powder is another form in which the fruit may be consumed. You may add lime juice or water to this.
Can insulin resistance be reduced by taking amla?
One research found that Amla helped reduce blood sugar levels. In addition, it improves glucose metabolism, reduces blood sugar, and prevents the accumulation of toxins in the body. Furthermore, its high antioxidant content helps alleviate diabetic symptoms by lowering insulin resistance in cells.
To what extent can Amla help with diabetes?
Diabetic-fighting Amla. It enhances glucose metabolism, lowers sugar levels, and stops the buildup of toxins in the body. In addition to alleviating diabetic symptoms, its high antioxidant content also reduces insulin resistance in cells.
Can amla and turmeric help diabetics?
A morning drink that includes a sprinkle of turmeric and two tablespoons of gooseberry (Amla) juice is also recommended. According to studies, persons with diabetes who consume gooseberry saw significant improvements in their cholesterol levels.
Are there any repercussions for the liver if you consume Amla?
The effects of amia on liver function, hyperlipidemia, and metabolic syndrome have all been documented to be positive. Experimental animal models have shown that Amia may prevent chemical-induced hepatocarcinogenesis.
Amla and metformin: friends or foes?
Alternatively, compared to Metformin alone, the combination of Metformin and Amla was considerably more effective in lowering blood glucose levels. When given together, the medications boosted the animals’ weight, even though the diabetic animals were already obese, to begin with.
Medicinal plant Amla’s pharmacodynamic interactions with Metformin increased the diabetes drug’s hypoglycemic efficacy.
Will Amla help my pancreas?
Amla, an Ayurvedic herb, stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase and promotes apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.
Exactly what is Amla’s downside?
Some persons with allergies may see an increase in bleeding after consuming Amla products. Amla should be taken with care by people with diabetes since it can potentially cause dangerously low blood sugar levels. Skin dryness may occur if too much Amla juice is consumed.
Disclaimer Please consult a qualified medical expert for any health-related questions since the content provided here is for informational purposes only. Given that each individual is unique, it is ultimately up to the reader’s physician or another healthcare provider to assess whether the advice given here is appropriate for them.
Blood Sugar Dropping
Blood Sugar Level Dropping
Hypoglycemia, or unusually low blood glucose, may develop if your blood sugar levels drop too low (less than four millimoles per liter).
A lack of glucose (sugar) in the blood means your body lacks the fuel to function normally.
Hypoglycemia is a frequent complication of diabetes and often results from excessive insulin use, skipping meals, or strenuous activity.
Occasionally, people who do not have diabetes may get hypoglycemia. Malnutrition, heavy alcohol use, and medical diseases like Addison’s disease may all bring on these symptoms.
Effects of low blood sugar
Most individuals will experience symptoms before their blood glucose levels drop dangerously low, giving them time to take preventative measures. When blood sugar drops below four mmol/L, symptoms often show themselves.
Feeling hungry is a common warning symptom, as is trembling, shaking, and profuse perspiration. More severe instances sometimes include mental fogginess and trouble focusing. Loss of consciousness is possible in those with severe hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia may also happen while you’re sleeping, leaving you sweating excessively, with a messed-up sleep cycle, and groggy and disoriented when you wake up.
The Treatment of Hypoglycemia
Food or drinks high in sugar, such as dextrose tablets or fruit juice, should be consumed immediately to cure hypoglycemia.
A longer-acting “starchy carbohydrate snack,” such as a sandwich or a few biscuits, may be necessary after consuming anything sweet.
Loss of consciousness due to hypoglycemia may be treated by an injection of the hormone glucagon, which raises blood glucose levels and returns awareness to the patient. Of course, this assumes that an injection can be given and that the person administering it understands what they’re doing.
When you need an ambulance, phone 911 if:
- More glucagon for injection is currently on hand.
- No one knows how to administer the shot.
- After 10 minutes, the injection loses its efficacy.
- Person is sleepy or unconscious and should never have anything placed in their mouth because they may choke. Some of the high-sugar concoctions intended for intraoral application fall into this category.
Reducing the Risk of Low Blood Sugar
The best strategy to prevent hypoglycemia if you have insulin-dependent diabetes is to monitor your blood sugar levels frequently and know the early warning signs.
Your risk of hypoglycemia rises if you skip meals or snacks or consume fewer carbohydrates than you had intended. Alcohol use should be monitored since it, too, may result in hypoglycemia, even long after ingestion has stopped.
Another possible trigger is strenuous physical activity; to counteract this, you may need to consume carbs before, during, or after your workout or change your insulin dosage.
As the quantity of insulin absorbed by your body varies depending on where it is administered, you should switch up the injection site often.
If you sense symptoms approaching or your blood glucose level is low, have a source of rapid-acting carbohydrates on your hands, such as glucose tablets, a carton of fruit juice (one that includes sugar), or some candies.
Inform your loved ones that you have diabetes and may experience hypoglycemia. If you have a medical condition that might need medical attention, it is a good idea to have some identification with you at all times.
When hypoglycemia happens due to anything other than diabetes, that other issue must be addressed to stop the hypos from happening again.
Indicators of low blood sugar
Hypoglycemia symptoms often present when your blood glucose level drops below four mmol/L.
It is recommended that people with diabetes, especially those whose condition is managed with insulin, use portable equipment called a blood glucose meter regularly.
Symptoms may manifest differently in different people; therefore, it’s crucial to recognize the precursors to diagnosis and treatment.
Hypoglycemia symptoms may include, but are not limited to:
- needing to eat
- sweating
- dizziness
- weariness (fatigue)
- Foggy perception
- symptoms of shaking or trembling
- decreasing in pigmentation
- rapid heartbeats
- Sensational lips
- irritability
- Concentration issues
- confusion
- disruptive or illogical conduct that may be taken for intoxication.
Untreated hypoglycemia may cause drowsiness or even loss of consciousness if blood glucose levels drop too low for too long.
Most persons who use insulin to manage their diabetes report that the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia shift and become less noticeable with time.
For others, the early warning signs diminish to the point that they are no longer effective, dramatically increasing their chance of experiencing disruptive episodes that need assistance from others.
If you notice this issue, be sure to notify your diabetes care team so that they can adjust your therapy accordingly.
Insomniac hypoglycemia
Nocturnal hypoglycemia is when a hypo occurs during sleep. More often occurs in those who use insulin to control their diabetes.
Symptoms of nocturnal hypoglycemia may not present until you awaken in the morning, even if they may have caused sleep disruptions the night before.
Nighttime hypoglycemia symptoms might include:
- a painful headache similar to the feeling of a hangover
- waking up with an abnormally low amount of energy
- sweat-soaked bedsheets and garments
Hypoglycemia’s Root Causes
Although hypoglycemia most often affects those with diabetes, it may also occur in other contexts.
Diabetes-related hypoglycemia
Toxic overdose from diabetic medicine
Too much insulin for the body’s requirements is a typical cause of hypoglycemia. Blood sugar levels may be managed with the use of insulin. It is widely used for the treatment of type 1 diabetes and is also sometimes advised for persons with type 2 diabetes.
Too much oral hypoglycemia treatment, such as sulphonylurea, which stimulates insulin release, may also cause a drop in blood glucose levels. The blood sugar levels of persons with type 2 diabetes are commonly lowered with this medicine.
Weightlifting, eating, and drinking.
Type 2 diabetics need to strike a delicate balance between their insulin dosage, the calories they consume from meals, and the number of calories they expend via physical activity to keep their blood glucose levels within normal ranges.
If you take your regular insulin dosage but eat fewer carbs than usual or burn through them more rapidly, hypoglycemia might result. It’s possible to experience this if you work out for longer than normal, doesn’t consume enough carbs, or skip meals.
Hypoglycemia may also occur in people who have diabetes and have consumed too much alcohol or alcohol on an empty stomach.
However, there are situations when there is no clear cause for a hypoglycemic episode, and doctors are left guessing.
Non-Diabetic Hypoglycemia
Non-diabetic persons seldom experience hypoglycemia. What follows is an explanation of the probable reasons.
Hypoglycemia reaction
People who do not have diabetes nevertheless risk developing hypoglycemia if their pancreas produces an abnormally high quantity of insulin in response to a substantial meal high in carbohydrates. The medical term for this illness is reactive hypoglycemia.
Although the exact cause of this phenomenon is unknown, it seems to be more common in people who are overweight or who have had surgery to do a gastric bypass.
Occasionally, a pancreatic tumor that is not cancerous may cause an excessive amount of insulin to be generated or utilize an excessive amount of glucose for its requirements.
Additional potential factors
Hypoglycemia may also occur in persons who don’t have diabetes for a variety of other reasons:
Binge drinking or heavy alcohol consumption is malnutrition, in which the body does not get enough nutrients for it to function normally fasting.
Addison’s disease is the name given to the condition that affects the adrenal glands (two small glands that sit on top of the kidneys)
Patients using quinine, which is used to treat malaria, salicylates, which are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, and propranolol have all been documented to have had hypoglycemia (for high blood pressure), an illness of the liver, kidneys, or thyroid.
Hypoglycemia treatment
Hypoglycemia is usually a self-treatable condition as long as you know what to look for.
The management of hypoglycemia
An urgent remedy for hypoglycemia is the consumption of sugary food or drink (about 15–20g of fast-acting carbohydrate) to stop the episode.
Here’s one example that could fit the bill:
a regular-sized soft drink or fruit juice
Three to five dextrose pills
a little bag of candies
At first, it’s best to stay away from high-fat foods and beverages like chocolate and milk since they don’t often have as much sugar, and the sugar they do have may be absorbed more slowly.
It would be best if you had a longer-acting carbohydrate snack after ingesting sugary meals. Some examples of this kind of snack are a few biscuits, a cereal bar, a piece of fruit, or a sandwich. This will help you maintain your energy levels.
Recovery from an episode of hypoglycemia that is considered to be slight normally takes around 15 minutes. Take another measurement in the next 15–20 minutes if you have access to a blood glucose meter. If your blood sugar level is still too low (below 4 mmol), consume anything with added sugar and take another test after 15 to 20 minutes. If your blood sugar level is still too low, seek medical attention immediately.
If you are caring for someone who is experiencing hypoglycemia and the methods described above are not successful in treating the condition, you can try rubbing the outside of their cheeks with glucose gel (or honey, treacle, or jam if glucose gel is not available) and applying it directly to the maid.
It might be between ten and fifteen minutes before they start feeling better. Because of the risk of choking, this procedure should not be carried out on a person who is dozing off or already sleeping.
Your diabetes care team should consider the matter if you regularly experience hypoglycemia. You may need a change in the dosage of your medicine, or you may need medical attention for an underlying condition that is the cause of your hypoglycemia.
Keeping blood sugar levels stable
For those with diabetes, maintaining a regular meal schedule and medication schedule helps reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Keep an eye on your blood sugar levels.
FAQ
Do you know what it’s like to have your blood sugar suddenly drop?
Hunger pangs, shakiness, and profuse perspiration are common early warning signals. It’s also possible, especially in more extreme circumstances, that you’ll experience confusion and find it hard to focus.
Why does glucose level decrease suddenly?
If you don’t eat enough or miss meals, your blood sugar might decrease dangerously fast. Extra exercise, using specific medications, or taking too much medication (including insulin) may cause this condition. If you have trouble detecting the symptoms of low blood sugar, you should avoid alcohol.
When glucose levels in the blood drop, what happens?
This may cause visual blurring, difficulties focusing, muddled thinking, slurred speech, numbness, and tiredness. Long-term hypoglycemia, in which the brain goes without glucose, may cause convulsions, unconsciousness, and even death.
When blood sugar drops too low, what usually happens?
Although insulin users are more likely to have low blood sugar, everyone taking diabetic pills runs the risk. An overdose of insulin or other diabetic medicine is a common cause of diabetic hypoglycemia. Under-consuming or not eating enough.
At what point do you notice a dip in blood sugar?
Neither prediabetes nor diabetes has been identified. After an increase in blood sugar levels, one to two hours should pass before the levels return to normal. If you want to speed things up, going for a stroll or doing some exercise will help.
What other conditions than diabetes may result in hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia may also be caused by factors other than diabetes, such as
- consuming drinks with alcohol.
- Drugs include antibiotics, malaria and pneumonia pills.
- kidney health issues.
- Issues with either the adrenal glands or the pituitary gland.
- Cystic adenomas of the pancreas.
- Deadly disease
- conditions affecting the liver.
- Malignant pancreatic tumor.
At what level of blood sugar is there a serious health risk?
Extreme hypoglycemia is defined as a blood sugar level below 55 mg/dL. Depending on how you’re feeling, you may not be able to do self-tests of your blood sugar or administer your treatment.
















