Archive for April 2023

Do Pine Nuts Lower Blood Sugar?
Many people around the world are struggling with medical conditions related to high blood sugar levels, such as diabetes. As a result, a growing number of studies have focused on the role that certain foods and nutrients play in regulating blood sugar levels.
Pine nuts are one such food that has gained interest and attention for its potential to lower blood sugar levels. In this article, we will look at the link between pine nuts and blood sugar levels, examine the existing research on the topic, and provide insights into incorporating pine nuts into a healthy diet.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels and Its Importance in the Body
Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is a type of sugar that travels through the bloodstream to provide energy to the body’s cells. It is an essential source of fuel for all the body’s functions, including the brain, muscles, and organs.
Why is Blood Sugar Important?
The body tightly regulates blood sugar levels, ensuring that they remain within specific ranges. The reason for this is that too much or too little blood sugar can lead to serious health complications.
When blood sugar levels are too high, it can lead to hyperglycemia, which is a condition that can damage vital organs like the brain and kidneys. At the same time, when blood sugar levels are too low, it can cause hypoglycemia, leading to lightheadedness, seizures, and even unconsciousness.
Blood sugar levels are an essential component of overall health and wellbeing. Understanding how the body’s regulation mechanisms work can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy blood sugar levels.
Consultation with healthcare professionals can also play a crucial role in preventing and managing conditions related to blood sugar levels.
What are Pine Nuts?
If you’ve ever enjoyed a pesto sauce or a nutty granola, then chances are you’ve tasted pine nuts. But what exactly are they?
Pine nuts, also known as pignoli, are the edible seeds harvested from pine trees. They’re usually found inside the cones of different species of pine trees, including the stone pine, Korean pine, and piñon pine.
These small, ivory-colored nuts pack a lot of flavor and nutrition into a tiny package.
Let’s explore details about these nuts:
Nutrition
- Pine nuts are a good source of healthy fats, protein, and fiber. They also contain vitamins and minerals like zinc, magnesium, and vitamin E.
- Studies have shown that consuming pine nuts (and other nuts) can reduce the risk of heart disease and lower cholesterol levels.
- Pine nuts are also a low-glycemic-index food, meaning they don’t cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels. This makes them a good snack option for people with diabetes.
Flavor
- Pine nuts have a rich, buttery flavor with a slightly sweet and nutty taste.
- They have a delicate texture that’s similar to sunflower seeds or almonds.
- Pine nuts are often used in Mediterranean cuisine, especially in dishes like pesto sauce, salads, and baked goods.
Harvesting and Processing
- Pine nuts are generally harvested by hand because the cones need to be opened to access the seeds inside.
- Harvesting and processing pine nuts can be a time-consuming and labor-intensive process, which is why they tend to be more expensive than other types of nuts.
- Once harvested, pine nuts need to be shelled to remove the hard outer shell before they can be eaten.
Uses
- Pine nuts are a versatile ingredient that can be used in many different types of dishes, from savory to sweet.
- They’re a popular ingredient in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisine, but can also be found in dishes from around the world.
- Some popular uses for pine nuts include as a topping for salads, roasted or baked in savory dishes, or blended into desserts like cakes and cookies.
How do Pine Nuts Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
- Several studies have been conducted to explore the link between pine nuts and blood sugar levels. One small study published in the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture found that consuming pine nuts with high-carbohydrate meals resulted in lower postprandial blood sugar levels compared to meals without pine nuts.
- Another study conducted by the University of Sydney found that consuming pine nuts as part of a low-glycemic index (GI) diet resulted in lower fasting blood sugar levels compared to a high-GI diet without pine nuts.
- The specific mechanisms by which pine nuts impact blood sugar levels are not yet fully understood. However, it is believed that the fiber, healthy fats, and minerals in pine nuts may play a role in regulating blood sugar levels. For example, the fiber in pine nuts can slow down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, reducing the likelihood of spikes in blood sugar levels after meals.
The Active Compounds in Pine Nuts That Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Pine nuts have long been a favorite snack in many cultures. These tiny, creamy-white nuts have a unique flavor and offer a range of health benefits. But did you know that they also contain active compounds that affect blood sugar levels? In this chapter, we will explore these compounds and how they work.
Phytosterols
- Phytosterols are compounds found in plant foods that have a similar chemical structure to cholesterol. However, unlike cholesterol, phytosterols can help reduce cholesterol levels in the body. This is because they block the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines. Pine nuts contain high levels of phytosterols, which can help reduce cholesterol levels and improve overall heart health.
Pinolenic Acid
- Pinolenic acid is a type of fatty acid found only in pine nuts. This fatty acid has been found to have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. Research has shown that pinolenic acid can increase the production of GLP-1, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This means that pine nuts may be beneficial for people with diabetes or those at risk of developing it.
Polyphenols
- Polyphenols are a group of compounds found in many plant-based foods, including pine nuts. These compounds have been found to improve insulin sensitivity, which can help regulate blood sugar levels. Polyphenols also have antioxidant properties that can help reduce inflammation and protect against chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Fiber
- Fiber is an essential nutrient found in plant-based foods, including pine nuts. Fiber is important for overall health, but it also plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. This is because fiber slows down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing blood sugar spikes.
- Pine nuts contain both soluble and insoluble fiber, making them an excellent choice for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
The Benefits of Pine Nuts for People with Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to several health problems. Pine nuts, however, have been found to provide numerous benefits to people with diabetes. Here are the top benefits of pine nuts for people with diabetes:
1. Lowering Blood Sugar Levels
One of the primary benefits of pine nuts for people with diabetes is their ability to lower blood sugar levels. They contain a high amount of magnesium, which helps improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels.
Pine nuts also have a low glycemic index (GI), which means they are slowly absorbed into the bloodstream, causing a gradual rise in blood sugar levels rather than an abrupt spike.
2. Reducing the Risk of Heart Disease
Heart disease is a common complication of diabetes, and people with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing heart disease. However, incorporating pine nuts into your diet can help reduce this risk.
Pine nuts are a rich source of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, both of which are beneficial for heart health. They also contain phytosterols, which have been found to lower cholesterol levels.
3. Decreasing Inflammation
People with diabetes are prone to chronic inflammation, which can lead to various complications. Pine nuts have anti-inflammatory properties and contain a high amount of vitamin E, which is a powerful antioxidant. Vitamin E helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can cause inflammation.
Pine nuts offer significant benefits for people with diabetes. They can help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and decrease inflammation. Adding pine nuts to your diet is an excellent way to incorporate a nutritious and delicious food that can help manage your diabetes and improve your overall health.
Other Health Benefits of Pine Nuts
In addition to potentially lowering blood sugar levels, pine nuts have several other health benefits. As previously mentioned, pine nuts are a rich source of healthy fats, including polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats. These fats have been shown to improve heart health by reducing inflammation and lowering cholesterol levels. Additionally, pine nuts are a great source of protein, an essential nutrient that is important for building and repairing tissues in the body.
Incorporating Pine Nuts Into a Healthy Diet
If you are interested in incorporating pine nuts into your diet for their potential blood sugar-lowering effects, there are several delicious and nutritious ways to do so. Pine nuts can be added to salads, sprinkled over roasted vegetables or used as a tasty topping for oatmeal or yogurt. Additionally, pine nuts can be blended into pestos or used as a nut butter substitute in recipes for a more savory flavor profile.
Conclusion
While more research is needed to fully understand the link between pine nuts and blood sugar levels, preliminary studies suggest that consuming pine nuts may have a positive impact on blood sugar regulation.
Additionally, pine nuts have numerous other health benefits, such as being a good source of healthy fats and protein. Incorporating pine nuts into a healthy diet is an easy and delicious way to boost your overall health and potentially lower your risk of conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
FAQ
How do pine nuts lower blood sugar?
Pine nuts contain certain nutrients that help regulate blood sugar levels. They contain magnesium, which has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
Are pine nuts effective in lowering blood sugar in the long term?
Pine nuts are not a magic solution, but can be an effective part of a balanced diet and exercise routine in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels in the long term.
How many pine nuts should I eat to see the benefits?
There is no set number of pine nuts that need to be consumed to see the benefits of blood sugar regulation. However, consuming a handful of pine nuts on a regular basis can be helpful.
Are pine nuts safe for people with diabetes to consume?
Yes, pine nuts are generally safe for people with diabetes to consume. However, it is recommended that individuals with diabetes follow a balanced diet and consult with their healthcare provider before adding pine nuts to their diet.
Can pine nuts be substituted for diabetes medication?
No, pine nuts cannot be substituted for diabetes medication. They can be consumed as a supplement to medication and a healthy diet and exercise routine.
Are there potential side effects of consuming pine nuts for blood sugar control?
Pine nuts are generally safe for consumption, but can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before introducing pine nuts to a diet.
Can pine nuts be consumed raw or do they need to be cooked?
Pine nuts can be consumed raw or cooked. They are commonly used in salads or added to dishes as a garnish.
Where can I find pine nuts to incorporate into my diet?
Pine nuts are commonly found online, in health food stores or grocery stores in the nut section. They can be added to salads, granolas, or eaten as a snack.
Can pine nuts be used to prevent the onset of diabetes?
While pine nuts can be an effective part of a balanced diet and exercise routine to maintain healthy blood sugar levels, there is no known cure or prevention for diabetes. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and consult with a healthcare provider for diabetes prevention advice.

Carb Cycling and Blood Sugar
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy for the body, but they also have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. Blood sugar refers to the amount of glucose present in the bloodstream. High blood sugar levels can lead to various health problems, including diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Carb cycling is a dietary approach that has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential to help manage blood sugar levels.
This article explores what carb cycling is and how it affects blood sugar.
What is Carb Cycling?
Carb cycling is a dietary approach that involves varying the number of carbohydrates consumed on a daily, weekly or monthly basis. This dietary approach has been around for decades and has gained immense popularity in recent years. Carb cycling has been lauded as an effective method for losing or maintaining weight, boosting athletic performance, and improving overall health markers.
There are technically two main types of carb cycling: high carb days and low carb days. Here are some additional details to help you understand this dietary approach better:
High Carb Days
- High carb days are usually followed on workout days, or days when you are more active.
- On these days, you increase your carb intake to refuel your glycogen stores, which will help fuel your workout and boost energy levels.
- High carb days are typically accompanied by a lower fat intake and moderate protein intake.
Low Carb Days
- Low carb days are typically used on rest days or days when your activity level is low.
- On these days, you decrease your carb intake to increase fat burning and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Low carb days are typically accompanied by a higher fat intake and moderate protein intake.
The cycles usually range from åa few days to several weeks, and the carbohydrate intake is usually adjusted depending on the individual’s needs. On high-carb days, individuals consume a higher amount of carbohydrates, usually up to 60% of their daily calorie intake, while on low-carb days, they consume a lower amount, usually around 10-20% of their daily calorie intake.
Blood Sugar
Blood sugar levels are tightly regulated, and the body’s ability to maintain stable levels is essential for overall health. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream and raises blood sugar levels. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, is responsible for transporting glucose into the cells, where it is used for energy.
If blood sugar levels remain high for an extended period, it can lead to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can result in high blood sugar levels, which may eventually lead to type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems.
How Carb Cycling Affects Blood Sugar
As carb cycling involves manipulating carbohydrate intake, understanding how carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels is essential. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main source of energy for your body.
When you consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose and absorbed into your bloodstream. This leads to a rise in blood sugar levels. However, the body must maintain blood sugar levels within a narrow range to ensure optimal health.
- High-Carb Days – On high-carb days, individuals typically consume a higher amount of carbohydrates, which leads to a higher increase in blood sugar levels after meals. However, the body’s insulin response should counteract this, allowing glucose to enter cells for energy and decreasing blood sugar levels. The body may also store some glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscles for later use.
- Low-Carb Days – On low-carb days, individuals consume fewer carbohydrates, which leads to a lower increase in blood sugar levels. This in turn leads to a lower insulin response. Instead, the body may switch to using stored glycogen or converting fats and proteins into glucose for energy. This is why low-carb diets are popular for weight loss, as the body is more likely to burn stored fats for energy.
Carb Cycling and Blood Sugar
When done correctly, carb cycling can help regulate blood sugar levels, thus reducing the risk of developing conditions like metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, carb cycling can help improve insulin sensitivity, which is essential for maintaining normal blood sugar levels. Insulin sensitivity refers to the ability of cells to respond to insulin and take up glucose effectively.
Carb cycling can also prevent the overconsumption of carbohydrates, which can lead to weight gain and increased blood sugar levels. The body has a limited capacity to store glucose as glycogen, and excess glucose is typically converted to fat for long-term storage. By cycling between high and low-carb days, individuals can ensure that their body is not overwhelmed by excess glucose and can effectively use stored glycogen for energy.
Carb cycling can help regulate blood sugar levels by altering carbohydrate intake. On high-carb days, the body increases insulin production to transport the increased amount of glucose into the cells. This results in lower blood sugar levels, which can be beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes.
On low-carb days, the body relies on stored fat for energy, which can lead to weight loss. This is because when carbohydrates are limited, the body switches to using stored fat as an energy source. This can also help improve insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance.
Benefits of Carb Cycling
- Weight Loss: Carb cycling can promote weight loss by increasing calorie burn and reducing fat storage.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: By cycling carbs, you can improve insulin sensitivity, which will help maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Athletic Performance: Carb cycling can help athletes perform better by providing the carbohydrate fuel needed for high-intensity workouts.
- Muscle Gain: By consuming more carbohydrates on high carb days, you can increase glycogen stores and enhance muscle growth
Tips for Successful Carb Cycling
Here are some tips on how to successfully implement a carb cycling diet.
1. Determine Your Macronutrient Ratio
The first step in carb cycling is to determine your macronutrient ratio. This means figuring out the amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats you need to consume each day. Your macronutrient ratio will depend on your fitness goals, age, gender, and activity level. A good starting point is to consume 1.5 grams of carbohydrates per pound of bodyweight on high carb days and 0.5 grams of carbohydrates per pound of bodyweight on low carb days.
2. Plan Your Meals
Once you have determined your macronutrient ratio, the next step is to plan your meals. You should aim to consume five to six small meals per day. On high carb days, the majority of your meals should consist of complex carbohydrates such as brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and whole grains. On low carb days, you should consume more proteins and healthy fats such as chicken, fish, eggs, avocado, and nuts.
3. Stick to Your Plan
Consistency is key when it comes to carb cycling. It is important to stick to your plan and to not deviate from it. If you cheat on your diet, it can undo all the progress you have made. Try to plan your meals in advance and take them with you when you are on the go.
4. Be Aware of Your Body’s Response
Lastly, it is important to be aware of your body’s response to carb cycling. If you find that you are not making progress, you may need to adjust your macronutrient ratio or tweak your meal plan. Additionally, some people may feel sluggish or fatigued on low carb days. If this is the case, you may need to increase your carbohydrate intake slightly.
Conclusion
As described above, carb cycling is a dietary approach that involves alternating between high-carb and low-carb days to manipulate carbohydrate intake. By doing this, individuals can achieve specific health and fitness goals, including improving blood sugar control and promoting weight loss.
Blood sugar regulation is crucial for overall health, and carb cycling can help individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes maintain stable blood sugar levels. However, carb cycling is not suitable for everyone and should not be used as a long-term dietary approach without consulting a healthcare professional.
Overall, carb cycling can be an effective dietary strategy for individuals looking to optimize their health and fitness goals, but it should be implemented cautiously, considering its potential risks and individual needs.
Please Note:
Consult with a doctor or healthcare provider before starting carb cycling or any other dietary program.
FAQ
Can carb cycling help you lose weight?
Yes, carb cycling is an effective way to achieve weight loss when combined with a healthy diet and exercise plan. The high-carbohydrate days provide the energy needed for physical activity while low-carb days promote fat burning.
Is carb cycling safe?
Carb cycling is a healthy dietary strategy and is safe when done correctly. However, as with any diet, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting as it may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with underlying medical conditions.
How Do You Implement Carb Cycling?
- Determine your carbohydrate needs: Your carbohydrate needs will depend on your goals, activity level, and body composition.
- Plan your meals: Plan your meals based on your carbohydrate needs. On high carb days, you’ll want to consume more carbohydrates, while on low carb days, you’ll want to consume fewer carbohydrates.
- Choose healthy carbohydrates: Choose healthy, nutrient-dense carbohydrates like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Be consistent: Consistency is key with carb cycling. Stick to your plan and make adjustments as needed.
What Role Does Exercise Play in Reversing Pre-diabetes?
Pre-diabetes is a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Unfortunately, pre-diabetes can progress to type 2 diabetes if lifestyle changes are not made. While diet and medication are commonly used to manage pre-diabetes, the role of exercise in reversing the condition is often overlooked.
Understanding Pre-Diabetes
Pre-diabetes is a condition where a person’s blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as Type 2 diabetes. It is a significant health issue as it can lead to the development of Type 2 diabetes and its associated complications. In this chapter, we will discuss what pre-diabetes is, what causes it, and how it can be diagnosed and managed.
What is Pre-Diabetes?
Pre-diabetes is a common condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 84 million adults in the United States have pre-diabetes. This condition is often referred to as impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance.
What Causes Pre-Diabetes?
Pre-diabetes occurs when the body is unable to use insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone that moves sugar from the blood into the cells of the body, where it is used for energy. When the body is unable to use insulin efficiently, it leads to high blood sugar levels.
Some of the risk factors for pre-diabetes include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being over the age of 45, and having high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels. In addition, physical inactivity, poor diet, and smoking can also increase the risk of developing pre-diabetes.
Diagnosis and Management of Pre-Diabetes
Pre-diabetes can be diagnosed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels after a person has fasted for at least eight hours. The two most common tests used to diagnose pre-diabetes are the A1C test and the fasting plasma glucose test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months, while the fasting plasma glucose test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
Once diagnosed, the goal of managing pre-diabetes is to prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes. This can be achieved through lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, following a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and quitting smoking. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels.
The Dangers of Progression to Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that can cause a host of serious health problems, including heart disease, kidney disease, blindness, and limb amputations.
- If left untreated, pre-diabetes can progress to type 2 diabetes in just a few years. In fact, around 15-30% of individuals with pre-diabetes develop type 2 diabetes within five years.
- Once diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes and/or medication may be necessary to manage the condition, and this can be both physically and financially taxing.
The Benefits of Prevention
- By preventing pre-diabetes from progressing to type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes, you can help reduce your risk of developing the associated health problems.
- Prevention can also mean avoiding the need for medication and other treatments associated with type 2 diabetes.
- The good news is that lifestyle changes, including healthy eating, regular physical activity, and weight loss, can significantly reduce the risk of progression to type 2 diabetes.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
- Early diagnosis of pre-diabetes is essential for prevention. Simple blood tests can detect pre-diabetes, and individuals who are diagnosed can take action to prevent progression to type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment for pre-diabetes may include lifestyle changes like those mentioned above, as well as medication in some cases.
- Diabetes educators and other healthcare professionals can help individuals with pre-diabetes make the necessary lifestyle changes and provide support for ongoing prevention efforts.
How Exercise Works in Reversing Pre-Diabetes:
1. Boosts insulin sensitivity: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps to regulate blood sugar levels. In pre-diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, and as a result, it is unable to use it effectively. Exercise helps to increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin, making it easier for the cells to use glucose for energy.
2. Reduces fat deposits: Excess body fat, especially around the waist, is a risk factor for pre-diabetes. Exercise helps to burn calories and reduce body fat. As a result, this reduces the risk of pre-diabetes and helps to reverse it.
3. Promotes weight loss: Exercise helps to burn calories, which promotes weight loss. This is crucial in reversing pre-diabetes because losing just 5-10% of your body weight can significantly improve blood sugar levels.
4. Strengthens the heart: Pre-diabetes, just like diabetes, can damage many organs, including the heart. Exercise helps to make the heart stronger and more efficient, which reduces the risk of heart diseases.
5. Improves energy levels: Exercise helps to improve overall fitness and energy levels, which makes it easier to perform daily activities.
Designing Your Exercise Plan
When designing an exercise plan, it is essential to take into account several factors such as age, fitness level, and medical history. These factors will determine the intensity, duration, and frequency of your exercise program.
Types of Exercise for Pre-diabetes
There are three main types of exercise that you should include in your exercise plan: aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Aerobic exercise such as brisk walking, cycling, and swimming helps to improve cardiovascular fitness and manage blood sugar levels. Strength training, on the other hand, helps to build muscle and boost metabolism. Flexibility exercises such as yoga and stretching help to improve range of motion and reduce the risk of injury.
How Much Exercise is Enough?
The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread over three to five days. In addition, resistance training should be done at least twice a week, with at least one set of 10-15 repetitions per exercise. It is also essential to avoid prolonged periods of sitting and to get up and move around every 30 minutes.
Getting Started with Exercise
If you are new to exercise, it is essential to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program. Consider working with a certified personal trainer who has experience working with people with pre-diabetes. Remember that exercise should be enjoyable and sustainable, so choose activities that you enjoy and fit into your lifestyle.
Conclusion
Pre-diabetes is a condition that can be reversed through lifestyle changes, including regular exercise. Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, promote weight loss, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By incorporating exercise into your daily routine, you can take control of your health and prevent the progression of pre-diabetes.
FAQ
Can a blood sugar supplement reverse pre-diabetes?
- While blood sugar supplements cannot cure pre-diabetes, they can help in controlling blood sugar levels and prevent the condition from progressing to type 2 diabetes.
How much exercise is needed to reverse pre-diabetes?
- Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week to help manage blood sugar levels and reverse pre-diabetes.
Should I consult my healthcare provider before starting an exercise program?
- It is always recommended to consult a healthcare provider before starting any exercise program, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
How long does it take to see the results of lifestyle changes such as exercise and diet in controlling blood sugar levels?
- The results of lifestyle changes may vary for each individual. However, incorporating regular exercise and a healthy diet can help lower blood sugar levels and improve overall health. It is important to stay consistent and monitor your progress with your healthcare provider.
Blood Sugar Dropping
Blood Sugar Level Dropping
Hypoglycemia, or unusually low blood glucose, may develop if your blood sugar levels drop too low (less than four millimoles per liter).
A lack of glucose (sugar) in the blood means your body lacks the fuel to function normally.
Hypoglycemia is a frequent complication of diabetes and often results from excessive insulin use, skipping meals, or strenuous activity.
Occasionally, people who do not have diabetes may get hypoglycemia. Malnutrition, heavy alcohol use, and medical diseases like Addison’s disease may all bring on these symptoms.
Effects of low blood sugar
Most individuals will experience symptoms before their blood glucose levels drop dangerously low, giving them time to take preventative measures. When blood sugar drops below four mmol/L, symptoms often show themselves.
Feeling hungry is a common warning symptom, as is trembling, shaking, and profuse perspiration. More severe instances sometimes include mental fogginess and trouble focusing. Loss of consciousness is possible in those with severe hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia may also happen while you’re sleeping, leaving you sweating excessively, with a messed-up sleep cycle, and groggy and disoriented when you wake up.
The Treatment of Hypoglycemia
Food or drinks high in sugar, such as dextrose tablets or fruit juice, should be consumed immediately to cure hypoglycemia.
A longer-acting “starchy carbohydrate snack,” such as a sandwich or a few biscuits, may be necessary after consuming anything sweet.
Loss of consciousness due to hypoglycemia may be treated by an injection of the hormone glucagon, which raises blood glucose levels and returns awareness to the patient. Of course, this assumes that an injection can be given and that the person administering it understands what they’re doing.
When you need an ambulance, phone 911 if:
- More glucagon for injection is currently on hand.
- No one knows how to administer the shot.
- After 10 minutes, the injection loses its efficacy.
- Person is sleepy or unconscious and should never have anything placed in their mouth because they may choke. Some of the high-sugar concoctions intended for intraoral application fall into this category.
Reducing the Risk of Low Blood Sugar
The best strategy to prevent hypoglycemia if you have insulin-dependent diabetes is to monitor your blood sugar levels frequently and know the early warning signs.
Your risk of hypoglycemia rises if you skip meals or snacks or consume fewer carbohydrates than you had intended. Alcohol use should be monitored since it, too, may result in hypoglycemia, even long after ingestion has stopped.
Another possible trigger is strenuous physical activity; to counteract this, you may need to consume carbs before, during, or after your workout or change your insulin dosage.
As the quantity of insulin absorbed by your body varies depending on where it is administered, you should switch up the injection site often.
If you sense symptoms approaching or your blood glucose level is low, have a source of rapid-acting carbohydrates on your hands, such as glucose tablets, a carton of fruit juice (one that includes sugar), or some candies.
Inform your loved ones that you have diabetes and may experience hypoglycemia. If you have a medical condition that might need medical attention, it is a good idea to have some identification with you at all times.
When hypoglycemia happens due to anything other than diabetes, that other issue must be addressed to stop the hypos from happening again.
Indicators of low blood sugar
Hypoglycemia symptoms often present when your blood glucose level drops below four mmol/L.
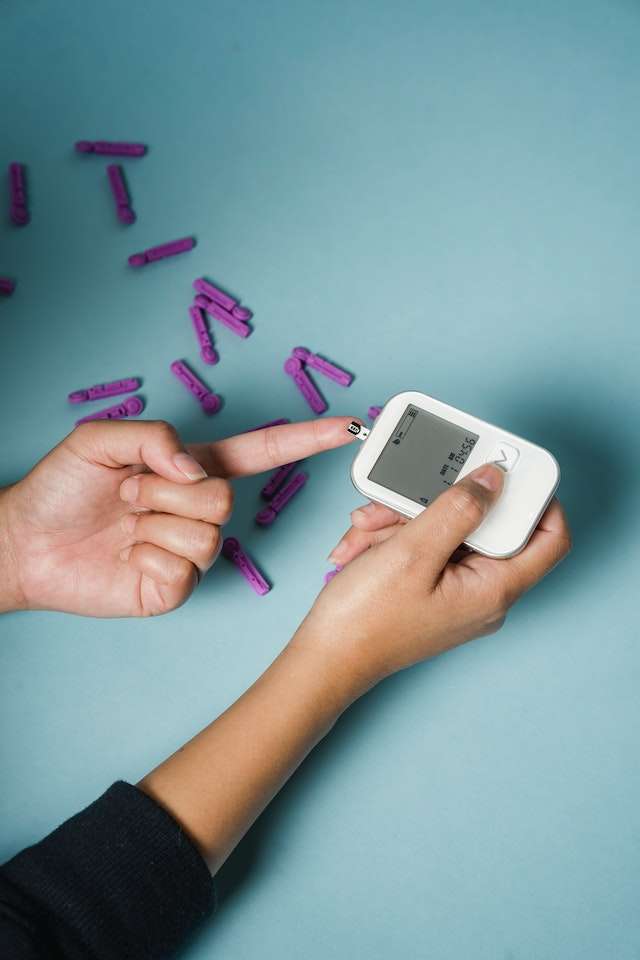
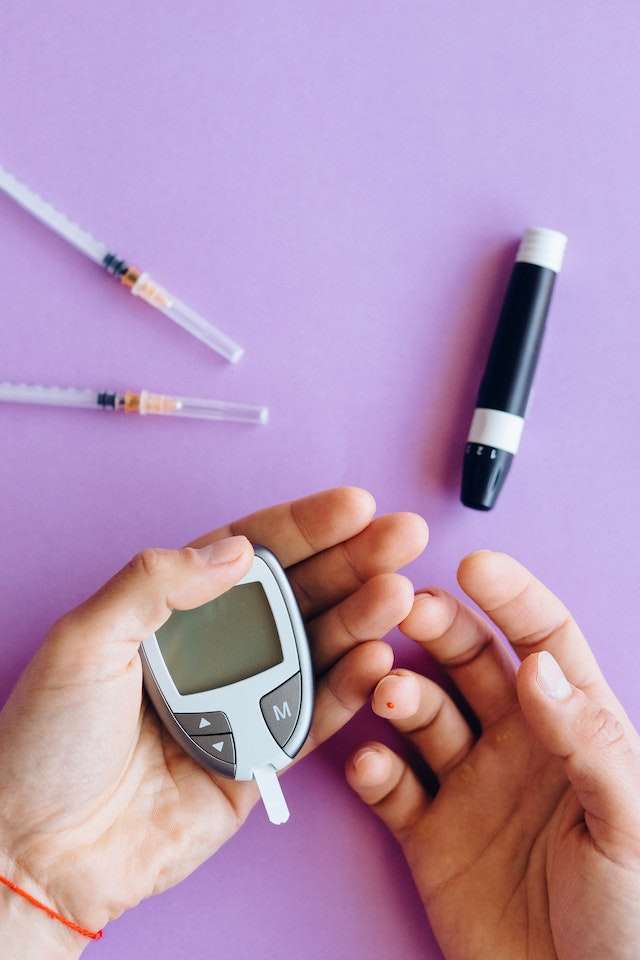
It is recommended that people with diabetes, especially those whose condition is managed with insulin, use portable equipment called a blood glucose meter regularly.
Symptoms may manifest differently in different people; therefore, it’s crucial to recognize the precursors to diagnosis and treatment.
Hypoglycemia symptoms may include, but are not limited to:
- needing to eat
- sweating
- dizziness
- weariness (fatigue)
- Foggy perception
- symptoms of shaking or trembling
- decreasing in pigmentation
- rapid heartbeats
- Sensational lips
- irritability
- Concentration issues
- confusion
- disruptive or illogical conduct that may be taken for intoxication.
Untreated hypoglycemia may cause drowsiness or even loss of consciousness if blood glucose levels drop too low for too long.
Most persons who use insulin to manage their diabetes report that the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia shift and become less noticeable with time.
For others, the early warning signs diminish to the point that they are no longer effective, dramatically increasing their chance of experiencing disruptive episodes that need assistance from others.
If you notice this issue, be sure to notify your diabetes care team so that they can adjust your therapy accordingly.
Insomniac hypoglycemia
Nocturnal hypoglycemia is when a hypo occurs during sleep. More often occurs in those who use insulin to control their diabetes.
Symptoms of nocturnal hypoglycemia may not present until you awaken in the morning, even if they may have caused sleep disruptions the night before.
Nighttime hypoglycemia symptoms might include:
- a painful headache similar to the feeling of a hangover
- waking up with an abnormally low amount of energy
- sweat-soaked bedsheets and garments
Hypoglycemia’s Root Causes
Although hypoglycemia most often affects those with diabetes, it may also occur in other contexts.
Diabetes-related hypoglycemia
Toxic overdose from diabetic medicine
Too much insulin for the body’s requirements is a typical cause of hypoglycemia. Blood sugar levels may be managed with the use of insulin. It is widely used for the treatment of type 1 diabetes and is also sometimes advised for persons with type 2 diabetes.
Too much oral hypoglycemia treatment, such as sulphonylurea, which stimulates insulin release, may also cause a drop in blood glucose levels. The blood sugar levels of persons with type 2 diabetes are commonly lowered with this medicine.
Weightlifting, eating, and drinking.
Type 2 diabetics need to strike a delicate balance between their insulin dosage, the calories they consume from meals, and the number of calories they expend via physical activity to keep their blood glucose levels within normal ranges.
If you take your regular insulin dosage but eat fewer carbs than usual or burn through them more rapidly, hypoglycemia might result. It’s possible to experience this if you work out for longer than normal, doesn’t consume enough carbs, or skip meals.
Hypoglycemia may also occur in people who have diabetes and have consumed too much alcohol or alcohol on an empty stomach.
However, there are situations when there is no clear cause for a hypoglycemic episode, and doctors are left guessing.
Non-Diabetic Hypoglycemia
Non-diabetic persons seldom experience hypoglycemia. What follows is an explanation of the probable reasons.
Hypoglycemia reaction
People who do not have diabetes nevertheless risk developing hypoglycemia if their pancreas produces an abnormally high quantity of insulin in response to a substantial meal high in carbohydrates. The medical term for this illness is reactive hypoglycemia.
Although the exact cause of this phenomenon is unknown, it seems to be more common in people who are overweight or who have had surgery to do a gastric bypass.
Occasionally, a pancreatic tumor that is not cancerous may cause an excessive amount of insulin to be generated or utilize an excessive amount of glucose for its requirements.
Additional potential factors
Hypoglycemia may also occur in persons who don’t have diabetes for a variety of other reasons:
Binge drinking or heavy alcohol consumption is malnutrition, in which the body does not get enough nutrients for it to function normally fasting.
Addison’s disease is the name given to the condition that affects the adrenal glands (two small glands that sit on top of the kidneys)
Patients using quinine, which is used to treat malaria, salicylates, which are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, and propranolol have all been documented to have had hypoglycemia (for high blood pressure), an illness of the liver, kidneys, or thyroid.
Hypoglycemia treatment
Hypoglycemia is usually a self-treatable condition as long as you know what to look for.
The management of hypoglycemia
An urgent remedy for hypoglycemia is the consumption of sugary food or drink (about 15–20g of fast-acting carbohydrate) to stop the episode.
Here’s one example that could fit the bill:
a regular-sized soft drink or fruit juice
Three to five dextrose pills
a little bag of candies
At first, it’s best to stay away from high-fat foods and beverages like chocolate and milk since they don’t often have as much sugar, and the sugar they do have may be absorbed more slowly.
It would be best if you had a longer-acting carbohydrate snack after ingesting sugary meals. Some examples of this kind of snack are a few biscuits, a cereal bar, a piece of fruit, or a sandwich. This will help you maintain your energy levels.
Recovery from an episode of hypoglycemia that is considered to be slight normally takes around 15 minutes. Take another measurement in the next 15–20 minutes if you have access to a blood glucose meter. If your blood sugar level is still too low (below 4 mmol), consume anything with added sugar and take another test after 15 to 20 minutes. If your blood sugar level is still too low, seek medical attention immediately.
If you are caring for someone who is experiencing hypoglycemia and the methods described above are not successful in treating the condition, you can try rubbing the outside of their cheeks with glucose gel (or honey, treacle, or jam if glucose gel is not available) and applying it directly to the maid.
It might be between ten and fifteen minutes before they start feeling better. Because of the risk of choking, this procedure should not be carried out on a person who is dozing off or already sleeping.
Your diabetes care team should consider the matter if you regularly experience hypoglycemia. You may need a change in the dosage of your medicine, or you may need medical attention for an underlying condition that is the cause of your hypoglycemia.
Keeping blood sugar levels stable
For those with diabetes, maintaining a regular meal schedule and medication schedule helps reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Keep an eye on your blood sugar levels.
FAQ
Do you know what it’s like to have your blood sugar suddenly drop?
Hunger pangs, shakiness, and profuse perspiration are common early warning signals. It’s also possible, especially in more extreme circumstances, that you’ll experience confusion and find it hard to focus.
Why does glucose level decrease suddenly?
If you don’t eat enough or miss meals, your blood sugar might decrease dangerously fast. Extra exercise, using specific medications, or taking too much medication (including insulin) may cause this condition. If you have trouble detecting the symptoms of low blood sugar, you should avoid alcohol.
When glucose levels in the blood drop, what happens?
This may cause visual blurring, difficulties focusing, muddled thinking, slurred speech, numbness, and tiredness. Long-term hypoglycemia, in which the brain goes without glucose, may cause convulsions, unconsciousness, and even death.
When blood sugar drops too low, what usually happens?
Although insulin users are more likely to have low blood sugar, everyone taking diabetic pills runs the risk. An overdose of insulin or other diabetic medicine is a common cause of diabetic hypoglycemia. Under-consuming or not eating enough.
At what point do you notice a dip in blood sugar?
Neither prediabetes nor diabetes has been identified. After an increase in blood sugar levels, one to two hours should pass before the levels return to normal. If you want to speed things up, going for a stroll or doing some exercise will help.
What other conditions than diabetes may result in hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia may also be caused by factors other than diabetes, such as
- consuming drinks with alcohol.
- Drugs include antibiotics, malaria and pneumonia pills.
- kidney health issues.
- Issues with either the adrenal glands or the pituitary gland.
- Cystic adenomas of the pancreas.
- Deadly disease
- conditions affecting the liver.
- Malignant pancreatic tumor.
At what level of blood sugar is there a serious health risk?
Extreme hypoglycemia is defined as a blood sugar level below 55 mg/dL. Depending on how you’re feeling, you may not be able to do self-tests of your blood sugar or administer your treatment.

Why a Diabetes Supplies Bag is a Game-Changer for Managing your Health
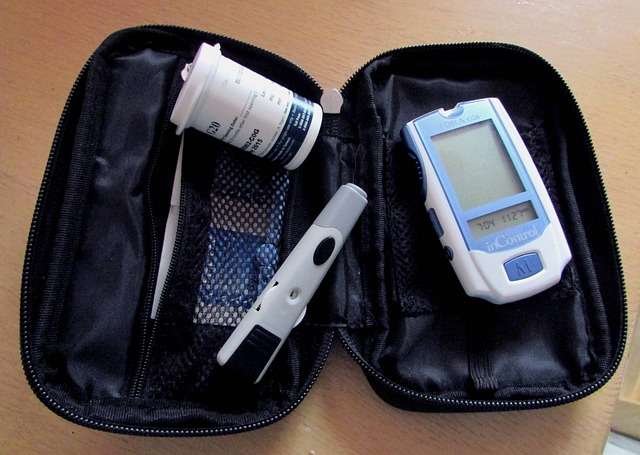
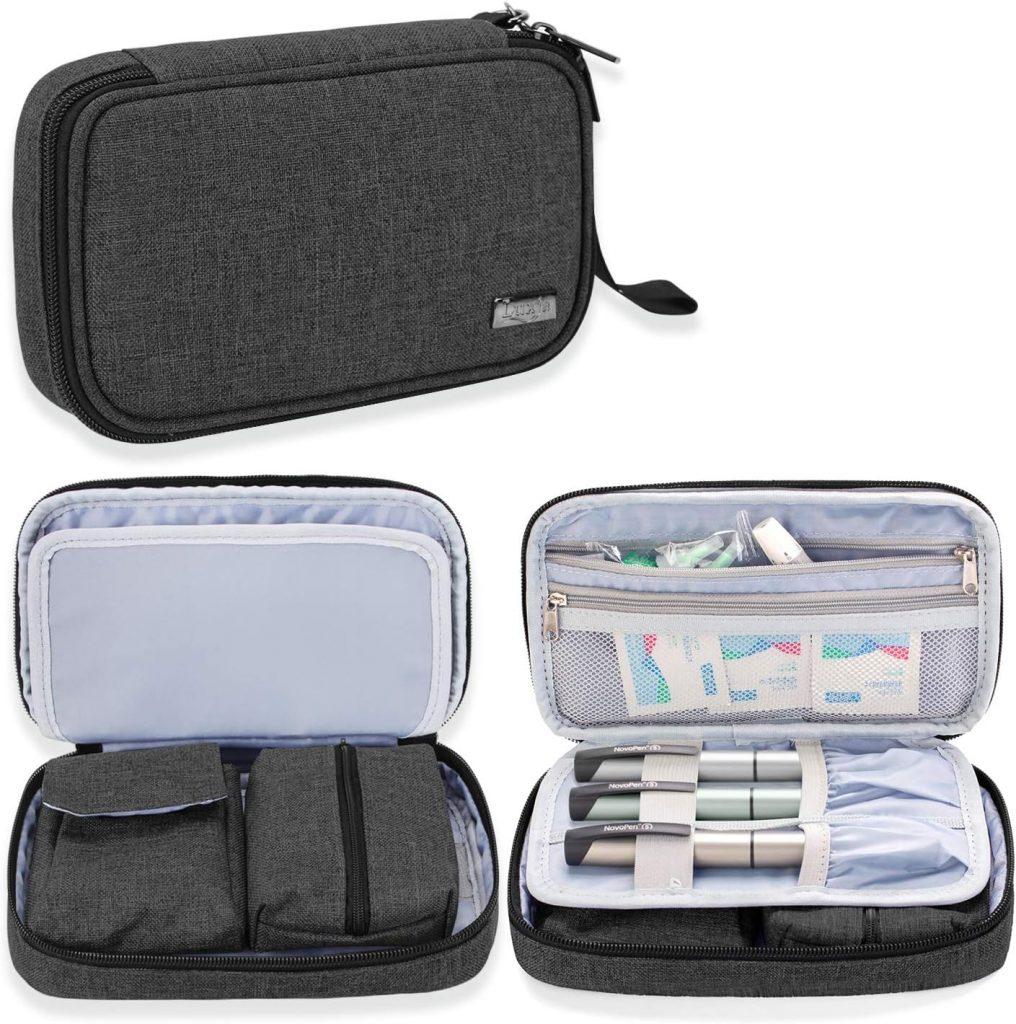
As a person living with diabetes, one of the biggest challenges you face every day is the need to stay organized and ensure that you have all the necessary supplies at hand. This is where a diabetes supplies bag can prove to be a true game-changer in helping you manage your health effectively. In this article, we will discuss why a diabetes supplies bag is essential and how it can help you take control of your diabetes.
Firstly, let’s understand what a diabetes supplies bag is. Simply put, it is a bag or a pouch that contains all the essential supplies that people with diabetes need to manage their condition on a daily basis. These supplies may include insulin pens, glucose meters, test strips, lancets, alcohol swabs, glucagon kits, and even snacks for managing low blood sugar.
Now, you may be wondering why you need a separate bag when you can easily carry all these items in your regular bag or pockets. The answer is simple – organization and convenience.
When you have a dedicated diabetes supplies bag, you can keep all your supplies together in a neat and organized manner. This ensures that you don’t waste time and energy hunting for individual items when you need them the most. Additionally, a dedicated bag reduces the risk of losing or misplacing your supplies, which can be disastrous for your health.
Moreover, a diabetes supplies bag provides convenience and peace of mind. When you leave your house or travel, you can easily grab your bag containing all your supplies and medications. This reduces the chances of leaving behind important items and running the risk of an emergency.
Benefits of a Diabetes Supplies Bag
Let’s now talk about the benefits of a diabetes supplies bag.
1. Reduces stress and anxiety
Living with diabetes can be stressful and overwhelming, especially when you have to constantly track your blood sugar levels and manage your medications. A diabetes supplies bag helps you stay organized and keeps all your supplies in one place. This reduces stress and anxiety and helps you focus on your health goals.
2. Helps you maintain healthy habits
A diabetes supplies bag contains all the necessary supplies you need to monitor your blood sugar levels and manage your medications. This helps you maintain healthy habits and ensures that you don’t miss any crucial doses or readings.
3. Increases independence and confidence
A diabetes supplies bag empowers you to take control of your health and increases your independence and confidence. With all your supplies in one place, you don’t have to rely on others to manage your medications or supplies.
4. Facilitates better communication with healthcare providers
A diabetes supplies bag makes it easy to communicate with your healthcare providers. You can easily take your bag containing all your supplies and medications to your appointments, which helps your healthcare provider get a better understanding of your condition and evaluate your progress.
5. Saves time and energy
A diabetes supplies bag saves time and energy by keeping all your supplies organized and readily accessible. This eliminates the need to rummage through different bags or pockets to find individual items, which can waste valuable time and energy.
6. Helps you avoid emergencies
A diabetes supplies bag equipped with emergency supplies can help you avoid emergencies. You can include items such as a glucagon kit and snacks to manage low blood sugar. Having these items readily available can help you avoid potentially dangerous situations.
Tips for Choosing the Right Bag
Now that you understand the benefits of a diabetes supplies bag, let’s talk about some tips for choosing the right bag.
1. Look for a bag that is spacious and organized
Choose a bag that has enough compartments and pockets to keep all your supplies organized. This reduces the risk of misplacing important items and helps you find what you need quickly.
2. Choose a bag that is easy to carry and visually appealing
Look for a bag that is easy to carry and visually appealing. You want a bag that you’re comfortable carrying around and that makes you feel good about yourself.
3. Choose a bag that is durable and easy to clean
Essential Items to Keep in a Diabetes Supplies Bag
Living with diabetes means that it’s important to always be prepared for any related medical emergencies. A key element of this is having a diabetes supplies bag with all the essential items you need to stay safe and healthy.
Here are some common items to keep in your Diabetes Supplies Bag:
1. Insulin
- Insulin is a hormone that helps the body regulate glucose, or blood sugar. Insulin dosage is often managed with a pump, a device that injects insulin into the body as it monitors glucose levels. A diabetes supplies bag should contain different dosages of insulin for pumps, and a syringe for manually injecting insulin, in case of emergencies.
2. Glucose Tablets
- In cases of a sudden drop in blood sugar level, glucose tablets are a must-have in diabetes supplies bags. They are small, easy to carry and can be quickly ingested for an instant boost of energy.
3. Ketone Strips
- Ketone strips are used to measure ketone levels in the body, providing useful information about a person’s diabetes management. A diabetes supplies kit should contain test strips designed to measure ketone levels.
4. Hypo Treatment
- Hypo treatments are snacks or drinks used to quickly raise a person’s blood sugar levels. A diabetes supplies kit should always have hypo treatments that are easy to carry and quick to consume, such as juice or chocolate.
5. Glucose Meter
- Glucose meters measure the amount of glucose present in the blood and allow people to keep close track of their glucose levels. The meter should be included in the diabetes supplies bag in case the person needs to reference their levels away from home.
6. Medical Identification
- People living with diabetes should always carry some type of medical identification on them. A diabetic supplies bag should contain an ID card, bracelet or necklace that indicates the person is diabetic, in case of emergency.
7. Insulin Pen Needles
- Insulin pen needles are critical to managing a diabetes supplies bag. The needles should be kept in the bag and replaced at least once a month.
8. Sharps Container
- The sharps container is a thick, puncture resistant container used to safely store used insulin pens, needles and syringes. The insulin supplies bag should always include a sharps container to store discarded materials.
9. Glucose Gels
- Glucose gel is a type of hypo treatment sold in tubes or single-serve sachets that can be quickly ingested if a person is experiencing a hypoglycemic attack. The gel should be included in the diabetes supplies bag in case of emergency.
10. Syringes
- Syringes are often used in place of insulin pens, and may be required to administer insulin manually. The diabetes supplies bag should contain at least one or two syringes in case the person needs to inject insulin manually.
11. Other Considerations
- In addition to the items listed above, diabetes supplies bags should also include any additional items a person with diabetes may need. These can include rubber gloves, alcohol pads, glucagon kits, insulin vials and sterile water. Any other items that are recommended by a doctor should also be included in the diabetes supplies bag.
Conclusion
Living with diabetes means it is essential to always be prepared for the unexpected. By having a diabetes supplies bag and keeping it stocked with all the essential items a person needs to manage their condition, they can feel safer and more confident in their health. This comprehensive guide can help you make sure your diabetes supplies bag is well stocked and ready to go!
Choose a bag that is durable and easy to clean. A diabetes supplies bag is likely to be used frequently and may come into contact with spills and other contaminants. A durable and easy-to-clean bag will ensure that your supplies remain safe and hygienic.
By choosing the right bag, you can take control of your health and live with confidence and independence.