Blood Sugar Levels

Carb Cycling and Blood Sugar
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy for the body, but they also have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. Blood sugar refers to the amount of glucose present in the bloodstream. High blood sugar levels can lead to various health problems, including diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Carb cycling is a dietary approach that has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential to help manage blood sugar levels.
This article explores what carb cycling is and how it affects blood sugar.
What is Carb Cycling?
Carb cycling is a dietary approach that involves varying the number of carbohydrates consumed on a daily, weekly or monthly basis. This dietary approach has been around for decades and has gained immense popularity in recent years. Carb cycling has been lauded as an effective method for losing or maintaining weight, boosting athletic performance, and improving overall health markers.
There are technically two main types of carb cycling: high carb days and low carb days. Here are some additional details to help you understand this dietary approach better:
High Carb Days
- High carb days are usually followed on workout days, or days when you are more active.
- On these days, you increase your carb intake to refuel your glycogen stores, which will help fuel your workout and boost energy levels.
- High carb days are typically accompanied by a lower fat intake and moderate protein intake.
Low Carb Days
- Low carb days are typically used on rest days or days when your activity level is low.
- On these days, you decrease your carb intake to increase fat burning and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Low carb days are typically accompanied by a higher fat intake and moderate protein intake.
The cycles usually range from åa few days to several weeks, and the carbohydrate intake is usually adjusted depending on the individual’s needs. On high-carb days, individuals consume a higher amount of carbohydrates, usually up to 60% of their daily calorie intake, while on low-carb days, they consume a lower amount, usually around 10-20% of their daily calorie intake.
Blood Sugar
Blood sugar levels are tightly regulated, and the body’s ability to maintain stable levels is essential for overall health. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream and raises blood sugar levels. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, is responsible for transporting glucose into the cells, where it is used for energy.
If blood sugar levels remain high for an extended period, it can lead to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can result in high blood sugar levels, which may eventually lead to type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems.
How Carb Cycling Affects Blood Sugar
As carb cycling involves manipulating carbohydrate intake, understanding how carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels is essential. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main source of energy for your body.
When you consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose and absorbed into your bloodstream. This leads to a rise in blood sugar levels. However, the body must maintain blood sugar levels within a narrow range to ensure optimal health.
- High-Carb Days – On high-carb days, individuals typically consume a higher amount of carbohydrates, which leads to a higher increase in blood sugar levels after meals. However, the body’s insulin response should counteract this, allowing glucose to enter cells for energy and decreasing blood sugar levels. The body may also store some glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscles for later use.
- Low-Carb Days – On low-carb days, individuals consume fewer carbohydrates, which leads to a lower increase in blood sugar levels. This in turn leads to a lower insulin response. Instead, the body may switch to using stored glycogen or converting fats and proteins into glucose for energy. This is why low-carb diets are popular for weight loss, as the body is more likely to burn stored fats for energy.
Carb Cycling and Blood Sugar
When done correctly, carb cycling can help regulate blood sugar levels, thus reducing the risk of developing conditions like metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, carb cycling can help improve insulin sensitivity, which is essential for maintaining normal blood sugar levels. Insulin sensitivity refers to the ability of cells to respond to insulin and take up glucose effectively.
Carb cycling can also prevent the overconsumption of carbohydrates, which can lead to weight gain and increased blood sugar levels. The body has a limited capacity to store glucose as glycogen, and excess glucose is typically converted to fat for long-term storage. By cycling between high and low-carb days, individuals can ensure that their body is not overwhelmed by excess glucose and can effectively use stored glycogen for energy.
Carb cycling can help regulate blood sugar levels by altering carbohydrate intake. On high-carb days, the body increases insulin production to transport the increased amount of glucose into the cells. This results in lower blood sugar levels, which can be beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes.
On low-carb days, the body relies on stored fat for energy, which can lead to weight loss. This is because when carbohydrates are limited, the body switches to using stored fat as an energy source. This can also help improve insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance.
Benefits of Carb Cycling
- Weight Loss: Carb cycling can promote weight loss by increasing calorie burn and reducing fat storage.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: By cycling carbs, you can improve insulin sensitivity, which will help maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Athletic Performance: Carb cycling can help athletes perform better by providing the carbohydrate fuel needed for high-intensity workouts.
- Muscle Gain: By consuming more carbohydrates on high carb days, you can increase glycogen stores and enhance muscle growth
Tips for Successful Carb Cycling
Here are some tips on how to successfully implement a carb cycling diet.
1. Determine Your Macronutrient Ratio
The first step in carb cycling is to determine your macronutrient ratio. This means figuring out the amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats you need to consume each day. Your macronutrient ratio will depend on your fitness goals, age, gender, and activity level. A good starting point is to consume 1.5 grams of carbohydrates per pound of bodyweight on high carb days and 0.5 grams of carbohydrates per pound of bodyweight on low carb days.
2. Plan Your Meals
Once you have determined your macronutrient ratio, the next step is to plan your meals. You should aim to consume five to six small meals per day. On high carb days, the majority of your meals should consist of complex carbohydrates such as brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and whole grains. On low carb days, you should consume more proteins and healthy fats such as chicken, fish, eggs, avocado, and nuts.
3. Stick to Your Plan
Consistency is key when it comes to carb cycling. It is important to stick to your plan and to not deviate from it. If you cheat on your diet, it can undo all the progress you have made. Try to plan your meals in advance and take them with you when you are on the go.
4. Be Aware of Your Body’s Response
Lastly, it is important to be aware of your body’s response to carb cycling. If you find that you are not making progress, you may need to adjust your macronutrient ratio or tweak your meal plan. Additionally, some people may feel sluggish or fatigued on low carb days. If this is the case, you may need to increase your carbohydrate intake slightly.
Conclusion
As described above, carb cycling is a dietary approach that involves alternating between high-carb and low-carb days to manipulate carbohydrate intake. By doing this, individuals can achieve specific health and fitness goals, including improving blood sugar control and promoting weight loss.
Blood sugar regulation is crucial for overall health, and carb cycling can help individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes maintain stable blood sugar levels. However, carb cycling is not suitable for everyone and should not be used as a long-term dietary approach without consulting a healthcare professional.
Overall, carb cycling can be an effective dietary strategy for individuals looking to optimize their health and fitness goals, but it should be implemented cautiously, considering its potential risks and individual needs.
Please Note:
Consult with a doctor or healthcare provider before starting carb cycling or any other dietary program.
FAQ
Can carb cycling help you lose weight?
Yes, carb cycling is an effective way to achieve weight loss when combined with a healthy diet and exercise plan. The high-carbohydrate days provide the energy needed for physical activity while low-carb days promote fat burning.
Is carb cycling safe?
Carb cycling is a healthy dietary strategy and is safe when done correctly. However, as with any diet, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting as it may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with underlying medical conditions.
How Do You Implement Carb Cycling?
- Determine your carbohydrate needs: Your carbohydrate needs will depend on your goals, activity level, and body composition.
- Plan your meals: Plan your meals based on your carbohydrate needs. On high carb days, you’ll want to consume more carbohydrates, while on low carb days, you’ll want to consume fewer carbohydrates.
- Choose healthy carbohydrates: Choose healthy, nutrient-dense carbohydrates like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Be consistent: Consistency is key with carb cycling. Stick to your plan and make adjustments as needed.
Blood Sugar Dropping
Blood Sugar Level Dropping
Hypoglycemia, or unusually low blood glucose, may develop if your blood sugar levels drop too low (less than four millimoles per liter).
A lack of glucose (sugar) in the blood means your body lacks the fuel to function normally.
Hypoglycemia is a frequent complication of diabetes and often results from excessive insulin use, skipping meals, or strenuous activity.
Occasionally, people who do not have diabetes may get hypoglycemia. Malnutrition, heavy alcohol use, and medical diseases like Addison’s disease may all bring on these symptoms.
Effects of low blood sugar
Most individuals will experience symptoms before their blood glucose levels drop dangerously low, giving them time to take preventative measures. When blood sugar drops below four mmol/L, symptoms often show themselves.
Feeling hungry is a common warning symptom, as is trembling, shaking, and profuse perspiration. More severe instances sometimes include mental fogginess and trouble focusing. Loss of consciousness is possible in those with severe hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia may also happen while you’re sleeping, leaving you sweating excessively, with a messed-up sleep cycle, and groggy and disoriented when you wake up.
The Treatment of Hypoglycemia
Food or drinks high in sugar, such as dextrose tablets or fruit juice, should be consumed immediately to cure hypoglycemia.
A longer-acting “starchy carbohydrate snack,” such as a sandwich or a few biscuits, may be necessary after consuming anything sweet.
Loss of consciousness due to hypoglycemia may be treated by an injection of the hormone glucagon, which raises blood glucose levels and returns awareness to the patient. Of course, this assumes that an injection can be given and that the person administering it understands what they’re doing.
When you need an ambulance, phone 911 if:
- More glucagon for injection is currently on hand.
- No one knows how to administer the shot.
- After 10 minutes, the injection loses its efficacy.
- Person is sleepy or unconscious and should never have anything placed in their mouth because they may choke. Some of the high-sugar concoctions intended for intraoral application fall into this category.
Reducing the Risk of Low Blood Sugar
The best strategy to prevent hypoglycemia if you have insulin-dependent diabetes is to monitor your blood sugar levels frequently and know the early warning signs.
Your risk of hypoglycemia rises if you skip meals or snacks or consume fewer carbohydrates than you had intended. Alcohol use should be monitored since it, too, may result in hypoglycemia, even long after ingestion has stopped.
Another possible trigger is strenuous physical activity; to counteract this, you may need to consume carbs before, during, or after your workout or change your insulin dosage.
As the quantity of insulin absorbed by your body varies depending on where it is administered, you should switch up the injection site often.
If you sense symptoms approaching or your blood glucose level is low, have a source of rapid-acting carbohydrates on your hands, such as glucose tablets, a carton of fruit juice (one that includes sugar), or some candies.
Inform your loved ones that you have diabetes and may experience hypoglycemia. If you have a medical condition that might need medical attention, it is a good idea to have some identification with you at all times.
When hypoglycemia happens due to anything other than diabetes, that other issue must be addressed to stop the hypos from happening again.
Indicators of low blood sugar
Hypoglycemia symptoms often present when your blood glucose level drops below four mmol/L.
It is recommended that people with diabetes, especially those whose condition is managed with insulin, use portable equipment called a blood glucose meter regularly.
Symptoms may manifest differently in different people; therefore, it’s crucial to recognize the precursors to diagnosis and treatment.
Hypoglycemia symptoms may include, but are not limited to:
- needing to eat
- sweating
- dizziness
- weariness (fatigue)
- Foggy perception
- symptoms of shaking or trembling
- decreasing in pigmentation
- rapid heartbeats
- Sensational lips
- irritability
- Concentration issues
- confusion
- disruptive or illogical conduct that may be taken for intoxication.
Untreated hypoglycemia may cause drowsiness or even loss of consciousness if blood glucose levels drop too low for too long.
Most persons who use insulin to manage their diabetes report that the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia shift and become less noticeable with time.
For others, the early warning signs diminish to the point that they are no longer effective, dramatically increasing their chance of experiencing disruptive episodes that need assistance from others.
If you notice this issue, be sure to notify your diabetes care team so that they can adjust your therapy accordingly.
Insomniac hypoglycemia
Nocturnal hypoglycemia is when a hypo occurs during sleep. More often occurs in those who use insulin to control their diabetes.
Symptoms of nocturnal hypoglycemia may not present until you awaken in the morning, even if they may have caused sleep disruptions the night before.
Nighttime hypoglycemia symptoms might include:
- a painful headache similar to the feeling of a hangover
- waking up with an abnormally low amount of energy
- sweat-soaked bedsheets and garments
Hypoglycemia’s Root Causes
Although hypoglycemia most often affects those with diabetes, it may also occur in other contexts.
Diabetes-related hypoglycemia
Toxic overdose from diabetic medicine
Too much insulin for the body’s requirements is a typical cause of hypoglycemia. Blood sugar levels may be managed with the use of insulin. It is widely used for the treatment of type 1 diabetes and is also sometimes advised for persons with type 2 diabetes.
Too much oral hypoglycemia treatment, such as sulphonylurea, which stimulates insulin release, may also cause a drop in blood glucose levels. The blood sugar levels of persons with type 2 diabetes are commonly lowered with this medicine.
Weightlifting, eating, and drinking.
Type 2 diabetics need to strike a delicate balance between their insulin dosage, the calories they consume from meals, and the number of calories they expend via physical activity to keep their blood glucose levels within normal ranges.
If you take your regular insulin dosage but eat fewer carbs than usual or burn through them more rapidly, hypoglycemia might result. It’s possible to experience this if you work out for longer than normal, doesn’t consume enough carbs, or skip meals.
Hypoglycemia may also occur in people who have diabetes and have consumed too much alcohol or alcohol on an empty stomach.
However, there are situations when there is no clear cause for a hypoglycemic episode, and doctors are left guessing.
Non-Diabetic Hypoglycemia
Non-diabetic persons seldom experience hypoglycemia. What follows is an explanation of the probable reasons.
Hypoglycemia reaction
People who do not have diabetes nevertheless risk developing hypoglycemia if their pancreas produces an abnormally high quantity of insulin in response to a substantial meal high in carbohydrates. The medical term for this illness is reactive hypoglycemia.
Although the exact cause of this phenomenon is unknown, it seems to be more common in people who are overweight or who have had surgery to do a gastric bypass.
Occasionally, a pancreatic tumor that is not cancerous may cause an excessive amount of insulin to be generated or utilize an excessive amount of glucose for its requirements.
Additional potential factors
Hypoglycemia may also occur in persons who don’t have diabetes for a variety of other reasons:
Binge drinking or heavy alcohol consumption is malnutrition, in which the body does not get enough nutrients for it to function normally fasting.
Addison’s disease is the name given to the condition that affects the adrenal glands (two small glands that sit on top of the kidneys)
Patients using quinine, which is used to treat malaria, salicylates, which are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, and propranolol have all been documented to have had hypoglycemia (for high blood pressure), an illness of the liver, kidneys, or thyroid.
Hypoglycemia treatment
Hypoglycemia is usually a self-treatable condition as long as you know what to look for.
The management of hypoglycemia
An urgent remedy for hypoglycemia is the consumption of sugary food or drink (about 15–20g of fast-acting carbohydrate) to stop the episode.
Here’s one example that could fit the bill:
a regular-sized soft drink or fruit juice
Three to five dextrose pills
a little bag of candies
At first, it’s best to stay away from high-fat foods and beverages like chocolate and milk since they don’t often have as much sugar, and the sugar they do have may be absorbed more slowly.
It would be best if you had a longer-acting carbohydrate snack after ingesting sugary meals. Some examples of this kind of snack are a few biscuits, a cereal bar, a piece of fruit, or a sandwich. This will help you maintain your energy levels.
Recovery from an episode of hypoglycemia that is considered to be slight normally takes around 15 minutes. Take another measurement in the next 15–20 minutes if you have access to a blood glucose meter. If your blood sugar level is still too low (below 4 mmol), consume anything with added sugar and take another test after 15 to 20 minutes. If your blood sugar level is still too low, seek medical attention immediately.
If you are caring for someone who is experiencing hypoglycemia and the methods described above are not successful in treating the condition, you can try rubbing the outside of their cheeks with glucose gel (or honey, treacle, or jam if glucose gel is not available) and applying it directly to the maid.
It might be between ten and fifteen minutes before they start feeling better. Because of the risk of choking, this procedure should not be carried out on a person who is dozing off or already sleeping.
Your diabetes care team should consider the matter if you regularly experience hypoglycemia. You may need a change in the dosage of your medicine, or you may need medical attention for an underlying condition that is the cause of your hypoglycemia.
Keeping blood sugar levels stable
For those with diabetes, maintaining a regular meal schedule and medication schedule helps reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Keep an eye on your blood sugar levels.
FAQ
Do you know what it’s like to have your blood sugar suddenly drop?
Hunger pangs, shakiness, and profuse perspiration are common early warning signals. It’s also possible, especially in more extreme circumstances, that you’ll experience confusion and find it hard to focus.
Why does glucose level decrease suddenly?
If you don’t eat enough or miss meals, your blood sugar might decrease dangerously fast. Extra exercise, using specific medications, or taking too much medication (including insulin) may cause this condition. If you have trouble detecting the symptoms of low blood sugar, you should avoid alcohol.
When glucose levels in the blood drop, what happens?
This may cause visual blurring, difficulties focusing, muddled thinking, slurred speech, numbness, and tiredness. Long-term hypoglycemia, in which the brain goes without glucose, may cause convulsions, unconsciousness, and even death.
When blood sugar drops too low, what usually happens?
Although insulin users are more likely to have low blood sugar, everyone taking diabetic pills runs the risk. An overdose of insulin or other diabetic medicine is a common cause of diabetic hypoglycemia. Under-consuming or not eating enough.
At what point do you notice a dip in blood sugar?
Neither prediabetes nor diabetes has been identified. After an increase in blood sugar levels, one to two hours should pass before the levels return to normal. If you want to speed things up, going for a stroll or doing some exercise will help.
What other conditions than diabetes may result in hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia may also be caused by factors other than diabetes, such as
- consuming drinks with alcohol.
- Drugs include antibiotics, malaria and pneumonia pills.
- kidney health issues.
- Issues with either the adrenal glands or the pituitary gland.
- Cystic adenomas of the pancreas.
- Deadly disease
- conditions affecting the liver.
- Malignant pancreatic tumor.
At what level of blood sugar is there a serious health risk?
Extreme hypoglycemia is defined as a blood sugar level below 55 mg/dL. Depending on how you’re feeling, you may not be able to do self-tests of your blood sugar or administer your treatment.

Blood Sugar Dropping
Blood Sugar Level Dropping
Hypoglycemia, or unusually low blood glucose, may develop if your blood sugar levels drop too low (less than four millimoles per liter).
A lack of glucose (sugar) in the blood means your body lacks the fuel to function normally.
Hypoglycemia is a frequent complication of diabetes and often results from excessive insulin use, skipping meals, or strenuous activity.
Occasionally, people who do not have diabetes may get hypoglycemia. Malnutrition, heavy alcohol use, and medical diseases like Addison’s disease may all bring on these symptoms.
Effects of low blood sugar
Most individuals will experience symptoms before their blood glucose levels drop dangerously low, giving them time to take preventative measures. When blood sugar drops below four mmol/L, symptoms often show themselves.
Feeling hungry is a common warning symptom, as is trembling, shaking, and profuse perspiration. More severe instances sometimes include mental fogginess and trouble focusing. Loss of consciousness is possible in those with severe hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia may also happen while you’re sleeping, leaving you sweating excessively, with a messed-up sleep cycle, and groggy and disoriented when you wake up.
The Treatment of Hypoglycemia
Food or drinks high in sugar, such as dextrose tablets or fruit juice, should be consumed immediately to cure hypoglycemia.
A longer-acting “starchy carbohydrate snack,” such as a sandwich or a few biscuits, may be necessary after consuming anything sweet.
Loss of consciousness due to hypoglycemia may be treated by an injection of the hormone glucagon, which raises blood glucose levels and returns awareness to the patient. Of course, this assumes that an injection can be given and that the person administering it understands what they’re doing.
When you need an ambulance, phone 911 if:
- More glucagon for injection is currently on hand.
- No one knows how to administer the shot.
- After 10 minutes, the injection loses its efficacy.
- Person is sleepy or unconscious and should never have anything placed in their mouth because they may choke. Some of the high-sugar concoctions intended for intraoral application fall into this category.
Reducing the Risk of Low Blood Sugar
The best strategy to prevent hypoglycemia if you have insulin-dependent diabetes is to monitor your blood sugar levels frequently and know the early warning signs.
Your risk of hypoglycemia rises if you skip meals or snacks or consume fewer carbohydrates than you had intended. Alcohol use should be monitored since it, too, may result in hypoglycemia, even long after ingestion has stopped.
Another possible trigger is strenuous physical activity; to counteract this, you may need to consume carbs before, during, or after your workout or change your insulin dosage.
As the quantity of insulin absorbed by your body varies depending on where it is administered, you should switch up the injection site often.
If you sense symptoms approaching or your blood glucose level is low, have a source of rapid-acting carbohydrates on your hands, such as glucose tablets, a carton of fruit juice (one that includes sugar), or some candies.
Inform your loved ones that you have diabetes and may experience hypoglycemia. If you have a medical condition that might need medical attention, it is a good idea to have some identification with you at all times.
When hypoglycemia happens due to anything other than diabetes, that other issue must be addressed to stop the hypos from happening again.
Indicators of low blood sugar
Hypoglycemia symptoms often present when your blood glucose level drops below four mmol/L.
It is recommended that people with diabetes, especially those whose condition is managed with insulin, use portable equipment called a blood glucose meter regularly.
Symptoms may manifest differently in different people; therefore, it’s crucial to recognize the precursors to diagnosis and treatment.
Hypoglycemia symptoms may include, but are not limited to:
- needing to eat
- sweating
- dizziness
- weariness (fatigue)
- Foggy perception
- symptoms of shaking or trembling
- decreasing in pigmentation
- rapid heartbeats
- Sensational lips
- irritability
- Concentration issues
- confusion
- disruptive or illogical conduct that may be taken for intoxication.
Untreated hypoglycemia may cause drowsiness or even loss of consciousness if blood glucose levels drop too low for too long.
Most persons who use insulin to manage their diabetes report that the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia shift and become less noticeable with time.
For others, the early warning signs diminish to the point that they are no longer effective, dramatically increasing their chance of experiencing disruptive episodes that need assistance from others.
If you notice this issue, be sure to notify your diabetes care team so that they can adjust your therapy accordingly.
Insomniac hypoglycemia
Nocturnal hypoglycemia is when a hypo occurs during sleep. More often occurs in those who use insulin to control their diabetes.
Symptoms of nocturnal hypoglycemia may not present until you awaken in the morning, even if they may have caused sleep disruptions the night before.
Nighttime hypoglycemia symptoms might include:
- a painful headache similar to the feeling of a hangover
- waking up with an abnormally low amount of energy
- sweat-soaked bedsheets and garments
Hypoglycemia’s Root Causes
Although hypoglycemia most often affects those with diabetes, it may also occur in other contexts.
Diabetes-related hypoglycemia
Toxic overdose from diabetic medicine
Too much insulin for the body’s requirements is a typical cause of hypoglycemia. Blood sugar levels may be managed with the use of insulin. It is widely used for the treatment of type 1 diabetes and is also sometimes advised for persons with type 2 diabetes.
Too much oral hypoglycemia treatment, such as sulphonylurea, which stimulates insulin release, may also cause a drop in blood glucose levels. The blood sugar levels of persons with type 2 diabetes are commonly lowered with this medicine.
Weightlifting, eating, and drinking.
Type 2 diabetics need to strike a delicate balance between their insulin dosage, the calories they consume from meals, and the number of calories they expend via physical activity to keep their blood glucose levels within normal ranges.
If you take your regular insulin dosage but eat fewer carbs than usual or burn through them more rapidly, hypoglycemia might result. It’s possible to experience this if you work out for longer than normal, doesn’t consume enough carbs, or skip meals.
Hypoglycemia may also occur in people who have diabetes and have consumed too much alcohol or alcohol on an empty stomach.
However, there are situations when there is no clear cause for a hypoglycemic episode, and doctors are left guessing.
Non-Diabetic Hypoglycemia
Non-diabetic persons seldom experience hypoglycemia. What follows is an explanation of the probable reasons.
Hypoglycemia reaction
People who do not have diabetes nevertheless risk developing hypoglycemia if their pancreas produces an abnormally high quantity of insulin in response to a substantial meal high in carbohydrates. The medical term for this illness is reactive hypoglycemia.
Although the exact cause of this phenomenon is unknown, it seems to be more common in people who are overweight or who have had surgery to do a gastric bypass.
Occasionally, a pancreatic tumor that is not cancerous may cause an excessive amount of insulin to be generated or utilize an excessive amount of glucose for its requirements.
Additional potential factors
Hypoglycemia may also occur in persons who don’t have diabetes for a variety of other reasons:
Binge drinking or heavy alcohol consumption is malnutrition, in which the body does not get enough nutrients for it to function normally fasting.
Addison’s disease is the name given to the condition that affects the adrenal glands (two small glands that sit on top of the kidneys)
Patients using quinine, which is used to treat malaria, salicylates, which are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, and propranolol have all been documented to have had hypoglycemia (for high blood pressure), an illness of the liver, kidneys, or thyroid.
Hypoglycemia treatment
Hypoglycemia is usually a self-treatable condition as long as you know what to look for.
The management of hypoglycemia
An urgent remedy for hypoglycemia is the consumption of sugary food or drink (about 15–20g of fast-acting carbohydrate) to stop the episode.
Here’s one example that could fit the bill:
a regular-sized soft drink or fruit juice
Three to five dextrose pills
a little bag of candies
At first, it’s best to stay away from high-fat foods and beverages like chocolate and milk since they don’t often have as much sugar, and the sugar they do have may be absorbed more slowly.
It would be best if you had a longer-acting carbohydrate snack after ingesting sugary meals. Some examples of this kind of snack are a few biscuits, a cereal bar, a piece of fruit, or a sandwich. This will help you maintain your energy levels.
Recovery from an episode of hypoglycemia that is considered to be slight normally takes around 15 minutes. Take another measurement in the next 15–20 minutes if you have access to a blood glucose meter. If your blood sugar level is still too low (below 4 mmol), consume anything with added sugar and take another test after 15 to 20 minutes. If your blood sugar level is still too low, seek medical attention immediately.
If you are caring for someone who is experiencing hypoglycemia and the methods described above are not successful in treating the condition, you can try rubbing the outside of their cheeks with glucose gel (or honey, treacle, or jam if glucose gel is not available) and applying it directly to the maid.
It might be between ten and fifteen minutes before they start feeling better. Because of the risk of choking, this procedure should not be carried out on a person who is dozing off or already sleeping.
Your diabetes care team should consider the matter if you regularly experience hypoglycemia. You may need a change in the dosage of your medicine, or you may need medical attention for an underlying condition that is the cause of your hypoglycemia.
Keeping blood sugar levels stable
For those with diabetes, maintaining a regular meal schedule and medication schedule helps reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Keep an eye on your blood sugar levels.
FAQ
Do you know what it’s like to have your blood sugar suddenly drop?
Hunger pangs, shakiness, and profuse perspiration are common early warning signals. It’s also possible, especially in more extreme circumstances, that you’ll experience confusion and find it hard to focus.
Why does glucose level decrease suddenly?
If you don’t eat enough or miss meals, your blood sugar might decrease dangerously fast. Extra exercise, using specific medications, or taking too much medication (including insulin) may cause this condition. If you have trouble detecting the symptoms of low blood sugar, you should avoid alcohol.
When glucose levels in the blood drop, what happens?
This may cause visual blurring, difficulties focusing, muddled thinking, slurred speech, numbness, and tiredness. Long-term hypoglycemia, in which the brain goes without glucose, may cause convulsions, unconsciousness, and even death.
When blood sugar drops too low, what usually happens?
Although insulin users are more likely to have low blood sugar, everyone taking diabetic pills runs the risk. An overdose of insulin or other diabetic medicine is a common cause of diabetic hypoglycemia. Under-consuming or not eating enough.
At what point do you notice a dip in blood sugar?
Neither prediabetes nor diabetes has been identified. After an increase in blood sugar levels, one to two hours should pass before the levels return to normal. If you want to speed things up, going for a stroll or doing some exercise will help.
What other conditions than diabetes may result in hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia may also be caused by factors other than diabetes, such as
- consuming drinks with alcohol.
- Drugs include antibiotics, malaria and pneumonia pills.
- kidney health issues.
- Issues with either the adrenal glands or the pituitary gland.
- Cystic adenomas of the pancreas.
- Deadly disease
- conditions affecting the liver.
- Malignant pancreatic tumor.
At what level of blood sugar is there a serious health risk?
Extreme hypoglycemia is defined as a blood sugar level below 55 mg/dL. Depending on how you’re feeling, you may not be able to do self-tests of your blood sugar or administer your treatment.

Broccoli Sprout Extract Improves Blood Sugar
Broccoli Sprout Extract Lowers Blood Sugar
Broccoli is a member of the cruciferous plant family, and its many health advantages have long been recognized partly because of its sulfur-containing chemicals.
The fasting blood sugar levels of obese persons with type 2 diabetes significantly improved after consuming a chemical contained in broccoli sprouts and other cruciferous vegetables.
It was also discovered that the substance, known as Sulforaphane, decreased glucose production in cultured liver cells and seemed to correct aberrant gene expression in the livers of rats.
The research by Annika Axelsson and coworkers at the Lund University Diabetes Center in Sweden was published in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Among the many positive effects of broccoli sulforaphane:
The risk of developing cancer is lowered by minimizing exposure to carcinogens and bypassing the body of these substances.
Removal of toxins from the liver (VIP: the active sulforaphane selective phase 2 detoxifying enzyme inducers without triggering the phase 1 enzyme induction, for example, c, cytochrome P450). The potential of anti-carcinogens to stimulate the production of phase 2 enzymes has been shown as a key characteristic of these substances.
- Promote a healthy inflammatory response by stimulating the production of anti-inflammatory, antioxidant enzymes.
- Enhances Glutathione, the predominant intracellular antioxidant
- It gives DNA a chance to defend and repair itself
- Maintenance of an optimal amount of the ulcer-causing H. pylori bacterium ( it is needed to a certain extent but not to the point where it causes stomach ulcers )
Type 2 Diabetes
About 90–95% of all instances of diabetes are classified as type 2, making it the most prevalent form of the disease.
A lack of proper insulin use leads to excessive blood glucose levels and the onset of this disease. Severe consequences, such as heart attack, stroke, nerve damage, and renal failure, may develop in people with type 2 diabetes if their blood glucose levels are not managed.
Although treatments like metformin may help persons with type 2 diabetes regulate their blood glucose levels, Axelsson and colleagues point out that some patients use these drugs owing to significant side effects such as kidney damage.
Therefore, more secure options are needed. Has Sulforaphane the potential to fill this void?
Liver gene expression and blood sugar were both increased by Sulforaphane. Axelsson and colleagues sought to address this topic by developing a genetic signature for type 2 diabetes based on the 50 risk factors previously identified.
Using this signature, the scientists analyzed freely available gene expression data. By doing so, they evaluated the impact of over 3,800 chemicals on the changes in gene expression in liver cells related to type 2 diabetes.
Sulforaphane, a chemical molecule found in cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli sprouts, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, and watercress, was shown to have the most impact, according to the study’s authors. Sulforaphane inhibited glucose synthesis in cultured liver cells. It was shown that when this chemical compound was given to diabetic rats, the liver’s gene expression changed for the better.
Following this, the team conducted a 12-week, randomized, controlled trial of broccoli sprout extract in 97 people who were overweight. A placebo-controlled trial means exactly what it says. Everyone in the adult population had been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and had poor glucose control.
Fasting blood glucose levels were significantly lower in those who took the broccoli sprout extract than those who did not. Additional studies are required to establish if Sulforaphane helps people with type 2 diabetes, although the results of this one are encouraging.
They are using genetic fingerprints to examine public gene expression data, as Axelsson and colleagues have done, which may be an efficient approach to finding chemicals that might aid in treating diabetes and other disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of broccoli sprout extract?
Broccoli sprout extracts reduce glucose levels in the blood. It has been shown in vitro and animal tests that a compound in broccoli sprouts may increase the body’s sensitivity to the hormone insulin, lowering blood sugar—improving articular health.
Do broccoli sprouts help lower estrogen levels?
Sulforaphane levels in broccoli sprouts are 30–100 times higher than in mature broccoli. Sulforaphane’s three incredible effects make it a game-changer: It acts as a natural ” estrogen blocker ” by binding to estrogen receptors and preventing the growth of malignant tissue caused by “bad” estrogens, such as in the case of breast cancer.
What does Sulforaphane do?
Sulforaphane inhibits the growth of cancer cells. That’s significant because it suggests it may make tumors grow more slowly or prevent them from spreading. It’s easy to get your hands on. You don’t have to do anything to gain the health benefits of Sulforaphane found in cruciferous vegetables.
Can Sulforaphane assist in liver detoxification?
By stimulating the production of liver enzymes that break down dangerous toxins, Sulforaphane facilitates the body’s natural detoxification processes and speeds up the disposal of these toxins.
Can Sulforaphane boost testosterone levels?
Type 2 diabetes has been linked to low testosterone levels. In men, Sulforaphane has been shown to boost testosterone.
To what extent does Sulforaphane benefit the kidneys?
Sulforaphane is effective in treating kidney illness by targeting the Nrf2 pathway.
Is there any truth to the claim that eating broccoli may reduce blood sugar levels?
Broccoli is considered a low-glycemic food since it does not significantly increase blood sugar levels after consumption. The Glycemic Index of broccoli is just 15, making it a good choice for those trying to control their blood sugar.
Do sprouts help to lower blood sugar?
However, since their starch content is reduced by 10% during the sprouting process, these foods are low in carbohydrates. As a bonus, they prevent a surge in blood sugar since they contain plenty of fiber. These two factors justify including sprouts in a diet for people with diabetes.
So, how exactly does one take in Sulforaphane?
Cruciferous plants, including broccoli, kale, cabbage, and watercress, are good sources of Sulforaphane. If you want to get the most Sulforaphane out of your diet, try eating raw veggies or cooking them at moderate temperatures with a dash of mustard seeds or powder.
When will I start to feel the effects of Sulforaphane?
Sulforaphane is usually effective within 14 days of treatment.
Will my blood pressure increase with Sulforaphane?
Reduced blood pressure and eradication of cardiac dysfunctions, including cardiac hypertrophy and decreased fractional shortening, are the outcomes of Nrf2 activation produced by Sulforaphane.
Will Sulforaphane cause drowsiness?
Since Sulforaphane boosts melatonin synthesis, it might lead to better sleep. Sulforaphane reduces the inflammatory compound prostaglandin D2. Sulforaphane’s melatonin and anti-inflammatory effects could make it easier to go to sleep.
Have any adverse reactions been reported with Sulforaphane?
At high dosages, Sulforaphane caused significant drowsiness (150-300 mg/kg) and hypothermia (150-300 mg/kg). Deaths (at 200-300 mg/kg), impaired motor coordination (at 200-300 mg/kg), and a loss in skeletal and muscular strength (at 250-300 mg/kg).

Are Blood Sugar Affected by the Circadian Rhythm?
We have known for more than half a century that our glucose tolerance decreases with the passing of the day; That is, the body’s ability to maintain blood sugar levels at a normal level decreases.
If you use an intravenous (IV) solution to drip glucose into your vein at a regular rate throughout the day, you’ll find that by 8 p.m. your blood sugar begins to rise, even though you haven’t eaten and the rate at which glucose pumps into your blood hasn’t changed.
It’s the same amount of sugar being pumped into your body every minute, but its ability to handle it deteriorates in the evening and returns to normal again in the morning.
Eating a meal at eight in the evening may double the blood sugar level, unlike eating the same meal at eight in the morning. That is, you ate twice the amount of food. Your body does not expect you to eat after nightfall. The human race only discovered how to use fire about a quarter of a million years ago , so our bodies are not used to always having restaurants open and eating all the time.
One test for diabetes, called a glucose tolerance test , tests how quickly the body gets rid of excess sugar in the blood. You take a glass of water dissolved in about four and a half tablespoons of regular corn syrup, and then your blood sugar is measured after two hours. At that point, your blood sugar should be less than 140 milligrams per deciliter.
If it is between 140 and 199, it is considered prediabetes, and if it is 200 or more, it is a sign of diabetes.
The circadian rhythm of changes in glucose tolerance is so powerful that a person’s test result may be normal in the morning and change to indicate prediabetes in the evening. And people with prediabetes with an average blood sugar of 163 at 7 a.m., end up testing out as a full-blown diabetic by 7 p.m., with a blood sugar level of over 200.
Choosing low-sugar foods may help you lose weight, but the timing of eating them is important.
Because the circadian pattern of glucose tolerance is affected by the timing of eating, eating a low-sugar food at night can lead to a greater rise in blood sugar than eating a high-glycemic food in the morning.
This happens because our metabolism slows down during the night, and researchers have found that eating a bowl of whole grains at 8 p.m. leads to a blood sugar spike that’s just as dramatic as eating a sweetened breakfast cereal at 8 a.m. Eating high-sugar foods in the evening is the worst thing to do.
So, if you plan on eating processed cereals that are full of sugar, they may be less harmful if you eat them in the morning. Thus, it is possible that decreased glucose tolerance throughout the day can help us understand and explain the positive results in terms of weight loss due to consuming the most calories at the beginning of the day.
The difference is also evident even in the comparison between eating lunch early and eating it late. Some people were randomly assigned to eat a large lunch at 4:30, and the result was a 46% increase in their blood sugar, compared to eating the same meal several hours earlier at 1 p.m.
Eating the same food at 7 a.m. can lower blood sugar by 37% than eating the same food at 1 p.m.
There doesn’t seem to be any difference between eating a meal at 8 pm and eating the same meal at midnight, both times being too late.
But eating that late, whether it’s 12 a.m. or even 11 p.m., can seriously disrupt your body’s circadian rhythm, and can disrupt your metabolism the next morning, leading to a spike in blood sugar after breakfast, compared to eating the same dinner at 6 pm the previous day.
Therefore, these discoveries in chronobiology bring the debate over the importance of breakfast back to its starting point.
Skipping breakfast not only impedes weight loss in general, but also impairs the body’s ability to control daily blood sugar in diabetics and non-diabetics.
See how people who skip breakfast have high blood sugar even in their sleep and 20 hours later?
This may help explain why people who skip breakfast are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes in the first place. They also have increased rates of heart disease and atherosclerosis in general.
Is this just because skipping breakfast often combines with other unhealthy choices like smoking and poor eating habits in general?
The association between skipping breakfast , heart disease, and early death in general appears unrelated, based on attempts to monitor for these confounding factors.
But we couldn’t verify that until after it was put to the test. Does skipping breakfast lead to high cholesterol, for example?
Yes, the result was a significant increase in LDL (bad cholesterol) in those randomized to a trial of skipping breakfast by 10 points in just two weeks.
An Israeli study found that the percentage of triglycerides in the group breakfast of kings, lunch of princes and dinner of the poor improved significantly and decreased by 60 points, while its percentage worsened in the group that ate meals in the reverse order, and increased by 26 points.
Thus, eating more calories in the morning than in the evening may have a triple benefit: greater weight loss, better blood sugar control, and a lower risk of heart disease.
So if you’re going to miss a meal, whether due to intermittent fasting or restricting eating times by keeping all of your meals in a fixed amount of time each day, it may be safer and more effective to skip dinner than to skip breakfast.
Estimate Your A1C Using Your Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Even though A1C has been the gold standard in diabetes care, there is a huge limitation that this type of measurement possesses.
One of the most critical is the fact that A1C test results are considered to be an average only.
Unlike the latest studies that compare the A1C tests with the GMI (Glucose Management Indicator), GMI provides diabetic patients with an estimated level based on a continuous source of monitoring.
As a result of these averages, an individual may spend a huge amount of their time with both low and high sugar levels. Yet, still, be on target (i.e.what’s expected for most people with diabetes) with an A1C of under 7%.
Limitations of A1C
Based on these findings, it is important to note that A1C measurements are not considered to be perfect. Even though there has been quite a bit of effort in the past to reach perfection in its accuracy, these tests are still accurate within a margin of error of about 0.4 % points.
For example, these results may equate to an A1C that ranges from about 6.4% to 7.2%. Typically, for anyone who wears a CMG (Continous Glucose Monitoring System), the GMI is primarily seen as an estimate of their A1C.
Without using data from drawing blood, 14 days of data is needed to calculate the GMI. The GMI, in this case, uses an average of the person’s glucose reading to provide an estimate of their A1C.
TIR, TBR, and TAB are 3 other ways to manage glucose levels. For instance, these measurements are as follows:
- TIR (Time in Range): Glucose Levels range from 70 to 180 mg/dl
- TBR(Time below Range: Glucose Levels range below 70 mg/dl
- TBR(Time above Range: Glucose Levels range over 180 mg/dl
These measurements can be very useful in determining if a patient is actually meeting their glucose targets or if they need to be adjusted with another course of action. For instance, based on the numbers provided above, in general, an A1C of 7% or less equates to a TIR of 70% or higher.
Differences Between GMI and A1C
It normally takes about 2 to 3 months for new red blood cells to form. This is also the timeframe that A1C turnover is based on.
This is one of the primary reasons why an A1C level is only taken on a quarterly basis. The GMI, on the other hand, can be checked on a more frequent basis. This is primarily due to the fact that this indicator is based on a CGM date instead.
How Accurate is the GMI?
The answer to this question usually varies based on a number of different factors. Because the A1C on the CGM report is affected by the following information:
- Red blood cell turnover may be falsely skewed due to medical illnesses and diseases like anemia, sickle cell, genetic conditions, and other things that can affect the hemoglobin
- Chronic conditions like kidney diseases may show a false low in average A1C levels
- Blacks, Asians, and Hispanics (i.e. People of color) usually see higher levels of their A1C
- Indigenous individuals
All of these continuous glucose monitoring system factors must be taken into account before these numbers are considered to be accurate.
Real World Analysis of Glucose Monitoring System
Even though both of these measurements are being used in the real world, there is still little real data that compares both of these measurements for their comparable accuracy.
Lately, however, the University of Washington looked at the differences between A1C and how it compares to the GMI and its accuracy. The study from the University of Washington was able to identify the following data.
Between the years 2012 and 2019, 641 people with diabetes were used in a study to compare the results documented in A1C within a 30-day window before or after their healthcare visits.
This CGM report was uploaded and the information was as follows:
- The data on the CGM report had to encompass at least 14 days of information with 95% data sufficiency or more.
- The accuracy of the data was dependent upon the completion of the information supplied
The profile of the study group was as follows:
- 46 years of age was the average age of the study group
- Female population 52%
- Caucasian 93%
- Type 1 Diabetes – 91%
The Dexcom G5 was the most commonly used (i.e. calibrated 2 times daily).
However, there were other devices also used in this study, including the following:
- Dexcom G6
- Freestyle Libre
- Medtronic Enlife
- Medtronic Guardian
The CGM report was also based on the following averages:
- 24.5 days
- A1C of 7.3%.
- Mean CGM glucose equated to 162 mg/dl
Findings in the Study
The findings in this study were surprising, particularly since the discrepancies were much higher than those that were observed in previous trials. There was a huge difference between GMI and A1C.
For instance, according to this report, the researchers found the following:
- Patients with type 1 diabetes were reported as having a.17 percentage points fewer difference between A1C and GMI in comparison to patients who had type 2 diabetes.
- A .19 percent point greater difference was reported between GMI and A1C, in specific for patients who had a reduction in kidney function.
- No discrepancies were found in any specific device
Study’s Limitations
It is also important to note that the results of this study had their limitations.
Some of the most notable include:
- The population was not controlled and did not take into account outside factors (i.e. changes in meds)
- CGM dates were not parallel
- Accuracy of devices
- The quality of the Calibrations vary
Applications to the Real World
In the real world, the GMI may be able to predict what future A1C may be. However, you cannot expect a perfect match. Yet, both results could be somewhat close based on a .5 percentage. Also, during COV19, a large number of health care centers relied on GMI for their results.
It is also important to remember that both of these measurements are seen as estimated averages. Therefore, everyone needs to see each of these forms of measurement in the best context possible.
For instance, you should not be disappointed in cases where you do not reach your target. Your primary focus may need to be on the TIR (Time in Range). This is especially true if you need the extra encouragement to keep going in a positive way.

Blood Sugar Fasting
A blood sugar fasting test measures your blood sugar (glucose levels) when you haven’t eaten for at least 8 hours.
The glucose level in your body is always expressed in mg/dL. The present glucose amount in your blood does fluctuate day and night.
Generally, metabolism is essential in our day-to-day activities, and the level of blood glucose is maintained by our body for this activity. When you have a healthy body, your fasting blood sugar readings should be between 90 to 100 mg/dL.
However, your fasting blood sugar levels may fluctuate; at times, the readings may go high and low. The fluctuating fasting blood sugar readings in your body, even if you are healthy, may be caused by various factors.
Fluctuating blood glucose levels that you may experience are healthy condition signs that require or need attention.
Additionally, there are multiple Diabetes Reversal Methods and medical attention that you can use to keep your fasting blood sugar at healthy levels.
Why does Blood Glucose Level Rise in Diabetes?
After eating, your blood sugar levels are always high. This is due to the fact that the food you have eaten is being released into your bloodstream, and for this to happen, it must be converted to glucose.
As the food is converted to glucose, the glucose level signals your pancreas, which then releases insulin.
Your body needs insulin to help in the absorption of glucose. This will reduce your blood glucose levels and return to normal. The cell absorption process is essential in regulating or maintaining normal glucose levels.
However, if you have diabetes, your body becomes resistant to insulin, leading to insulin deficiency.
With you having insulin deficiency, your body loses the capability to absorb blood glucose. This will lead to you having diabetes due to high blood glucose levels.
There are various health condition issues that are associated with diabetes that you may have. Some of the problems you may have by being diabetic include thyroid, stress, muscle weight loss, acidity, low energy levels, insomnia, and many more.
Further, if your high blood glucose levels persist for long, it may cause damage to your nerves, kidneys, eyes, and even heart. Luckily, diabetes is reversible.
You will need to observe and maintain correct changes in your exercising, eating habits, sleeping patterns, and stress management.
It has been proven that over 10,000 diabetic patients have reversed their diabetes by following the right changes.
You must maintain good fasting blood sugar readings at some acceptable values if you have diabetes.
You can attain some of these typical accepted values by having and maintaining a healthy lifestyle which will help in reversing your diabetes.
Moreover, it is also important that you follow a sustainable diet plan which includes having staple food readily available in your kitchen. Supplements should be included in your diet.
Healthy Individual Normal Sugar Level (Fasting & After Food)
Blood sugar levels are also referred to as blood glucose levels. Your blood glucose levels may be normal, high, or low. Generally, the best time to measure your fasting blood sugar levels should be around 8 hours after eating.
When you are healthy and not diabetic, your normal fasting blood sugar range should be > 70 mg/dL. And your blood sugar readings should range between 90 to 100 mg/dL. two hours after eating if you do not have diabetes.
Factors that may cause your blood glucose levels to change during the day
Throughout the day, your blood glucose levels change.
There are multiple factors that may cause your blood glucose levels to change during the day, and they include:
- The variety of food we eat during the day. For example, your blood sugar levels might increase during the day if you eat rich-carb food and high-calorie food.
- The quantity of food. Your normal blood sugar readings may increase if you eat too much during the day.
- Physical activities. Your blood glucose levels are likely to increase if you do less physical activity during the day, while heavy and rigorous work and physical activity during the day reduce your blood sugar levels.
- There are certain medicines that may have an impact on your blood glucose level during the day.
- Your normal blood sugar levels are likely to change if you have medical conditions such as hypoglycemia, diabetes, and liver disease.
- Your good fasting blood sugar level is likely to drop due to alcohol consumption.
- You are likely to suffer from Type 2 Diabetes if you are smoking.
- Age Matters! There are increased chances of you having diabetes as you age. This is because insulin tolerance in your body reduces as you grow old.
- Your normal blood sugar levels can increase due to mental and physical stress.
- You are likely to have low blood glucose levels during the day due to dehydration.
The good thing is that most of these listed factors that may cause your blood sugar levels to change during the day can be solved.
All you have to do is ensure you are in the correct surroundings with the right guidance. Additionally, suppose you want to reverse your diabetes.
In that case, you also need to be doing what other diabetic patients who are on a similar journey as you are doing in the right environment and guidance.
Children and Teens with Diabetes – Normal Blood Sugar Levels According to Age
There is variation in fasting blood sugar levels in children from the time they wake up to the time they have taken their meals. Therefore, it is essential that you monitor your children’s normal blood sugar levels regularly.
The normal blood glucose levels for children at the age of six should range from 80 to 200 mg/dL. A blood sugar test is a must if your child has complaints of hypoglycemia, especially in the middle of the night.
The blood glucose level reading of between 80 to 180 mg/dL. is considered healthy if your kids are aged between 6 to 12.
However, it has been found that normal blood sugar level reading increases after meals for kids around this age. Therefore, to ensure they have a healthy glucose level at bedtime, limiting their snack intake before sleep is essential.
Blood glucose level reading of between 70 mg/dL. to 150 mg/dL. is considered healthy for teenagers. One of the reasons for irregular blood glucose levels in teenagers could be heredity.
Mood swings, stress, and lifestyle issues are common among kids around this age. These are the critical challenges in managing healthy blood glucose levels in teenagers.
Despite managing blood sugar levels in teens being critical, it is possible. You can regulate blood sugar levels in teens by implanting good eating, sleeping habits, and other lifestyle modifications at the right age.
Introducing the right lifestyle modifications to teens at the right age will help them in their entire life. Besides, as teenage, motivation and a little push are essential in regulating sugar levels.
It is alarming, and your children will require medical attention if their blood sugar level readings are 180 mg/dL.
Random Blood Sugar Level Chart
There are scheduled blood sugar testing durations during the day. However, you can still do random testing at any time of the day.
Random blood sugar testing should be done outside the regular testing timetable.
When you do random blood sugar testing, it will confirm diabetes if you do the random test during and after treatment of diabetes.
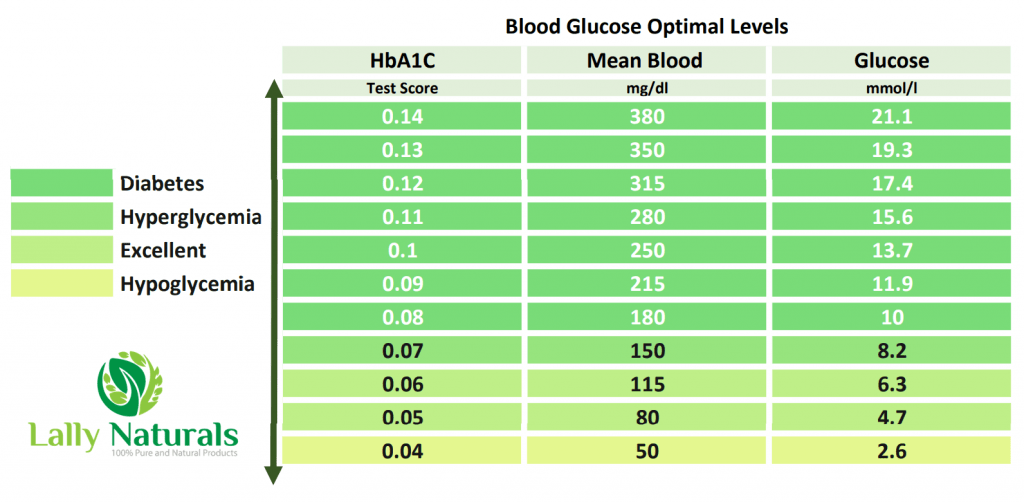
When the blood sugar level reading is 200 mg/dL or more, then it is an indication of diabetes mellitus.
Checking random blood sugar levels is the main aim of an RBS test. When the range is 200 mg/dL or greater during an RBS, it clearly indicates diabetes.
Doing a random blood sugar test will help in the timely treatment of diabetes via monitoring during and after treatment. It is recommended that you do a random blood sugar test if you have the following symptoms:
- Unexpected weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Constant dehydration and dry mouth
- When your wounds take time to heal
- Urinating recurrently
Healthy Normal Sugar Levels in Diabetic Adults (Men or Women)
Your blood sugar level should range between 100 mg/dL to 180 mg/dL the entire day if you are a diabetic person above 20 years of age.
To avoid diabetic complications, your fasting blood sugar range should be between 70 mg/dL to 100 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar levels should be between 100 and 140 mg/dL at bedtime to avoid diabetic complications.
Normal blood sugar readings for women in the blood sugar levels chart should be between 100 to 140 mg/dL at bedtime. It is considered dangerous and requires medical attention if your blood sugar readings at bedtime are> 70 and 180 mg/dL.
When your body has insulin deficiency or cannot use the insulin properly, then hyperglycemia occurs.
Some of the common signs of high blood sugar levels include:
- You experience fatigue
- Abnormal thirst
- Urinating frequently
- Difficulty concentrating and headache
- Cloudy vision
- Unexpected weight loss
Hyperglycemia can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis if left untreated. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening condition.
Besides, it can lead to you having heart-related complications, kidney issues, and liver complications.
Remedies for High Sugar Level
You should seek medical advice and take medicine if your blood sugar level is between 180 to 250 mg/dL.
You should also avoid sugary items and processed foods and cut off a fast-acting carb diet.
You should seek immediate medical attention if your blood sugar level is >250 mg/dL.
If your blood sugar level is > 250 mg/dL and you do not seek medical attention, it may lead to you having a coma and high ketones in your blood.
Therefore, you should take a ketones test and get insulin therapy once you find your blood sugar levels are >250 mg/dL.
You are advised to do the following if you experience high sugar levels on a regular basis:
- Maintain a low sugar food diet with a low glycemic index
- Avoid taking fruit juices and processed foods.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle and do mild exercises.
- Consult medical experts for recommended insulin dosages
- Take medication in time.
- Regular monitoring of your glucose levels
Many diabetic persons cannot follow the changes they need to make in their diet or daily routine despite being aware of them for multiple reasons. The most common reason is a lack of motivation and proper knowledge.
FAQs:
1. What is a normal blood sugar level after fasting for 8 hours?
Suppose you do not have diabetes and have fasted for at least 8 hours. In that case, your fasting blood sugar level must be below 100 mg/dL to be considered normal if you are an adult.
2. Is fasting sugar of 110 mg/dL normal?
A fasting sugar level of under 100 mg/dL is considered normal. A person with prediabetes has a fasting blood sugar level between 100 and 125 mg/dL.
If your fasting sugar level is 126 mg/dL or above, you have diabetes. Prediabetes is fasting blood glucose levels between 110 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL.
Normal blood sugar levels are less than 110 mg/dL, and diabetes is defined as levels more than 126 mg/dL.
3. What is a good blood sugar level in the morning?
In the morning, before taking your breakfast, it is advisable that you keep your fasting blood sugar level readings in the range of 70 – 130 mg/dL.
Additionally, your blood glucose readings at other times must range between 70 – 180 mg/dL.
Bottom Line
Depending on your medical condition, your blood glucose levels can go high or low. Therefore, it is advisable to visit an endocrinologist and get professional advice about the fluctuations in your blood glucose levels and the reasons for them.
You should also monitor your blood glucose levels and keep them normal if you have diabetes. Doing this will help you avoid diabetic complications and lead a normal life.
The diabetes reversal method using diet, exercise, and lifestyle step by step is a great way of keeping your blood sugar levels healthy.

Ways to Reduce Blood Sugar
According to a National Diabetes Statistics Report in 2020, an estimated 34.2 million people in the U.S. have been diagnosed with diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes is also constantly rising in both low-income and middle-income populations. Even though this rise in number is actually frightening to think about, there are many different things that people can do to combat this disease. One of the most important is to make specific types of lifestyle changes. And here is why.
Diabetes and prediabetes are caused by complications of high blood sugar levels over time. Actually, when blood sugar (blood glucose) levels remain high for a certain amount of time, it can lead to dangerous consequences including the loss of life.
Therefore, it is important that everyone understands how high blood sugar levels affect the body and the health risks involved in failing to treat this condition properly.
So, let’s get started by discussing the signs and symptoms and other related information that can help to reduce blood sugar levels fast.
Signs and Symptoms of High Blood Sugar
Unlike high blood pressure levels, high blood sugar is not a silent killer. In fact, in all actuality, there are many signs and symptoms that indicate that your blood sugar (glucose levels) are high. Here’s what to look out for.
- Thirst increases due to higher amounts of sugar in the blood
- Extra water in the body from this thirst will also increase the need to urinate frequently
- Eye vision is blurry
- Even though the hunger increases, the person begins to lose significant amounts of weight
- Increase in fatigue and tiredness (sugar in the body does not convert to energy but remains stored inside the blood)
- Increase infections and the wounds are slow to heal
- Feeling of numbness in the feet and other parts of the body
- Chronic gastrointestinal problems and heart disease
- Kidney damage
All of these symptoms and more usually indicate that the sugar levels in the body are too high and treatment is needed. To get ahead of these problems, it is important that you are aware of your own health status. For instance, your blood glucose can be tested regularly in your home.
Or, you may want to visit your physician to follow up on the signs and symptoms caused by these issues.
When visiting a physician, they may order one of the following tests to check for prediabetes or diabetes.
- A1C – fasting blood glucose
- OGTT – Oral glucose tolerance test
How Can You Reduce Your Blood Sugar Levels Fast

Once the testing for your blood glucose has been tested at home or at your physician’s office, you may need to take action right away. Based on your set of circumstances, there are a number of different things that you may be required to do.
- Under Medical Care of a Doctor
If you are already under the care of a medical physician, it is important that you follow the instructions closely that were given to you. For instance, you need to make sure that you are taking your medication as prescribed without skipping doses.
Since the approach that your physician uses may be different from other patients, you need to know exactly what to do in certain situations. Typically, whenever a diabetic patient skips a dose of their medications, the doctor may instruct them to take that dose right away.
Whatever the situation, it is important that you ask these questions in advance before you live their office.
- Drink Water
In some situations, lowering your blood glucose levels may be as simple as drinking water. This is because water helps to dilute the sugar in the blood. You should also avoid drinking sugary and low calorie beverages, especially since these beverages can increase glucose levels in the blood.
- Exercise
Though there are many effective ways to lower your blood sugar, some are much more effective than others. For example, if you want to reduce your blood glucose levels quickly, physical activity is extremely effective.
In fact, if you want to keep your blood glucose levels in check, you should go walking regularly. Or, you may choose to go to the gym. As a general rule, at least 15 minutes of cardio exercise can help to regulate these numbers. Also, before starting any strenuous exercise program, you need to consult with your physician.
- Eat Protein
Eating protein is ideal for helping to keep your blood sugar glucose levels down. Therefore, you may want to add protein to your diet as a snack (i.e. hard boiled eggs, almonds, cottage cheese, or low-fat cheese). Here are some of the primary benefits of making these dietary changes.
- Protein helps to reduce cravings
- Satisfying
- Eating more protein is also one of the best ways to lower blood sugar
- Digests in the body slower than sugary beverages and sweets
Ways to Reduce Blood Sugar in Pregnancy
Some women are at risk of suffering from a wide range of medical conditions when they are pregnant. One of the most notable and problematic is gestational diabetes. While not all women are at risk of developing gestational diabetes, there is a certain part of the population that is. Here is a profile of the women who are more at risk than others
- Women who are obese
- Specific races: Black, Asian, Hispanic or American Indian
- 25 years or older when you are pregnant
Gestational diabetes can also lead to a variety of different complications, including affecting the baby’s health (i.e. born with low blood sugar). Therefore, it is important for women to exercise regularly and eat the right nutritious foods to protect the baby and their own health.
According to information published by AACE, when pregnant women are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, specific goals must be established to protect their health. Under the guidance of the ADA , here are some of the key recommendations that should be followed.
- Upon getting up in the morning, the fasting level should be in the range of 60 to 90 mg/dl
- Prior to eating a meal, the range should be 60 to 90 mg/dl.
- After eating a meal ( i.e.1 hour), the ranges should be between 100 to 120 mg/dl
To control blood sugar levels in women with gestational diabetes, the same approach is used in the management of type 2 diabetes. The physician will also prescribe the following to these patients.
- Eliminate sweets and processed foods from the diet.
- Select healthy food choices like fruit, vegetables, and whole grains. Women with gestational diabetes must also practice portion control since these foods will also increase blood sugar glucose levels.
- Whenever physician feels that it is safe for their patients, they should also recommend a certain amount of physical activities like walking and swimming.
Based on the doctor’s prescribed treatment, the patient should take oral sugar medication or insulin injections.
Foods to Avoid When Your Blood Glucose is High
Eating the right types of food is an essential part of remaining healthy and active. Particularly, if you have been tested for insulin sensitivity and your blood sugar is high. In fact, if you are experiencing problems in this area, here are foods that you need to avoid.
1. Sugary Snacks for Treats
- You should always pay close attention to the snacks that you eat. This is especially true if you are thinking about eating any of the snacks in the following list.
- Ice cream and cookies
- cakes, pies, and muffins,
- sweetened yogurt sweetened
- Doughnuts
- Onion Rings
2. Beverages with sugar
- Drinking beverages with sugar can also lead to high levels of glucose in the blood. Therefore, it is normally time to avoid drinking these beverages with sugar.
- Energy drinks and sports drinks
- Coffee and Tea with sugar
- Soft drinks with sugar
- Fruit Juices
3. Foods with White Flour
Do not eat foods that have been made with white flour-based products. Some of the more commonly known foods that you should avoid include the following:
- Rolls and English muffins
- White Bread
- Pretzels and crackers
4. High Carb Grains
Refined grains are high in carbohydrates, which are foods that spike your insulin and increase your blood glucose levels. Therefore, you need to make sure to avoid eating.
- Rice
- Pasta
- Refined breakfast cereals
- White boiled potatoes
5. Fried Foods
To keep control of your blood glucose level properly, it is also best to eliminate fried foods. Instead, it is normally best to bake and broil your foods. For instance, here are some foods that need to be baked and broiled instead of fried.
- Chicken
- Fish
- Potatoes
6. Processed Meats
As with many other healthy diets, processed meat is also off-limits and should be avoided at all costs. This is because some processed meats will often contain higher amounts of fats, preservatives, and salt.
- Pepperoni
- Sausage
- Salami
- Ham
- Luncheon Meats
- Hot dogs
Foods You Can Eat on Your Diet
Even though it may appear to be a lot of foods that you cannot eat, there are some foods that can help to regulate your blood glucose level properly.
You need to know, however, how to mix and match them with your meals. For instance, you should avoid eating refined carbs (i.e. sugars and starches) only as a meal. Instead, you may want to eat refined carbs with one of the following dishes.
- Veggies and whole grains
- Healthy fats like nuts and peanuts
- Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, egg whites, and tofu
Ways to Lower High Blood Sugar Quickly
First off, you need to know that there is no food that can lower your high blood sugar levels instantaneously. This is primarily because it normally takes about 10 to 20 minutes for your food to be fully digested and released into your bloodstream.
On the other hand, if you are looking for foods that will have a quick effect on lowering your blood glucose levels, you may want to incorporate the following foods into your diet regimen.
- Peanuts and other low-carb nuts
- Tuna and Salmon
- Avocado
- Hard-boiled eggs
- Plain Greek Yogurt
- Unsweetened Chocolate
Exercise and Healthy Diet is Good for Lowering Blood Sugar Levels
Even though a physician may prescribe injections and other types of diabetic medications, this is not the only solution to lowering your blood sugar levels.
In fact, if you want to lower your blood sugar levels with all-natural solutions, you may want to consider the positive effects of eating healthy and exercising have on the body.
For instance, if you are looking to take this approach, here are some effective things that you can do.
- Exercise Regularly
Unfortunately, one of the worst things that people can do is lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Actually, to combat this problem, it is best to increase your activities. From taking a short walk to break up the sedentary time to signing up for dance classes, kickboxing, tennis, basketball, or golf, there are so many different activities that you can participate in.
To start, you may want to set a specific goal that you can commit to. Just adding 30 minutes of activities 3 or more times a week, can help you to manage your blood sugar levels properly.
- Eat a healthy Diet Regimen
As mentioned earlier, you need to make sure that you are eating a diet that excludes added sugars, refined carbs, and high-carb foods. By changing your diet, you can lower your blood sugar levels naturally. Here are some of the foods that you should incorporate into your regular diet regimen.
- Vegetables
- Cut portion sizes in half
- To control ingredients, eat less at restaurants
- Replace sugary beverages with water
- Bake, grill, and steam foods versus frying with lots of fat
- Eat lots of vegetables
- Reducing High Blood Sugar by Using Effective Home Remedies
Even though exercise and eating the right foods can help you to manage your blood sugar levels properly, there are other things that you can do to keep things under control. In fact, there are some home remedies that are very effective. Here are 5 of the most beneficial.
- Get adequate Sleep
Getting an adequate amount of sleep at night is essential to keeping your blood sugar levels under control. Just like poor food choices can raise glucose levels in the body, the lack of sleep can cause a variety of issues in the body, including hormonal changes and high blood sugar.
- Apple Cider Vinegar
You may be surprised to know that apple cider vinegar is also a good aid for reducing high blood sugar. Based on information published by the Journal of Diabetes Research, vinegar is great for increasing glucose uptake by muscles and elevating insulin sensitivity.
- Chromium
A deficiency in chromium can lead to unnecessary issues with high blood sugar. Therefore, it is important that you eat foods like spinach, oysters, and cheese broccoli since they are excellent sources of chromium. Also, if you choose to do so, you may want to add this supplement to your daily diet regimen.
- Stress
Most people know that bad stress has a devastating effect on the body. Just like not getting enough rest, stress can also raise your blood sugar level greatly. This is also why some people may perform deep breathing exercises to help eliminate the stress that they feel.
- Immunity
Another key to reducing blood sugar glucose is to strengthen the immune system. You can do this in a number of different ways including:
- Taking vitamin C supplements regularly
- Washing your hands frequently
- Eating foods like bell peppers, oranges, and leafy greens to get an adequate amount of Vitamin C
Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels
Learning how to manage your blood sugar levels regularly is one of the best ways to prevent high blood sugar levels. As you keep track of the foods that you eat, you will also see how your body reacts. There are also diabetic apps available to assist you in making the appropriate behavioral changes.

What Should My Blood Sugar Be When I Wake Up?
The most important thing that you should do each morning as you wake up is to check your blood sugar. Essentially, you can be able to determine how you go about the activities for the rest of your day by fasting blood sugar readings. Having a morning blood sugar level chart will help you know how high or low your fasting blood sugar is every morning. This will then enable you to set your morning target or what things you can do for you to achieve your target. Continue reading to find out more details about morning blood sugar.
What should my blood sugar be when I wake up?
Managing your overnight and morning readings is crucial if you want to control your blood sugar. Here are some of the details on what your morning blood sugar range reading should be as you wake up: –
– Fasting/ On Waking Up
- If you are not diabetic, your blood sugar reading should be around 70 – 99 mg/dl.
- If you are diabetic then your blood sugar reading should be between 80 – 130 mg/dl.
- Should your blood sugar reading be below 70 mg/dl then you have low blood sugar and it indicates a hypoglycemic reaction. Moreover, you have a high blood sugar condition should the reading indicate over 130 mg/dl.
– 2 hours after Meals
Your blood sugar should compare as following if you check it 2 hours after taking your meals:
- When you do not have diabetes then your normal blood sugar reading should be less than 140 mg/dl.
- If you have diabetes then your normal blood sugar reading should be less than 180 mg/dl.
– With HbA1c (Hemoglobin A1c)
Taking a Hemoglobin (HbA1c) test will enable you to determine your average blood sugar readings for the last 2 or three months. Additionally, you can take this test if you have not checked your blood sugar level reading for quite some time or if you have never checked it before since you think you do not have diabetes. After taking the test, your results are normal if:
- Your reading is less than 5.7% and you do not have diabetes.
- The reading is less than 7.0% and you have diabetes.
Symptoms of high blood sugar in the morning
You can determine whether or not you are experiencing the early morning hyperglycemia by having a routine check of your blood glucose each morning or by wearing a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). Further, you may be experiencing some signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia if you have the following: –
- Increased thirst
- Urination frequently and excessively.
- Eating more than you are used to.
- If you do not have a clear vision. Everything appears blurred.
How to Test Your Blood Sugar
You already have details on what your morning blood sugar range should be when you wake up. Consequently, you should also have information on the right way to test your morning blood sugar level. First, you should check your blood sugar level within the first 10 to 15 minutes after waking up in the morning for you to get an accurate reading. Second, it is recommended that you wash your hands thoroughly prior to taking or checking your blood sugar level when you wake up in the morning. Washing your hands thoroughly will help in getting rid of any contaminants that can cause inaccuracies in the results. Third, taking any caffeinated beverages before the test may lead to a spike in your blood sugar level. Therefore, you should avoid taking any caffeinated beverages at all costs if you want to get the correct blood sugar level.
What if Your Morning Blood Sugar Level is High?
You may have relatively higher blood sugar levels in the morning which is quite natural. The relatively higher blood sugar levels in the morning are because of certain hormonal changes in your body. Should this happen, your body will produce enough insulin that will aid in normalizing your morning blood sugar level. However, if you have diabetes, this may not happen.
You may also have a condition in which the fat cells and muscles in your body fail to use insulin effectively. This condition is called insulin resistance and it may lead to your blood glucose levels staying higher. Besides, if you have this condition, it will affect your liver functions and therefore lead to changes in the manner it processes and releases sugar, mostly during nighttime as you sleep.
However, when you have type-2 diabetes, the situation may be different since your liver will start releasing a large amount of glucose than is required in your blood. Therefore, it will lead to your blood sugar level elevating in your system because of your hormones and liver. When your hormones cause your blood sugar to spike and your liver also releases more glucose than is required the level of your morning blood sugar will stay higher unless you maintain a strict diet and exercise. Moreover, you may be required to take medications for better management of your blood sugar levels.
Ways to Help You Prevent High Morning Readings
As you already know, your blood sugar level when you wake is determined by whether you are diabetic or not. Luckily, there are certain things that you can do to help in preventing your blood sugar levels from rising above normal in the morning and they include: –
- Manage Your Body weight
Losing weight is essential in managing your glucose levels especially if you are overweight and have been diagnosed with type-2 diabetes recently. Losing weight will help in regulating your hormones and increasing your insulin sensitivity hence lowering the sugar levels in your blood. When you are overweight and you want to lose weight, you should start by checking your diet for example by avoiding processed foods and eating a lot of fruits and veggies. You should also reduce the intake of less healthy foods in your diet. You can also improve your physical activities.
- Check your blood glucose before bed.
The glucose levels in your blood are likely to stay constant the entire night especially if they are high as you are going to sleep. You can lower your glucose levels if they are high before going to bed by changing the content of your food and eating time. Additionally, you can do light physical exercise like walking from 10 – 15 minutes to reduce your blood glucose levels should they be high. Despite adding some light exercise before bed, and changing what time you eat and what you eat, you may also need to adjust the quantity of mealtime insulin that you take to cover it.
- Avoid certain foods
The duration at which you take certain food before bedtime should also change. You should avoid taking large, late dinner or nighttime snacks right before going to sleep. Besides, it is recommended that you eat low-carb, take early dinner, and then no snacks afterward as per One strategy from Adam Brown.
- Insulin
Taking enough insulin quantity to cover your evening meal is also great in preventing high morning blood sugar readings. For example, your glucose levels will be elevated the entire night and in the morning readings if you take a low insulin dose. Therefore, you should ensure to take the right insulin dosage.
- Have a Bedtime snack
Before going to bed, you should eat something to help in stabilizing your blood sugar. However, whatever you eat should not contain more than 20g of carbs. Taking a bedtime snack will prevent your liver from producing an unwanted amount of glucose as you sleep. Some of the low-carb bedtime snacks that you can take include low-fat yogurt, frozen grapes, soybeans, a serving of fresh salsa and tortilla chips, and a small piece of fruit.
- Evening exercise
Another way of reducing your glucose levels in the morning is by doing exercise in the evening. Despite exercising before bed helping in bringing the levels of glucose down in the morning, it may be dangerous. This is because the exercise may lead to a lowering of glucose over the hours as you sleep hence leading to dangerous hypoglycemia.
- Morning exercise
The dawn phenomenon or another reason may cause your blood glucose levels to be high. You can lower the high glucose levels in your blood by doing morning exercise.
A Quick Tip
You should talk to your doctor before trying to manage your blood sugar levels. Additionally, you should also keep in mind your blood sugar reading, your lifestyle, your A1C results, and any other medication that you may be taking before trying to manage your morning blood sugar levels.
Your fasting blood sugar readings are also crucial since they will let you know how your body has worked while you are sleeping at night. Therefore, with the fasting blood sugar readings, you will be able to make the necessary changes that you may need for better control of your situation.

When to Check Blood Sugar
If you are wondering when should you test your blood sugar then you are in the right place!
A glucometer helps in measuring blood sugar for people who are living with diabetes. The important thing is to know when to measure blood sugar. A Continuous Glucose Meter also helps in measuring blood sugar. It does so every few minutes and it’s a type of sensor.
You may think about when to check your blood sugar! And whether it’s for those who suffer from diabetes only.
Let’s find out today.
Why Checking Blood Sugar Is Important
It’s vital that you know why it’s important to check your blood sugar. Not checking the blood sugar means, it can vary and thus may lead to complications of the heart, kidney, and even problems in the vision.
It doesn’t matter whether someone suffers from Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, checking the blood sugar level is important. It can help in keeping your health in check.
Lack of insulin, too many carbohydrates, certain medications, and a lot more can lead to rising in sugar levels. While too much insulin, too much physical activity, and other factors can also contribute to lower blood sugar levels.
The goal of checking the blood sugar levels is to keep the sugar levels in the blood in balance.
Constantly checking the blood sugar level may sound like a hassle but it’s important for the health of those who are suffering from diabetes. It’s also vital to be aware of your lifestyle and be mindful of your health.
When to Check Blood Sugar Level?
It’s vital to understand when it’s best to measure blood sugar levels. When you are aware of your blood sugar levels, it would give you a better understanding of how food affects your health.
Consider the following:
It’s best to measure the blood sugar level after taking the insulin. But it depends on whether the person needs to take the insulin or not. So, the best source of information and guidance here is the doctor.
Those with Type 1 diabetes would need to check before their breakfast, lunch, and dinner. They would also need to check two to three hours after their meals!
For those with Type 2 diabetes, it would depend on the condition and how well they are maintaining their health. So, the doctor would give the best information. But, it’s possible to check first thing in the morning before eating breakfast, two hours after they have a meal, and before bedtime also! It can be up to four times a day.
Each individual is unique so it’s vital that you understand what works for you and what doesn’t. A healthy and active lifestyle would always help. Eating a well-balanced diet is always ideal. Always consult your doctor when it comes to diabetes!
How to Measure Blood Sugar Level?
Now that you have some idea about the significance of measuring the blood sugar level, it’s vital that you also know how to measure it correctly.
Consider the following:
A blood sugar monitor can help in measuring the sugar level in the blood. You may know this device by the name of a glucometer. People using this device would need to prick their finger and test the sugar level in the small amount of blood.
It’s also possible to use a continuous glucose monitor that senses information from the fluids that are between your cells. It goes under the skin, but it’s worn on the belly or arm. It monitors and tells about the blood sugar, but it’s usually a prescription device.
The data would be on your smartphone or any smart device. You can share the data with your healthcare provider. The purpose of using such modern means of technology is to keep a close watch on your overall health. After all, your health matters a lot for everyone around you and also for yourself.
Friends and family members can help in measuring blood sugar levels. It’s also possible to do it yourself. You can ask your doctor to guide you more! It’s always best to let your doctor guide you.
When using any device for the first time, you can definitely ask someone to help you. Once you are used to it, it would be easier!
You can also follow the instructions that come with the device. It’s best to know how to use it and make the most of it. All such modern means of technology are here to make your life better and help you live a better and longer life. Your health matter to the world and to everyone who is around you.
Consult Your Doctor
Despite tons of information available online and video tutorials, it’s best to talk to your doctor or Endocrinologist about your health. Your best source of information is your doctor. Your doctor can suggest the medicine and would tell you what works best for your health! With an active lifestyle and managing your health based on the plan of your doctor, it would be easy to know more about your blood sugar levels.
Living with diabetes may sound hard, but there are many people around the world who are managing their lifestyles. Start by controlling your weight and make a plan with your doctor that works in your favor. Your doctor knows what’s best for your overall health so bear that in mind.
The good thing is that if Type 2 diabetes is well maintained then people would not need to check blood sugar levels that often, but when it’s still there so keeping an eye would be important.
Wrapping It Up
Knowing and understanding your blood sugar levels is essential for your well-being. When you know what affects your health, it would be easy for you to manage. A healthy lifestyle can help, but you need to discuss your health and overall situation with the doctor.