Diabetes Symptoms
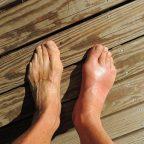
Diabetic Gout: The Overlooked Complication of Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is one of the most widely-known metabolic disorders, but even within the diabetes community, the association between diabetes and gout is not widely discussed.
Gout is a form of arthritis that can occur in diabetic patients. It is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, and it is estimated that approximately 15-20% of people with type 2 diabetes will eventually develop gout.
Diabetic gout is a potentially-debilitating complication which can impact quality of life. Therefore, it is important to understand the condition and how it is related to diabetes. This article outlines the symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diabetic gout.
What is Gout and How is it Related to Diabetes?
Gout is an inflammatory type of arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid in the joints. This leads to the formation of crystals, which can cause intense pain and inflammation.
It is also characterized by the formation of tophi (hard deposits of uric acid) on the skin, which can lead to swellings and deformities. Gout is linked to type 2 diabetes because it is often caused by an elevated level of blood sugar.
In diabetics, the body’s natural defense mechanisms against high sugar levels have malfunctioned, leading to a buildup of uric acid in the joints.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Gout?
Symptoms of diabetic gout are similar to those of regular gout, but may be more severe due to the additional impact of diabetes on the joints.
- Pain: Pain is the most common symptom of gout and diabetes. Pain resulting from diabetic gout tends to be more chronic and severe than regular gout.
- Inflammation: Diabetic gout can cause inflammation and swelling in the joints, leading to stiffness and difficulty moving. In severe cases, the joints may become deformed.
- Redness and Warmth: Diabetic gout can lead to redness and warmth around the affected area. This is caused by the accumulation of uric acid in the joint.
- Tophi: Tophi are hard deposits of uric acid that form on the skin as a result of diabetes and gout. They appear as nodules or plaques, and can cause itchiness and irritation.
What Causes Diabetic Gout?
Diabetic gout is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, which results from diabetes. When diabetics have elevated levels of blood sugar, their body’s natural defense mechanisms malfunction, leading to a buildup of uric acid in the joints. This uric acid then crystallizes and causes gouty arthritis.
What Are the Risk Factors for Diabetic Gout?
There are several risk factors associated with diabetic gout, including:
- Diabetic Complications: Diabetics who suffer from other complications, such as eye, kidney and nerve damage, may be more prone to developing gout.
- Family History: A family history of gout or diabetes increases the risk of diabetic gout.
- Diet: Diabetics who consume high-purine diets are at an increased risk of developing gout.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can increase the risk of gout in diabetes patients.
- Alcohol: Alcohol consumption can lead to gout in both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals.
- Age and Gender: Older men and women are more likely to develop gout than their younger counterparts.
How is Diabetic Gout Diagnosed?
Diabetic gout can be diagnosed with a variety of tests, including a physical examination, uric acid test, x-rays, and joint fluid analysis. The physical examination is used to check for swelling, redness, and warmth around the affected area.
The uric acid test measures the levels of uric acid in the blood, which can indicate gout. X-rays can be used to look for tophi and joint damage, while a joint fluid analysis can detect the presence of uric acid crystals.
How is Diabetic Gout Prevented?
There are several steps that can be taken to prevent the development of diabetic gout, including:
- Maintaining Blood Sugar Levels: It is important for diabetics to keep their blood sugar levels under control, as elevated levels can lead to gout.
- Eating a Low-Purine Diet: Diabetics should follow a low-purine diet to reduce their risk of developing gout. Foods high in purines, such as red meats, shellfish and organ meats, should be avoided.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put strain on the joints, leading to an increased risk of gout.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Excessive consumption of alcohol can increase the risk of gout.
- Taking Estrogen Supplements: Post-menopausal women may consider taking estrogen supplements to reduce their risk of diabetic gout.
- Taking Medication: Diabetics can take medications to reduce the risk of gout, such as Allopurinol and Uricosuric Drugs.
How is Diabetic Gout Treated?
Diabetic gout can be treated with a variety of medications and lifestyle changes, including:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen can be used to reduce pain and inflammation in the joints.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids can help to reduce inflammation.
- Colchicine: Colchicine can be used to reduce the risk of tophi formation.
- Changes in Diet and Exercise: Diabetics should adopt a healthy diet and exercise routine to reduce the risk of gout. This includes limiting purine-rich foods, alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Conclusion
Diabetic gout is a potentially-debilitating complication of type 2 diabetes. It is caused by the accumulation of uric acid in the joints and is characterized by pain, inflammation, and tophi formation.
There are several risk factors associated with diabetic gout, including diabetic complications, family history, diet, medications, and gender. Diagnosis is made through a physical examination, blood tests, x-rays, and joint fluid analysis.
Prevention of diabetic gout includes controlling blood sugar levels, eating a low-purine diet, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and taking medications.
Treatment of diabetic gout can involve taking NSAIDs, corticosteroids, colchicine, and making lifestyle changes. It is important that diabetics be aware of the risks associated with diabetic gout, as well as the steps that can be taken to prevent and treat it.
FAQ
What is Diabetic Gout?
- Diabetic Gout is a medical condition that occurs when excess levels of uric acid accumulate in the blood due to increased insulin resistance in diabetic patients. This leads to the formation of urate crystals in the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
How does Diabetic Gout affect patients?
- Patients with Diabetic Gout may experience recurrent episodes of joint pain, swelling, and tenderness. These symptoms can significantly impact their quality of life, limit their mobility, and affect their ability to carry out daily activities.
What treatment options are available for Diabetic Gout?
- Treatment for Diabetic Gout typically involves managing blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation and pain, and preventing further joint damage. This can include medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercise regime can also be helpful.
Can Diabetic Gout lead to other complications?
- Yes, if left untreated, Diabetic Gout can lead to other complications such as chronic joint damage, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as symptoms arise.
Is Diabetic Gout preventable?
- As with many health conditions, prevention is key. In the case of Diabetic Gout, lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying physically active can help prevent the development of the condition.
What are some common risk factors associated with Diabetic Gout?
- Common risk factors for Diabetic Gout include obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and a family history of the condition. Poorly managed blood sugar levels in diabetic patients can also increase the risk.
How can I tell if I have Diabetic Gout?
- If you are experiencing joint pain, swelling, and tenderness, it is important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. They may conduct tests such as blood tests, joint fluid tests, or imaging tests to confirm the presence of Diabetic Gout.
Is Diabetic Gout curable?
- Diabetic Gout is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management but can be effectively treated to reduce symptoms and prevent complications. While there is currently no cure for the condition, prompt diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life.
Can I continue to work and participate in physical activities with Diabetic Gout?
- Individuals with Diabetic Gout can continue to work and participate in physical activities as long as they receive appropriate treatment and follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations. However, it is important to listen to your body and avoid activities that exacerbate pain and inflammation.
Are there any dietary restrictions for Diabetic Gout patients?
- Patients with Diabetic Gout may benefit from limiting their intake of foods high in purines, which can increase uric acid levels in the blood. This can include organ meats, seafood, and alcohol. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider and/or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.

Do You Have Cloudy Urine?
If your pee is not a typical, clear, light-yellow hue and instead appears milky or murky, you have cloudy urine. Although murky urine is typically not harmful, it may be an indication of a medical concern if it occurs frequently and repeatedly.
What is cloudy urine?
When your urine is milky in color and not clear, it is said to have cloudy urine. Cloudy urine is usually not harmful, but it can be a sign of a medical disease if it occurs frequently and repeatedly.
What does cloudy urine look like?
The color of typical urine is a translucent light yellow. As opposed to the typical straw yellow color, the color of cloudy urine ranges from foggy white to light yellow.
What causes cloudy urine?
The presence of alkaline is the most frequent reason for cloudy urine. Water, salts, and waste products from the kidneys make up urine; the ratio of these elements determines whether the urine is alkaline or acidic (pH). pH values for normal urine range from 4.5 to 8 in terms of acidity to alkalinity.
Pee that measures 8 pH or higher is alkaline, whereas urine that measures 5 pH or lower is considered acidic (basic). Urine that is murky is due to high alkalinity.
The following are additional potential reasons for cloudy urine:
- Dehydration.
- Kidney leakage (chyluria).
- Infection.
- High fruit and vegetable diet.
- Vaginal discharge.
What if I have cloudy urine during pregnancy?
Frequent urination is typical throughout pregnancy. As a result, you could occasionally notice that the color of your urine changes. Pregnancy-related reasons for cloudy urine include:
- Vaginal discharge.
- Dehydration (from morning sickness). Infection.
- Preeclampsia.
Visit your healthcare practitioner for a more thorough evaluation if you frequently have cloudy or discolored urine, or if you develop any symptoms like a headache, blurred vision, abdominal pain, or swelling.
What foods cause cloudy urine?
Some foods might increase your level of alkalinity, which can result in hazy urine. You are more likely to have greater levels of alkalinity, which can result in cloudy urine if you consume a diet high in fruits and vegetables and low in meats, grains, and cheeses (low-PRAL).
Urine changes to look for
Your urine’s qualities can vary from day to day based on a number of factors, but in general, healthy urine is light yellow and has a faint odor.
What diseases/disorders have cloudy urine as a side effect?
Cloudy urine is a symptom of a number of illnesses or conditions, including the following:
- Diabetes.
- Chyluria.
- Infection (urinary tract infection,).
- Preeclampsia.
- Kidney disease or kidney stones.
Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic, progressive condition that causes a lengthy range of symptoms, including nerve damage, eye issues, and frequent urination. It develops when your body is unable to balance the amount of sugar in your blood. Urine that is hazy can also result from it.
The color and scent of your blood alter when you have a lot of sugar and protein in it. Urine that is cloudy and has a sweet scent is a typical sign of type 2 diabetes.
Dehydration
When you do not drink enough, your pee may become hazy. Urine becomes more concentrated when there is a fluid deficit. The hue will also darken.
The solution to this issue is to increase your daily water intake. Your urine will be clear and light yellow after you have had enough fluids.
Urinary tract infection
Bacteria that enter your bladder, kidneys, or urethra can cause a urinary tract infection (UTI). Urine leaks from the location. You will have the following signs in addition to hazy urine:
- The burning or agony when urinating
- An increased urge to use the restroom pee leaks
- Odorous or bloody urine
- Lower abdominal pain
Most likely, your doctor would advise taking antibiotics to get rid of the infection. To ensure that all of the bacteria are killed, take all of the medications that have been prescribed.
Kidney Stones
The minerals and salts in your urine cause crystals called kidney stones to grow in your kidneys. Urine can become backed up in your bladder or another area of your urinary tract if there are large stones present. Sometimes they can result in really painful pain. Your lower back, side, or even when you urinate, could pain.
You run the risk of having blood or murky urine. Moreover, it could smell bad or have a red, pink, or brown appearance.
You can also experience the following symptoms:
• Fever and chills
• vomit and feel sick
In your urine, some kidney stones may naturally dissolve. Large stones that cannot be broken up by urination can be divided up by doctors using a noninvasive method. Stone removal surgery is occasionally required.
Does cloudy urine mean that I have a sexually transmitted disease (STD) or a sexually transmitted infection (STI)?
Urine that is cloudy is a symptom of some STDs and STLs. Although cloudy urine is not the only sign of many STDs or STls, it may help your doctor make a diagnosis. Cloudy urine is a sign of a number of ailments or infections, including
• Chlamydia.
• Gonorrhea.
• Vaginitis.
How is cloudy urine treated?
The following steps can be taken to treat hazy urine:
• Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated.
• Taking vitamin C to lower alkaline levels.
• Using antibiotics to treat any infections.
• Eating a healthy diet.
How can I prevent cloudy urine?
By leading a healthy lifestyle that includes drinking plenty of water and eating a diet that is balanced, you can avoid having hazy urine. You can also go see your doctor to get infections treated right away before they become more dangerous to your health.
FAQs
Is foamy urine the same as cloudy urine?
Urination occurs quickly, which results in air pockets forming in the urine and giving it a frothy quality, which is the source of foamy urine. In contrast to the typical, light-yellow tone, cloudy urine is not clear and appears to have a milky hue.
You should get evaluated by your doctor if you notice that your urine is continuously frothy as this could be an indication of kidney issues.
Is cloudy urine serious?
An issue in your urinary tract could be the cause of hazy urine. It can be a sign of a major medical issue even though it normally doesn’t suggest a medical emergency. Dehydration is one factor that might contribute to cloudy urine.
Is cloudy urine smelly?
The smell of urine can alter, although it often is not harmful and only lasts a short while. Your diet and any vitamins or minerals you are taking can alter the smell of your urine. For instance, vitamin B-6 pills and asparagus both leave a noticeable odor in the urine.
Keeping hydrated can help prevent occasional hazy urine as well as a strong odor. Contact your healthcare physician if the smell of your urine lasts more than a few days.
Can urine be cloudy without infection?
Can urine be cloudy without an infection? Other than diseases, urine can become hazy for a variety of reasons. Cloudy urine can be brought on by dehydration, diabetes, diet, kidney stones, and more.
What does protein in urine look like?
Urine that is foamy or bubbly. Your hands, feet, tummy, and face swelling (edema). urinating more frequently. breathing difficulty.
When should I see my healthcare provider for cloudy urine?
Urine that is occasionally cloudy is typical. Get in touch with your doctor if you have persistently hazy urine that doesn’t clear up in a few days.
Does standing help with insulin sensitivity?
Can insulin sensitivity be restored
An individual can lower their risk of acquiring type 2 diabetes, even if they are overweight, by standing up during extended periods of sitting, according to a recent study.
By 2030, the UN wants to reduce noncommunicable disease-related fatalities by one-third. This is the third of the Sustainable Development Goals.
The fight against chronic diseases caused by a sedentary lifestyle must begin now, quite literally. According to a recent study, standing can aid in the prevention of significant medical diseases, including type 2 diabetes.
Standing is associated with improved insulin sensitivity, according to research from the Turku PET Centre and UKK Institute in Finland.
Blood sugar levels and metabolic processes in the body are controlled by insulin. However, factors like being overweight can interfere with the way the body’s insulin hormone works, resulting in a reduction in insulin sensitivity and a higher chance of developing chronic illnesses like type 2 diabetes.
The body’s cells’ receptivity to insulin is referred to as their insulin sensitivity. The body’s cells can utilize blood glucose more efficiently when there is high insulin sensitivity, which lowers blood sugar levels. This sensitivity may benefit from some dietary and lifestyle adjustments.
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin tolerance, or reduced insulin sensitivity, is a condition in which a person’s body has developed a resistance to the hormone, decreasing its potency. More insulin is therefore required to convince the liver to continue storing glucose and the fat and muscle cells to take up glucose.
Low insulin sensitivity occurs when there is insulin resistance. The opposite is true if you have low insulin resistance and are sensitive to insulin. The health benefits of insulin sensitivity outweigh those of insulin resistance. When cells stop responding to the hormone insulin, it is said that insulin resistance occurs.
What are the symptoms of insulin resistance?
You will not experience any symptoms if you have insulin resistance and your pancreas is able to produce more insulin to keep your blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Although the cells in your pancreas that produce insulin might deteriorate and insulin resistance can worsen over time. A raised blood sugar level (hyperglycemia), which does result in symptoms, is eventually caused when your pancreas is no longer able to generate enough insulin to overcome the resistance.
Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
• Increased thirst.
• Frequent urination (peeing). Increased hunger.
• Blurred vision.
• Headaches.
• Vaginal and skin infections.
• Slow-healing cuts and sores.
Prediabetes frequently goes unnoticed for years by many people. It is possible for prediabetes to go undetected before turning into Type 2 diabetes. The following signs and symptoms are possible in some prediabetic individuals: –
People with diabetes are more prone to consequences like heart disease, stroke, blindness, kidney failure, and kidney stones, as well as an increased risk of dying young. The disease, which accounts for 1.5 million deaths annually throughout the world, affects one in eleven people.
Standing improves insulin production.
Although it is well known that exercise can benefit people with diabetes and other noncommunicable diseases, the Finnish study was unique in that it focused specifically on how inactivity affects the production of the hormone insulin.
The results, which were reported in the Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, showed that even among inactive adults who were more likely to acquire type 2 diabetes, insulin function improved when research participants broke up extended periods of sitting by standing up. No matter how long a person sat, how active and fit they were, or whether they were overweight, standing improved their insulin levels.
A worldwide problem
All around the world, noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes, heart disease, cancer, stroke, and chronic lung illnesses are becoming more and more of an issue. So much so that the third Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) of the United Nations sets a 2030 aim of a reduction of one-third in premature deaths due to noncommunicable diseases.
The World Health Organization estimates that these lifestyle diseases account for 41 million deaths annually or more than 70% of all fatalities globally (WHO). The fact that more than two-thirds of these fatalities occur in low- and middle-income nations highlights the connection between a poor lifestyle and diseases.
Diabetes, which accounts for 1.5 million annual fatalities worldwide, affects 1 in 11 people.
An individual can lower their risk of acquiring type 2 diabetes, even if they are overweight, by standing up during extended periods of sitting, according to a recent study.
By 2030, the UN wants to reduce noncommunicable disease-related fatalities by one-third. This is the third of the Sustainable Development Goals.
Take a literal stance against chronic diseases of a sedentary lifestyle now. According to a recent study, standing can aid in the prevention of significant medical diseases, including type 2 diabetes.
Standing is associated with improved insulin sensitivity, according to research from the Turku PET Centre and UKK Institute in Finland.
Blood sugar levels and metabolic processes in the body are controlled by insulin. However, factors like being overweight can interfere with the way the body’s insulin hormone works, resulting in a reduction in insulin sensitivity and a higher chance of developing chronic illnesses like type 2 diabetes.
A stroke, blindness, renal failure, and heart disease are among the consequences that can affect people with diabetes.
Diabetes patients are more at risk for early death as well as complications like heart disease, renal failure, blindness, and stroke. The illness, which affects one in eleven people globally and results in 1.5 million deaths annually, is a killer.
Standing improves insulin production.
Although it is well known that exercise can benefit people with diabetes and other noncommunicable diseases, the Finnish study was unique in that it focused specifically on how inactivity affects the production of the hormone insulin.
The results, which were reported in the Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, showed that even among inactive adults who were more likely to acquire type 2 diabetes, insulin function improved when research participants broke up extended periods of sitting by standing up. No matter how long a person sat, how active and fit they were, or whether they were overweight, standing improved their insulin levels.
Noncommunicable diseases like type 2 diabetes can be avoided with regular physical activity.
Along with a poor diet, inhaling tobacco smoke, abusing alcohol excessively, and lack of physical activity are four long-term key risk factors. 1.6 million fatalities per year are thought to be brought on by inactivity or inadequate exercise.
What’s the solution?
The WHO urges people to alter their bad dietary and lifestyle habits in order to prevent the emergence of NDCs.
Programs for detection, screening and treatment are essential components of managing NDCs, but many individuals in low- and middle-income countries have inadequate access to healthcare.
Even while there is not a single way to guarantee that more people have access to global healthcare systems, policy initiatives like the WHO’s Global Coordination Mechanism on the Prevention and Control of NDCs serve as a foundation for cooperation in the effort to address this rising issue.
FAQ
Does standing lower insulin?
Even for sedentary adults who were more likely to acquire type 2 diabetes, the study’s findings, which were published in the Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, showed that when participants broke up extended periods of sitting by standing up, their insulin function improved.
How do you reduce insulin sensitivity?
The greatest strategy to fight insulin resistance is likely to be through exercise. In both the short and long terms, exercise can significantly lower insulin resistance. Insulin resistance can be decreased with weight loss. In order to treat insulin resistance, no drugs have been explicitly approved.
Does sitting increase insulin resistance?
Acute exercise is insufficient to reverse all of the alterations caused by sitting since it raises insulin resistance and affects the transport and oxidation of fatty acids in muscle tissue.
Does walking spike insulin?
The findings of this study demonstrate that walking exercise dramatically reduces serum levels of the cytokine known to be associated with insulin resistance, as well as insulin function and the insulin resistance index by lowering abdominal fat.
Can insulin sensitivity be reversed?
Your body may respond to insulin more favorably if you exercise and, if necessary, lose weight. In those with prediabetes, making simple changes, such as eating healthier foods and exercising more to lose weight, can help reverse insulin resistance and prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
What does high insulin sensitivity feel like?
Severe hunger or thirst having a hunger pang even after eating. Frequent or increased urinating tingling in the feet or hands.
How long does it take to fix insulin sensitivity?
To begin the process of correcting insulin resistance, a minimum initial lengthy fast of 36 to 3 days may be required. Fung recommends initial fasts ranging from 7 to 21 days for people who are very fat. The longest known fast under medical supervision lasted more than a year in a person weighing more than 460 lbs.
Should diabetics keep their feet up?
Additionally, have a thorough inspection performed by your foot doctor every year (or more frequently if you have nerve damage), during which the feeling and blood circulation in your feet will be examined. Continually pump blood. Put your feet up when you’re sitting and spend a few minutes at various points during the day wriggling your toes.
Does belly fat mean insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are more likely to occur as a result of abdominal fat accumulation than any other type of body fat. Inflammation of abdominal fat is recognized to be hazardous, but the cause of the inflammation has been difficult for researchers to pinpoint.
Does weight loss fix insulin resistance?
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can help people who already have diabetes or are at high risk of developing it reduce their risk of developing insulin resistance, prediabetes, diabetes, and the health complications that can arise from these conditions.
The Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Despite having names that sound similar, type 1 and type 2 diabetes are two separate illnesses with distinctive causes.
Type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are fundamentally distinct from one another since type 1 is thought to be brought on by an autoimmune response and manifests in infancy.
Long-term lifestyle variables like inactivity and obesity are linked to the development of type 2 diabetes, which occurs over a number of years. The diagnosis is typically made in adults.
However, family history may be important. Type 1 diabetes risk factors are not completely understood.
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The immune system of the body defends against outside intruders, such as dangerous germs and viruses.
• It is thought that an autoimmune response is what causes type 1 diabetes. When a person has type 1 diabetes, their immune system misidentifies healthy cells from their body as foreign invaders.
• The insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas are attacked by and destroyed by the immune system. The body is unable to manufacture insulin if these beta cells are gone.
Why the immune system occasionally targets the body’s cells remains a mystery to researchers. It might be influenced by genetic and environmental elements, such as virus exposure.
There is a continuous investigation into autoimmune illnesses. Type 1 diabetes is not brought on by diet or way of life.
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
- Insulin resistance is a complication of type 2 diabetes. Although the body continues to manufacture insulin, it is unable to utilize it efficiently.
- Although there are a number of lifestyle factors, such as being sedentary and being overweight, that may be involved. Researchers do not yet fully understand why some people develop insulin resistance while others do not.
- Additional genetic and environmental factors might also be important. Your pancreas will attempt to make up for this by generating more insulin if you acquire type 2 diabetes. Glucose builds up in your bloodstream as a result of your body’s inability to utilize insulin properly.
How Does Diabetes Affect the Body?
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the two most common varieties.
• Each kind of diabetes is a chronic illness that interferes with your body’s ability to control blood sugar or glucose levels. Your body’s cells run on glucose for fuel, but glucose needs a key to get into your cells. That key lies in insulin.
• Insulin production is absent in those with type 1 diabetes. It is comparable to being locked out.
• In the later stages of the disease, type 2 diabetics frequently produce insufficient insulin and do not respond to insulin as well as they should. It’s comparable to having a key that is broken.
• Chronically high blood sugar levels are a risk for both types of diabetes. Diabetes problems are now more likely as a result.
What Are the Risk Factors for Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes risk factors are less understood than type 2 diabetes risk factors.
Some known risk factors are:
- Family history: A person is more likely to develop type 1 diabetes if they have a parent or sibling who has the disease.
- Age: Although type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, children and teenagers are the age group where it most frequently does.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
Type 2 diabetes is a possibility for you if you:
• Possess prediabetes or have just raised blood sugar
• Have a weight problem or are obese
• Excessive belly fat
• Are not active three times a week or more
• Are older than 45
• Own a history of gestational diabetes, or diabetes while pregnant, and have given birth to a child that weighed greater than 9 pounds.
• Are Black, Hispanic or Latino, American Indian, or Alaska Native people more likely to experience health inequalities because of structural injustices?
• Possess a type 2 diabetic member in close family
• Afflicted with polycystic ovary syndrome
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetes?
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes both have symptoms that might develop if not treated, including:
• Frequent urination
• Feeling very thirsty and drinking a lot.
• Feeling quite hungry.
• Feeling extremely worn out.
• Having vision haze
• Not having your cuts or sores heal completely.
• Extremely dry skin
• Being sick more frequently than usual
• Mood swings, impatience, and accidental weight loss are among the symptoms that type 1 and type 2 diabetics may face.
• Diabetes and tingling in the hands and feet. Diabetes of any kind, including type 1 and type 2, can cause tingling and numbness in the hands and feet. According to the American Diabetes Association, type 1 diabetes patients’ chance of experiencing tingling and numbness is greatly decreased by good glucose control (ADA).
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes show in completely different ways, although sharing many of the same symptoms.
Many types 2 diabetics do not have symptoms for many years, and when they do, they often progress slowly and gradually.
When type 2 diabetes first develops, some people do not even have any symptoms and do not know they have it until serious consequences. Typically, over the course of several weeks, type 1 diabetes symptoms appear suddenly. This kind, formerly known as juvenile diabetes, typically appears in childhood or adolescence. Later in life, type 1 diabetes is, however, a possibility.
How Are Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Treated?
Right now, type 1 diabetes has no known cure. Insulin must be regularly given, and blood sugar levels must be tested often in those with type 1 diabetes because they cannot make any.
A few people inject themselves multiple times a day into soft tissue like the stomach, arm, or buttocks. Pumps for insulin are used by others. The body receives insulin through a tiny tube from insulin pumps in a consistent dosage.
Due to the rapid ups and downs in blood sugar levels, blood sugar testing is a crucial component of managing type 1 diabetes.
However, many patients require further assistance. Type 2 diabetes can be controlled and even prevented with diet and exercise. Medications that improve the way your body uses insulin may be prescribed by your doctor if lifestyle changes are ineffective.
A crucial component of managing type 2 diabetes is regularly checking your blood sugar. You cannot determine whether you are achieving your target levels without it.
Blood sugar checks may be advised more frequently or on an as-needed basis by your doctor. Your physician might suggest insulin injections if your blood sugar levels are high.
Can Diabetes Be Prevented?
It is impossible to prevent type 1 diabetes. With certain lifestyle modifications, such as keeping a reasonable weight, you may be able to reduce your chance of getting type 2 diabetes.
Working with your doctor to create a healthy weight-loss plan, increasing your exercise levels, eating a balanced diet, and consuming fewer sugary or highly processed foods are all ways to lose weight if you are overweight.
Careful monitoring can restore your blood sugar levels to normal and stop the onset of serious problems even if you are unable to prevent the disease.
FAQ
Is type 2 diabetes better or worse?
Many times, type 2 diabetes is less severe than type 1. However, it still has the potential to have severe health consequences, particularly in the sensitive blood vessels of your kidneys, nerves, and eyes. A stroke and heart disease are also become more likely by type 2.
Can type 2 diabetes go away?
Type 2 diabetes has no known treatment options. However, it might be feasible to reverse the disease to the point where you no longer require medicine to manage it, and your body is not adversely affected by having blood sugar levels that are too high.
Can walking cure diabetes?
Walking can help lower blood glucose levels and thus improve diabetes control, according to research studies.
Is fasting good for diabetes?
Fasting routines have been shown to be effective in reducing the signs and symptoms of diabetes and addressing some of its underlying causes, according to preliminary studies. However, not everyone should engage in the practice, and many dieticians and medical professionals continue to provide warnings about potential harm to metabolic and blood sugar health.
How do you reset your pancreas?
US researchers claim that by following a certain fasting diet, the pancreas might be encouraged to rebuild itself. In animal studies, diabetes symptoms were cured by restoring the organ’s ability to manage blood sugar levels. According to the study, which was published in the journal Cell, a diet “reboots” the body.

Finger Nails Ridges and Diabetes
Look at your fingernails closely. If you look closely, you could find that your nails are not as smooth as you originally believed.
Think of them like wrinkles in your nail; they frequently grow more obvious as we age. There are several reasons why you could have ridges on your fingernails, from stress to renal and thyroid illness. Fingernail ridges are typically not harmful.
Find out more about the meaning and possible causes of ridges on your fingernails.
Vertical Ridges
Normally harmless, vertical ridges frequently develop along the length of our fingernails. Your fingernails’ tips to the cuticle form vertical ridges, which are furrows. They are referred to as bands or longitudinal striations at times.
Vertical ridges in the nails can also result from vitamin shortages or poor diet in addition to aging but are typically not a cause for alarm.
Additionally, vertical ridges and alterations to your nails’ tops that cause them to be concave or spoon-shaped can be brought on by iron deficiency anemia and cause these modifications.
As a result of a delay in cell turnover, older persons frequently develop slightly vertical ridges in their fingernails. During this process, new skin cells created under the skin’s surface rise to replace the dead cells removed from the surface.
Further, a medical problem could be to blame if you also have other symptoms, such as nail color or texture changes. The ridges could appear brittle or glossy if you have trachyonychia (twenty-nail dystrophy). You may have onychorrhexis, a disorder requiring medical attention if your nails have vertical ridges and brittle, breaking nails.
Horizontal Ridges
On your fingernails, horizontal ridges may indicate an issue, whereas vertical ridges may not be harmful. Horizontal ridges are frequently brought on by Beau’s lines, a condition.
It frequently occurs in conjunction with uncontrolled diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and deficits in zinc. Scarlet fever, measles, mumps, and pneumonia are a few other ailments that can result in Beau’s lines.
It might just be your body fending against an illness if these horizontal ridges in your nails start to form periodically. You might wish to check to see if a chronic ailment is to blame if these ridges recur frequently. If Beau’s lines develop, the acute renal disease may also be present.
The development of Beau’s lines on all 20 nails could be a sign of:
• Mumps
• Parathyroid disease
• Unmanaged diabetes
• Syphilis
• Respiratory conditions
• Illnesses that cause prolonged high fevers
• Zinc deficiency
Chemotherapy may also cause Beau’s lines.
Red or brown spots may develop beneath your nails as a result of trauma. If you see dark brown, black, or red color changes under your nails without having had nail trauma, it may be a sign of a more serious problem, such as endocarditis or melanoma.
Diagnosing the cause of fingernail ridges
Examining changes in your nails should be done by a doctor. If an injury causes damage to your nails, you can wait a few weeks to decide whether to visit a doctor to watch how the nail and your finger heal. If the damage causes any of the following, you should see a doctor immediately.
• A clean or rugged cut through your nail
• A crushed nail
• A nail that is torn off
• Bleeding under your nail
In addition to looking at your nails at your appointment, your doctor will inquire about any additional symptoms you may be having. In cases where renal disease, diabetes, or nutritional deficiencies are suspected, your doctor may also request urine and blood testing.
If it appears that the ridges are brought on by a skin problem, a dermatologist can help you develop a treatment strategy. Your dermatologist might request some fingernail clippings to have them examined in a lab for indications of infection if the source of your fingernail ridges is unclear.
Treating ridges in fingernails.
Treatment focuses on the underlying cause of the changes in your nails because fingernail ridges are frequently indicators of other health issues.
For instance, if you have diabetes and have developed Beau’s disease, controlling your blood sugar may help to lessen these horizontal fingernail ridges.
Moisturizers for your hands or topical ointments to lessen eczema symptoms may be used as part of the treatment for skin disorders like eczema. If you have low levels of minerals or vitamins, you can be encouraged to change your diet or take supplements such as Magnesium to increase them.
Consult a dermatologist for guidance on how to care for your nails; you’ll want to be careful not to do any more harm.
Diabetic Nail care
A highly essential subject is diabetic nail care. It’s also crucial to remember that the condition of your nails is a fairly reliable indicator of your general health. Diabetic neuropathy is a disorder that frequently affects people with diabetes. This illness lessens the sensation in the fingers and toes.
• You should ensure that you visit your doctor to get your feet examined a few times a year.
• Frequently check your own feet.
• Make sure your shoes are the right size.
• Keep your nails trimmed at least once every six to eight weeks, but avoid going too short.
• Use diabetic nail clippers properly.
The bottom line
In most cases, fingernail ridges are a telltale symptom of age. In older persons, little vertical ridges frequently form. However, it’s crucial to be aware of fingernail ridges and other alterations to the nails. These could be the initial symptoms of a significant health issue.
FAQs
What do diabetic fingernails look like?
The nails might turn yellow in diabetic patients. This coloration frequently results from the way sugar breaks down and how that affects the collagen in nails.
What causes diabetic nail ridges?
Gram-negative bacteria or fungi, which can cause nail infections, are more likely to affect people with diabetes.
Additionally, damage to the nail or nearby skin, such as that caused by deformed or sharply edged nails, neuropathy, and hyperglycemia, raises the risk.
Why do my fingernails suddenly have ridges?
What causes nail ridges? In addition to being a sign of poor nail care, nail damage, vitamin deficiency, or even a more serious medical disease, nail ridges are typically caused by aging.
What do ridges in your nails mean?
Although they might mean several things, nail ridges are mostly harmless. Age is frequently indicated by vertical ridges. Horizontal ridges may be an indication of a variety of conditions, including Beau’s lines, severe nail injuries, and starvation.
Why must people with diabetes be careful when cutting their nails?
Fungi and bacteria can spread from clipping or foot care equipment to open wounds, making diabetes patients more susceptible to illness.
Does type 2 diabetes affect nails?
Uncontrolled diabetes can have detrimental consequences on a variety of organ systems, including the cardiovascular, nervous, ocular, renal, and cutaneous, as well as its impact on the skin, hair, and nails.
Can metformin affect your nails?
There was a noticeable improvement in the nails three months after stopping metformin. Clinicians should be aware of the yellow staining of nails caused by metformin, which is treatable and reversible if caught early.
What vitamins should I take for ridges on nails?
The prevention of vertical ridges in your nails depends on your magnesium intake. The development of new nails and the synthesis of proteins are two more benefits of this mineral.
Iron, zinc, vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin D, in addition to other vitamins, can benefit nail health. Research from 2018 indicates that biotin is strongly advised for improving nail health, although additional studies are required to fully grasp the advantages.
Can you buff out ridges in nails?
You can lightly buff your nails to get rid of ridges, according to some dermatologists. However, it is advised to continue nourishing your nails, maintaining good nail hygiene, and consulting a dermatologist for additional guidance.

What is Diabetes Retinopathy?
What’s Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetes retinopathy is a complication that affects the eyes, causing many symptoms, including eye floaters, blurred vision, and difficulty differentiating or seeing colors.
The retina’s blood vessels swell, leak, or close, stopping blood flow entirely. It is important to note that although diabetes retinopathy might cause no or mild symptoms, eventually, it can lead to blindness.
Also, this complication can develop in people with type 1 diabetes or type 2. Remember, the longer you have diabetes, the longer the retina’s blood vessels are damaged and the higher the chance of developing eye problems.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Non- proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR)
This is the early stage of diabetic retinopathy, with mild symptoms. High blood sugar typically causes the blood vessels to leak, causing the retina to swell. Alternatively, the blood vessels in the retina can close off, causing blurry vision. The main symptom of NPDR is blurry vision, and most diabetic people are in this stage.
Proliferative Diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
This is an advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy. The stage starts when the blood vessels begin to regenerate. Sometimes, the eye can develop new blood vessels to replace the ones damaged by the high blood sugar level.
However, the new blood vessels are usually weaker, thus leaking or bleeding easily. Common symptoms of PDR include eye floaters or sudden loss of vision.
Symptoms of Diabetes Retinopathy
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy are not seen during the early stages. However, as the condition advance, the symptoms become more noticeable. Diabetes retinopathy affects both eyes, making it hard for diabetic people to see clearly. Here are common symptoms:
- Impaired color vision
- Blurred vision
- Poor night vision or night blindness
- Eye floaters, i.e., spots or strings that blur the field of vision. Eye floaters tend to move in the direction a person looks, making it hard to see objects clearly.
- Patches or partial streaks which block vision/fluctuating vision
- Dark or empty spots form in the center of the field of vision.
- Sudden total loss of vision
When Should See an Eye Doctor?
Careful blood sugar management is the best way to prevent vision loss. Therefore, if you know you have diabetes, you must visit an eye doctor yearly for a thorough examination.
Remember, you should see an eye doctor even if you think your vision is fine. Women who develop diabetes when they are pregnant, i.e., gestational diabetes, or women who have diabetes before becoming pregnant, are at a higher risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Ergo, if you are pregnant, your eye doctor can recommend additional eye examinations throughout your pregnancy to ensure your vision is not impaired. As a rule of thumb, diabetic people should visit their eye doctor immediately if their vision becomes spotty, hazy, or blurry.
Diabetics can develop diabetic retinopathy. It is crucial to understand that this eye condition can increase due to the following factors:
- Pregnancy
- High cholesterol
- Uncontrolled blood sugar
- Using tobacco
- Being diabetic for a long time
- Poor blood sugar level control
- Being Hispanic, Black, or Native American
Diabetes Retinopathy Diagnosis
Although the condition starts with no or mild symptoms, an ophthalmologist can detect early signs through the following methods:
Dilated Eye Exam
The ophthalmologist places a drop in your eye to dilate the pupil. Then, using a special lens, the eye doctor looks inside the eye to determine the presence of:
- New or regenerating blood vessels
- Cataracts
- Scar tissue
- Any abnormalities in the retina, blood vessels, or retina
- Eye pressure changes
- Detachment of the retina
Fluorescein Angiography
The eye doctor places a few drops in your eye and then injects fluorescein (a dye) into an arm’s vein. As the dye circulates, the doctor takes pictures to determine if the retina vessels are blocked or leaking. With the help of fluorescein, the eye doctor can see if any new blood vessels are growing.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
This is a newer technique where the doctor uses a machine to scan the retina. The device provides high-resolution images to reveal the retina’s thickness. Using the images, it is easier for the eye specialists to determine if the retina has swollen or if there are any developing cysts.
Also, eye doctors can perform scans before and after treatment to determine if it works and how well they can manage the patient’s condition.
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
Treatment of this condition depends on factors like its severity and how well it responds to treatment. Initially, most eye doctors monitor the eye’s condition and how it is proceeding. However, after some time, the doctor can recommend other treatment options, including:
Laser Treatment
Eye doctors use targeted lasers to seal leaks and shrink blood vessels. Laser surgery effectively stops or slows down blood leakage in the eye.
It is crucial to note that the bright light can make some people uncomfortable, and the patient might have blurred vision for the rest of the day.
While you may need more than one laser treatment session, it is important to know that this treatment option comes with certain risks, for example, loss of the night, peripheral, and color vision.
Therefore, talk to your doctor about the pros and cons before undertaking this treatment.
Injections
Your eye doctor can recommend certain medicines to reduce the swelling or stop/slow down the leakage. Corticosteroids and anti-VEGF drugs are popular examples.
If you opt for an eye injection, the doctor will place a numbing medicine on the eye, clean the eye thoroughly to prevent infections and inject medication into the eye.
Eye Surgery
If you have severe problems with the retina, eye surgery, also known as vitrectomy, is the recommended treatment. In eye surgery, the doctor removes some of the vitreous from the eye. After removing the vitreous or blood from the eye, clear gas or liquid is inserted to improve vision.
If you have diabetes, you can lower the risk of developing diabetes retinopathy via:
- Exercising regularly
- Quit smoking
- Keeping your blood sugar level in check
- Have annual eye exams
- Take medications as prescribed
With timely treatment, diabetic people can prevent sudden vision loss and delay diabetes retinopathy. The best way to prevent this eye complication is by controlling your blood sugar levels and managing your diabetes. Finally, if you notice any vision changes, schedule an appointment with your eye doctor.

What is the Best Lotion for Diabetic Skin?
The Best Lotion for Diabetic Skin
Skin conditions are often dreaded by a majority of people given the health and beauty complications that often accompany them. This problem is however prevalent among those diagnosed with diabetes.
For instance, several studies conducted on the matter a while back revealed that nearly 30% of individuals diagnosed with diabetes mellitus usually experience some form of skin problem at some stage of their sickness.
The majority of these skin disorders prevalent among diabetics are usually attributed to comorbid health conditions such as candida and impetigo infections among others.
Subsequently, those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes further have double the risks of developing the common scaly disease, psoriasis, compared to non-diabetics.
Diabetic dermopathy
Diabetic dermopathy is one of the major skin conditions found to occur in nearly 30% of patients diagnosed with diabetes. This skin problem is usually characterized by unique and distinguishing features that most often appear on the shins of the affected.
They usually resemble solar lentigines and due to their location on the body, they are occasionally referred to as shin spots or in some circles as pigmented pretibial patches.
What are the causes of diabetic dermopathy?
Experts in the field are yet to pinpoint the exact cause of diabetic dermopathy. Nonetheless, several studies and theories have often been put forward regarding the matter. For instance;
Some scholars have associated the condition with diabetic neuropathic and vascular complications as relevant studies indicated diabetic dermopathy to be more prevalent among diabetic patients with neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
Subsequently, other studies have also pinpointed that it tends to occur among older patients especially those who have had diabetes for at least 10-20 years.
Others have also linked diabetic dermopathy to increased glycosylated hemoglobin, an indicator of poor control of blood glucose levels.
It is also thought that diabetic dermopathy may be a magnified response of the body to an injury or trauma in bony parts of the body like the shin.
This is because, lesions often occur over body parts of the body and several studies have also discovered that shin spots usually appear in response to traumas with heat, cold or blunt objects among diabetic patients.
Signs and symptoms of diabetic dermopathy
Identifying this condition is usually straightforward given the manifestations that often appear on the skin and in particularly one region of the body. They are commonly found on the shins.
However, on rare occasions, few lesions can often be found on the front of the thighs, forearm, side of the foot, scalp, and even along the body trunk.
Their distinguishing features include the fact that the lesions are often;
- Round or oval shaped
- Reddish-brown in color
- Initially scaly but later on flattens out and becomes indented
- Commonly appear on both shins
Having four or even more lesions is usually a direct indication of diabetes and as such, undiagnosed individuals presenting with shin spots are always advised to seek medical testing and further investigations as this could help rule out the possibility of an early case of diabetes.
The treatments for diabetic dermopathy
The condition is usually harmless and as such does not require any form of treatment as they tend to decline and go away in just a couple of years. This is usually fast-tracked by improved blood glucose control.
Diabetic Bullae
This is another skin condition associated with individuals with diabetes. Also known as Bullosis diabeticorum, this condition usually appears in the form of blister-like lesions occurring spontaneously on the hands and feet of individuals with diabetes.
The condition is however quite rare but similarly significant as it is usually among the distinct markers for diabetes.
Several studies conducted on the condition revealed that it is usually more prevalent among men than women and between the ages of 17 to 84 years. They are also common in patients with long-standing diabetes or comorbid diabetic complications like neuropathy among others.
Diabetic bullae is usually characterized by few but distinct signs and symptoms. These include;
- The blisters usually appear on the hands or feet
- They are usually painless
- The blisters measure 0.5 to 17 centimeters in diameter
- They have irregular shapes
There are two common and properly defined types of diabetic bullae and they are;
Intraepidermal bullae – these usually boast unique blisters filled with clear and sterile viscous fluid. The blisters normally heal spontaneously without scarring or atrophy in 2-5 weeks.
Subepidermal bullae – the blisters in this category are usually filled with blood and healing may sometimes exhibit scarring and atrophy. Nonetheless, they are usually less common among diabetics.
Diabetic bullae often heal spontaneously without applying any form of treatment in most of cases. To guarantee this, diabetic patients are usually encouraged to avoid breaking the blisters at all costs as this would prevent secondary infection which may complicate the healing process.
Diabetic stiff skin
Also referred to as diabetic cheiroarthropathy or digital sclerosis, diabetic stiff skin is another common skin condition among diabetics especially those with long-standing type 1 diabetes. The condition is often characterized by;
- Restricted mobility of the joints of an individual’s hands
- Stiff, waxy, thickened, and yellowed skin
- Patients may also suffer from Dupuytren contracture (tendon tightening) which bends their fingers
The condition is thought to develop due to the reaction of glucose with proteins in the skin and essentially increased amounts of glycation end products.
Other dermatological conditions associated with diabetes
Apart from the few significant skin conditions associated with diabetes mentioned above, there are several others which include;
Foot ulcers
Necrobiosis lipoidica – manifests as yellow, waxy plaques on the skin
Reactive perforating collagenosis and Kyrle disease – common among diabetics with renal failure
Scleroderma – a rare type 2 diabetes complication causing skin thickening in the neck and upper back
Eruptive xanthoma – this is associated with high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides. Appears on the hands, arms, feet, legs, and even buttocks
Skin tags
Xanthelasma – manifests as multiple yellowish scaly patches on and around the eyelids
Vitiligo – this is an autoimmune condition that sometimes develops due to type 1 diabetes
Acanthosis nigricans – this usually manifests as darkening and thickening of skin folds. Thought to manifest as a result of insulin resistance
Pruritus – is associated with numerous causes such as yeast infection, dry skin, neuropathy, or poor blood flow
Cutaneous dysaesthesia – associated with small fiber neuropathy
Bacterial skin infections – these are several and inclusive of stye, boil, abscess, paronychia, cellulitis
Fungal infections – specifically Candida albicans
Top 5 lotions for diabetic skincare
Whereas most of these dermatological conditions associated with diabetes do not require treatment, they often require proper management to ensure that they stay hydrated, soft, and unbroken.
This is because, without proper care, even managing your blood glucose level may not make them go away since some may invite infections further complicating a diabetic’s life.
As such, the following lotions are some of the best and most recommended by experts to ensure you manage your skin condition effectively until they effectively heal. They include;
- Gold Bond Ultimate Hydrating Lotion Diabetics’ Dry Skin Relief, Moisturizes & Soothes
- Terrasil Wound Care – 3X Faster Healing, Infection Protection Ointment
- CeraVe Diabetics Dry Skin Relief Bundle
- EASE-Z Diabetic Lotion for Dry Skin
- GOLD BOND ULTIMATE Diabetics Dry Skin Relief Foot Cream
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does diabetes cause skin changes?
Yes. This is because skin changes are one of the most common signs of diabetes and can often be used in diagnosing an individual not yet tested.
The skin is one of the major body organs massively affected by diabetes. Nevertheless, an early diagnosis and proper glucose level regulation may limit these skin changes thereby preventing any associated major complications.
What does diabetic skin look like?
Several individuals may often present with varying skin configurations when suffering from diabetes. In fact, some may even present with normal skin composition depending on the stage, severity, and type of diabetes they suffer from.
For instance, diabetes may cause some changes in the small blood vessels in the skin resulting in several manifestations.
An example is diabetic dermopathy which often looks like oval/circular reddish-brown scaly patches, another one is diabetic bullae presenting as skin with blister-like lesions among other varieties.
What is diabetes dermatitis?
Also referred to as Acanthosis nigricans, this skin condition is usually characterized by dark, thick velvety patches in body folds and creases.
It is thus often more prevalent on the skin around the neck, groin, and armpit regions. It is common with type 2 diabetics as it is caused by high blood insulin levels, insulin resistance, which causes skin cells to reproduce faster than the normal rate.
Can you reverse sugar damage to the skin?
There is no definitive way to reverse sugar damage to the skin as it is a one-way process. The process known as sugar sag develops when your skin loses its resiliency and starts to wrinkle and sag.
Essentially, the process leads to cross-linking of the collagen fibers in the skin, an irreversible process.
Does metformin affect your skin?
Metformin, which is a widely used drug among diabetic and obese individuals, has been found to exert several effects on the skin. As such, it could potentially induce a variety of dermatoses.
For instance, some of the commonly identified drug-induced reactions among associated individuals like diabetics include the manifestation of rashes, urticarial, and lichenoid eruption, among others.
How long after quitting sugar doe one’s skin improve?
Sugar is often associated with numerous skin conditions among them acne which affects a great number of people. Therefore, quitting sugar should have some positive effects on the skin.
Nonetheless, these changes are not usually instantaneous and thus take time to reflect. As such, studies have shown that changes may start to manifest after six weeks of behavior modification, however, big visible changes on the skin may take even longer, about 3 to 4 months after cutting down on sugar.
What is CARB face?
This is the extra puffiness often manifested in the faces of those who over-indulge in eating excess carbs like too much bread, pasta, and pizza among others. It is thus prevalent among those with a weakness for carbohydrate-filled foods.

Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
When someone with diabetes does not have enough glucose (sugar) in his or her blood it may lead to diabetic hypoglycemia. If you do not have glucose, you cannot function well since it is the main source of fuel for the brain and body.
A blood sugar level below 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 3.9 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) is a low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) for many people. However, there might be a variation in your numbers. Therefore, when you want to know the appropriate range to keep your blood sugar, you should ask your health care provider.
Treat low blood sugar promptly while also being observant of the early warning signs of hypoglycemia. Eating or drinking a simple sugar source like glucose tablets, hard candy or fruit juice can help you to raise your blood sugar quickly.
Additionally, what to do if you are not able to treat the condition yourself and what symptoms to look for should be told to your family and friends.
Early warning signs and symptoms
There are multiple signs and symptoms of diabetic hypoglycemia. However, some of the early indications are:
- Pallor (unhealthy pale appearance)
- Shakiness
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Sweating
- Nausea or hunger
- Fast or an irregular heartbeat
- Difficulty concentrating
- Fatigue and feeling weak
- Anxiety or irritability
- On your cheek, tongue, or lips, they will be tingling
Nighttime signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms that may disrupt your sleep id diabetic hypoglycemia happens when you are sleeping include:
- Due to perspiration, they will be damp sheets and nightclothes
- Nightmares
- Tiredness, irritability, or confusion upon waking
Severe signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia may worsen if diabetic hypoglycemia is not treated. These signs and symptoms include:
- Strange behavior, perplexity, or both, such as the inability to do simple tasks
- Speaking slowly or with difficulty
- eyesight tunneling or haziness
- Inability to eat or drink
- Muscle weakness
- Drowsiness
Severe hypoglycemia may lead to:
- Seizures or convulsions
- Unconsciousness
- Death but or rare occasions
From episode to episode or from person to person, the symptoms can differ. Noticeable symptoms may not be there in some people and therefore there is a possibility of you having hypoglycemia and not having any symptoms.
Because of this, apart from keeping track of how you are feeling when your blood sugar is low and it is important to regularly monitor your blood sugar level.
When to see a doctor
Serious problems such as seizures or unconsciousness that require emergency care can be caused by severe hypoglycemia. Therefore, in an emergency, it is advisable that you ensure your co-workers, friends, and family know what to do.
The people you trust should be informed of hypoglycemia. You might be alerted to early symptoms by others who know what symptoms to look for.
A potentially serious situation can be easier to safely manage if your family members and close friends know where you keep glucagon and how to administer it. The release of sugar into the blood is stimulated by a hormone known as glucagon.
If you are someone who is losing consciousness (not responding) or cannot swallow due to low blood sugar, here is some emergency information to give to others:
- Your blood sugar levels will drop even further if you inject insulin. Therefore, you should never inject it.
- Choking can be caused if given food or fluids and therefore should be avoided.
- Use injection or nasal spray when giving glucagon.
- If glucagon is not on hand, you do not know how to use it or the person is not responding, you should call 911 or emergency services in your area for Immediate treatment.
See your health care provider if you have symptoms of hypoglycemia multiple times a week or more. You may otherwise adjust your diabetes treatment regimen, or need to change your medication timing or dosage.
Causes
If you are taking certain diabetes medications or taking insulin, you are likely to have low blood sugar.
- There are multiple causes of diabetic hypoglycemia and some of the common include: –
- Intake of too much diabetes medication or insulin
- Low appetite
- Skipping or postponing a snack or meal
- Increasing exercise or physical activity without eating more or adjusting your medications
- Drinking alcohol
Blood Sugar Regulation
Food is the main source of the body’s glucose. When blood sugar is too high, blood glucose(sugar) levels are lowered by the insulin hormone.
Taking more insulin than you need can cause your blood sugar level to drop too low and result in hypoglycemia if you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes and need insulin to control your blood sugar.
Further, if you eat less than usual after taking your diabetes medication or if you exercise more than you typically do leading to your body using extra glucose, your blood sugar can also drop too low. It is always not easy to maintain the balance between activity, insulin, and food.
However, you can work with the following people to try to prevent low blood sugar levels: your healthcare provider, registered dietitian, and certified diabetes care and education specialist.
Risk Factors
A greater risk of diabetic hypoglycemia is in some people and they include:
- Those who use insulin
- Sulfonylureas, or diabetes medications, such as glipizide (Glucotrol), glimepiride (Amaryl), or glyburide, are used by patients (Diabeta, Glynase).
- Older people and your kids those whose kidney or liver function is affected
- People with diabetes who have had it for a long period
- Those using several drugs; those who do not experience low blood sugar symptoms (hyperglycemia unawareness)
- Anyone having a condition that makes it difficult for them to react quickly when their blood sugar drops
- Those that consume alcohol
Complications
You may lose consciousness if you ignore the symptoms of hyperglycemia for too long. This is because the functioning of your brain requires glucose.
If hypoglycemia is untreated it can lead to seizures, loss of consciousness, and death hence you should recognize its signs and symptoms early.
The risk of serious or even deadly accidents can be brought by diabetic hypoglycemia and therefore your early symptoms should be taken seriously.
Prevention
To lessen the risk of diabetic hypoglycemia:
- Monitor your blood sugar. You may check and record your blood sugar level several times a week or multiple times a day depending on your treatment plan. The only way to make sure that your blood sugar level remains within your target range is by careful monitoring.
- Do not skip or delay meals or snacks. Be consistent about the amount you eat and the timing of your meals and snacks if you take insulin or oral diabetes medication.
- Measure medication carefully and take it on time. Follow your doctor’s advice when taking your medication.
- If you increase your physical activity, adjust your medication or eat additional snacks. What medications you take, the type and length of the activity, and the blood sugar test results determine the adjustments. When making adjustments, follow your diabetes treatment plan.
- If you choose to drink, eat a meal or snack with alcohol. Hypoglycemia can be caused by drinking alcohol on an empty stomach. Blood sugar monitoring is even more important when drinking alcohol since it may cause delayed hypoglycemia hours later.
- Record your low glucose reactions. You and your medical team may be able to use this to spot tendencies that lead to hypoglycemia and figure out how to stop them.
In an emergency and to let others know that you have diabetes, carry some form of diabetes identification. A wallet card or bracelet and medical identification necklace can be used.
FAQs
Does diabetes cause hypoglycemia?
When a person with diabetes does not have enough glucose(sugar) in his or her blood it may lead to diabetic hypoglycemia. If you do not have glucose, you cannot function well since it is the main source of fuel for the brain and body.
What does diabetic hypoglycemia feel like?
When blood sugar levels fall below four millimoles (mmol) per liter, symptoms of diabetic hypoglycemia usually occur.
Sweating, trembling or shakiness, and feeling hungry are some of the typical early warnings. You may also feel confused and have difficulty concentrating in more severe cases.
Can you have hypoglycemia with untreated diabetes?
When the sugar levels (glucose) in your blood are too low is when a condition known as hypoglycemia occurs. This condition can occur in people who do not have diabetes despite many people thinking that it only occurs in people with diabetes.
What happens when a diabetic has a hypoglycemic episode?
When blood sugar levels are too low i.e., below 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) it may lead to a severe hypoglycemia.
Such low levels of blood sugar can lead to seizures and become life-threatening without treatment. With such low levels of blood sugar, it becomes a medical emergency.
What foods should hypoglycemics avoid?
Your blood sugar levels can fluctuate significantly if you eat the following foods and therefore, they are not suitable for people with hypoglycemia:
- White bread, pasta, and white rice
- Trans fats
- Sugar-sweetened drinks
- Fruit-flavored yogurt
- Sweetened breakfast cereals
- Honey, agave nectar, and maple syrup.
- Dried fruit.
What will happen if hypoglycemia is not treated?
Any of these severe symptom’s seizures, unconsciousness, and eventual death can be caused if hypoglycemia is left untreated. Because of this, no matter the cause, it is critical to treat low blood sugar immediately.
Can hypoglycemia lead to death?
Apart from severe hypoglycemia being fatal and accounting for up to 10% of deaths among young people with type 1 diabetes, it also causes coma, seizures, and brain damage.
How long does it take to recover from hypoglycemia?
Recovery from any acute cognitive decrement after severe hypoglycemia was completed by 1.5 days as per general suggestion results.
Does hyperglycemia cause weight gain?
Since people with hyperglycemia use food to raise their blood sugar, they may find they gain weight because they are eating more calories than they would normally.
Does stress cause hypoglycemia?
Serious changes in blood sugar levels can be caused by repeated episodes of stress and it is important to be aware.
This aids in increasing the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) since it is harder for diabetics to manage their condition.
Can hypoglycemia cause stroke?
There is both a higher risk of stroke and poor stroke outcomes in diabetic patients compared to non-diabetic subjects. In both T1D and T2D patients, frequent hypoglycemia is observed.
Hypoglycemia may increase the risk of stroke in diabetic patients according to suggestions from pre-clinical studies.
How can I fix my hypoglycemia fast?
Get fast-acting carbohydrates and eat or drink 15 to 20 grams of them. These sugary foods or drinks are easily converted to sugar in the body since they are without protein or fat.
15 minutes after treatment, recheck your blood sugar levels and then have a meal or snack.

Diabetic Feet Swollen?
Are your diabetic feet swollen?
You are at an increased risk of developing serious diabetic foot issues if you have either type 1 or 2 diabetes and high blood sugar levels.
Diabetic foot care is critical, and it is up to you to deal with your situation. Every year, up to 100,000 adults undergo diabetes-related lower limb amputations in the USA alone.
Luckily, there is a way to help you avoid developing severe diabetic foot problems. Following the proper diabetic foot care routine is an excellent way that can help you stay away from foot complications.
Additionally, the best way you can prevent foot problems is by keeping your blood sugars in range and ensuring your HbA1c is below 7%.
Further, you can considerably help reduce the risk of diabetic foot issues by wearing recommended footwear for diabetes and neuropathy, getting your early diabetic foot exams, and following a flawless diabetic foot care routine.
Why Is Diabetic Foot Care Important?
You are at a higher risk of developing severe foot issues than the general population if you have diabetes.
Two main complications are likely to arise should you not manage your diabetes properly. The two main complications are diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) which damages the nerves in your feet, and peripheral artery disease (PAD), which impedes proper blood circulation in your lower limbs.
Diabetic foot care can considerably prevent these two main complications that may lead to you having severe foot issues.
Diabetes damages the nerves in the feet

Peripheral neuropathy affects around 50% of persons that have type 2 diabetes. If you have type 2 diabetes, the nerves of your body’s extremities (feet and hands) are likely to be damaged by high blood glucose over time.
There is a variety of symptoms caused by damaged nerves ranging from mild to extremely debilitating. Further, the symptoms of diabetic neuropathy vary from one individual to the other. Some of the symptoms associated with diabetic neuropathy include:
- Cramps
- Diabetic foot pain
- Tingling
- Burning sensations
- Loss of feeling (numbness)
- Loss of balance
- Increased sensitivity to touch
If you are diagnosed with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, good foot care is essential for you. Good foot care is vital for you since it can likely help in the following:
- Slow down the progression of your nerve damage
- Reduce or get rid of the pain
- Prevent complications that may happen further such as infections, diabetic foot ulcers, and in the worst-case scenario, lower-limb amputations.
Diabetes reduces blood circulation in the feet.
You are at an increased risk for peripheral artery disease if you have diabetes. This is because a sticky plaque of fats and cholesterol builds up on the walls of your arteries.
The build-up on the walls of your arteries can slow down blow circulation drastically, and this can lead to the lack of delivery of oxygen and nutrients to your lower limbs and feet. You are at risk of increased foot infections, foot ulcers, and even foot gangrene with PAD.
Apart from preventing most complications caused by peripheral artery disease, diabetic foot care can also help boost blood circulation and decrease swollen feet.
Diabetic Foot Care Guidelines
Diabetes is harmful to your feet, and if you have it, poor diabetic foot care can result in having to amputate your toes, foot, or even your leg.
You might not notice an infection from a small cut or blister until it is too late. If you have either type 1 or 2 diabetes, you must adhere to a strict daily schedule at home to care for your feet. This is especially true if you have been identified as having peripheral artery disease or diabetic neuropathy.
Diabetes foot care guidelines that can help you prevent the most serious complications
1. Keep your HbA1c below 7%
Your blood sugar level has the utmost impact on the health of your feet. When you have diabetes, and it is not managed properly, and your blood glucose levels are not controlled, you are likely to have diabetes-related foot complications.
Therefore, if you want to stay away from foot problems, the first rule is to ensure that your HbA1c is kept below 7% and your blood sugars are in the range.
Following a healthy lifestyle, taking your medications, balancing your meals, exercising daily, and asking your doctor for advice regularly is the best way to keep your HbA1c below 7% and your blood sugars in range.
2. Get a diabetic foot exam once a year.
Medicare will pay for yearly foot tests for diabetic peripheral neuropathy patients. A podiatrist, your general practitioner, or another healthcare professional will perform a series of painless and risk-free medical tests.
Diabetes foot exams can identify issues that you might not be able to notice on your own.
It is advisable that you see your doctor immediately if you notice or feel any of the following apart from your yearly diabetic foot exam:
- If you have pain in your feet or legs
- Prickling sensations, burning or tingling
- Numbness or loss of sensation
- Should you notice any deformities on your toes or feet
- Loss of hair
- Cracks on your skin
- Any changes in your skin color
- When your toenails turn yellow
- Fungus infections
- Ingrown toenails, ulcers, sores, or blisters
You can considerably reduce the risk of foot problems and their aggravation through early diagnosis and prevention.
3. Inspect your feet daily
Diabetic neuropathy can lead to cuts and wounds staying unnoticed because of possible decreased sensation (numbness) in your feet.
Therefore, it is advisable that you inspect and check each side of your feet and toes on a daily basis. When inspecting your feet, you should check if your feet have redness, blisters, cuts, swelling, nail issues, bruises, calluses, and many more.
While inspecting your feet, it is also essential to check in between your toes and under your feet. You can use a mirror if you are physically unable to do so.
Additionally, if you have diabetes, you should never try to treat a foot problem by yourself. You should consult your doctor for advice if you notice anything unusual.
4. Gently wash and dry your feet.
If you want to avoid diabetes-related foot problems, then foot hygiene is a must. It would be best if you washed your feet daily in lukewarm water.
Using cold or too hot water is not advisable since it could do damage to your skin. While washing your feet, you should use a gentle foot wash or a mild soap. To dry your feet and between your toes, you should gently pat or blot your feet.
5. Wear shoes for diabetes & neuropathy
You can help prevent and alleviate the most common diabetic foot problems by donning diabetic shoes.
Diabetic shoes are different from regular shoes since they are medically and professionally designed for this purpose. These shoes are equipped with unique features that prevent and alleviate problems related to common diabetic feet.
The features include the protective inner linings that help in preventing your foot from blistering and irritating. Additionally, for improved foot stability and overall balance, diabetic shoes have enhanced foot support and extra-cushioning.
The shoes have a non-binding design which aids in the promotion of blood circulation to your foot. When it comes to neuropathy shoes, they are even more protective than diabetic shoes despite having almost similar features. Depending on your needs, you should consider having at least a pair.
Moreover, the pair of shoe fitting is essential. You should ensure that the diabetic shoes or neuropathy shoes are not too loose or too tight.
You can confirm this by inspecting the shoes before inserting them into your feet. Last, you should also ensure that there are no pebbles or foreign objects in the shoes that could harm your feet before wearing them. Too tight shoes with foreign objects or pebbles may lead to your diabetic feet getting swollen.
6. Consider socks for people with diabetes.
Socks are also essential in playing a role in diabetes foot care. You should change your socks on a daily basis if your feet sweat a lot to ensure your feet stay dry.
Additionally, the socks you wear should also be dry. If you have cold feet, especially at night when sleeping, it is recommended to wear socks to keep your feet warm. The socks also should not be too tight to compress your feet.
Diabetic socks have unique features. Some of the impressive features of diabetic socks include their soft elastic or no elastic at all. This will help in allowing blood flow to your feet by not constricting your leg and blocking blood flow.
These socks also will ensure that your feet stay in a dry, healthy environment thanks to the anti-bacterial fabrics used in making them.
The breathability of the socks will allow optimal airflow to your feet, while the moisture-wicking features in the socks will help in getting rid of any sweat and moisture hence leaving your diabetes feet dry and comfortable.
Furthermore, diabetic socks are designed to prevent blistering and irritations on your feet since they have extra padding for extra comfort and seamless construction.
7. Moisturize your feet
Your skin can be affected by dehydration caused by high blood sugars. The effects of dry skin include skin peeling, crackdown, or itch, which may cause further issues to your diabetic feet, such as foot ulcers and infections.
You should apply moisturizing lotion after washing your diabetic swollen feet every time after washing if you have dry skin on your feet. However, you should not apply moisturizing lotion between your toes since it may cause a fungal infection.
Further, there are moisturizers and foot care products of poor quality, and using them can be harmful to your diabetic feet.
Diabetic skins are fragile, and using poor quality products and moisturizers that contain chemicals can be too aggressive for your skin despite also not being efficient.
Therefore, it is advisable that you go for diabetic creams and lotions that have been carefully formulated. Only if you have dry skin should you use a moisturizer. If not, and your skin does not feel rough, you should wash and dry your feet each time after washing.
8. Keep your feet dry
Despite your feet needing to stay dry if you have diabetes foot issues, the skin of the feet should always stay moist. Dry feet are necessary with diabetic swollen feet since moist areas aid the development of fungal and bacterial infections. After being under the rain or snow, you should not let your feet stay wet for too long. If necessary, you should wear or use waterproof shoes.
You should choose appropriate socks and shoes with moisture-wicking and anti-bacterial fabrics if you tend to have swollen diabetic feet. It would be best if you changed your socks any time, they were wet.
9. Keep your feet warm.
People with diabetes tend to have cold feet because of poorer blood circulation. Generally, skin irritation, dryness, and foot problems are likely to increase due to cold.
Therefore, if you have diabetes feet, you should ensure that your feet are kept warm. However, they should not be too warm since too much warmth causes sweat.
It would be best if you chose socks with quality materials such as Merino wool, Alpaca fibre, or thick bamboo fibers during the winter and cold seasons to keep your feet warm. If needed, wear socks at night to keep your feet warm.
10. Trim your toenails properly
You may have foot issues such as ingrown toenails that can easily get infected if you trim your toenails badly. Additionally, at least once every week, you should inspect and clip your toenails.
- After taking a bath or shower, when your toenails are softer and more flexible, trim them.
- Make a straight cut across with a nail clipper. Avoid trimming the sides or rounding the corners.
- Avoid having your toenails cut too short. Leave around one millimeter of white showing at the tip of your nail.
- Never pull the cuticles back. They aid in preventing the entry of bacteria and infection into your nail matrix.
- To avoid jugged edges after clipping, smooth your nails with a nail file.
Can diabetics soak their feet?
You can help calm down neuropathy symptoms by soaking your feet in a basin filled with warm water or in a foot spa.
An excellent way to incorporate natural pain-relieving and soothing ingredients such as Epson salts, essential oils for neuropathy, medicinal herbs, or cannabidiol (CBD) products are to soak your feet in a basin of warm water or foot spa.
In conclusion, foot soaking is great, and it can help persons living with diabetic neuropathy foot pain. However, foot soaking is not a treatment for diabetic neuropathy.
Soaking your feet cannot repair damaged nerves but can relieve diabetic nerve pain. Any way to reverse diabetic peripheral neuropathy has not been found or proven scientifically up to date.
Therefore, soaking your feet in Epsom salts or apple cider vinegar has a well-appreciated pain-relieving effect you would be fond of, but it would not reverse neuropathy.
Foot soaks can help relieve nerve pain.
You can reduce nerve pain in your diabetic nerve pain feet by soaking them in warm water.
Additionally, while soaking and bathing your diabetes feet, you can take the opportunity to try some other home solutions for neuropathy.
You can do this by adding Epsom salts, medicinal herbs, or essential oils. You can be provided instant relief for neuropathic pain through warm water baths and foot soaks.
Warm water baths and foot soaks have proven to do the following:
- Relieve pain
- Reduce stress
- Relax muscles
- Increase blood circulation
Foot soak is no danger for persons with diabetes or neuropathy if used reasonably and wisely. However, you should be aware that your feet are fragile and prone to multiple conditions once your feet are affected by neuropathy and diabetes.
Therefore, to avoid injury, you should:
- The damaged nerves in your feet are not reliable enough for judging water temperature, and you could burn your skin without even noticing it. Therefore, you should always check the water temperature with a thermometer.
- Dry your feet but gently soak, particularly in the space between your toes. This is because you can easily get wounded and infected if you have wet skin blisters.
- Limit your soak time. More than 30 minutes of foot soaking time, three to four times per week, can weaken your skin’s barrier of defense.
- Take care when adding items to your foot bath. Some online foot soak recipes for neuropathy are too forceful and could harm you. It is advisable that you consult your doctor for advice first.

Common Diabetic Skin Conditions
When a person has diabetes, it throws their whole body off balance. They not only have to worry about the natural things that come with everyday life like eating healthy, getting enough sleep and exercising, but they also have to be mindful of all the complications that arise from their disorder. Diabetic skin problems is one of the most common concerns diabetics face. 30% of diabetics will develop skin conditions related to their diabetes.
Some of the most common skin conditions diabetics face are dry skin, and also itchy, red, and scaly legs. For the ones with type 2 diabetes, they are more vulnerable to developing a skin condition. Here is a close look on the common diabetic skin conditions.
Diabetic Dermopathy
This is a common skin condition that occurs in people with diabetes. It is characterized by reddish or light brownish spots on the legs. In most cases, it is found on top of the feet, thighs and shins. There have been reports that diabetic dermopathy can lead to permanent skin discoloration if left untreated.
Cause of Dermopathy
Dermopathy is the damage caused on the skin that leads to the formation of these brownish spots. This can be caused from dryness and itching due to poor circulation and itching. The disease is more common in older people and those with type 2 diabetes.
Mostly, after trauma or injury, these spots will take up to 2 weeks to form. Dermopathy is considered as a complication of diabetes and the lack of blood in the area where the skin damage occurs is responsible for this condition.
Dermopathy Signs and Symptoms
When the skin is in contact with water, it will form a dark ring around the damaged area. This dark ring is commonly seen when you are taking a bath or shower. Dermopathy will appear on the legs in areas like ankles, knees and thighs. The spots will turn brown and scaly as they enlarge.
Dermopathy Treatment
Dermopathy is not a serious skin condition. However, it is important to address the problem early to avoid further complications. People with diabetes should take good care of their skin by practicing good hygiene and using moisturizers to prevent further damage.
Diabetic Bullae
Also known as diabetic blisters, this skin condition develops when a person’s skin is exposed to too much moisture. It is usually found in the neck and armpits.
Cause of Bullae
In diabetes, the blood vessel in the skin becomes fragile, thus leading to increased blood flow and heat. When this happens, the blood vessels within the skin experience damage. In response to this damage, the skin will raise a blister on its surface.
Bullae Signs and Symptoms
The first sign of this condition is a reddish spot on the skin. The spot will expand and it will turn up to become red, painful, and itchy. The blisters should be popped and treated to prevent infection.
Bullae Treatment
To prevent infection of the affected area, it is best to wash the affected skin with antibacterial soap at least twice each day. The blisters should be popped as soon as they appear.
Diabetic Stiff Skin Syndrome
Also known as diabetic dry skin, this skin condition develops when a person’s skin cannot return back to its normal state after being stretched. It is usually found on joints like the fingers and toes.
Cause of Stiff Skin Syndrome
The stiffness of the skin is caused by the lack of collagen in your blood vessels. In diabetes, the amount of collagen produced by your body is less than normal. When this happens, the skin cannot return back to its normal state after being stretched.
Signs and Symptoms of Stiff Skin Syndrome
When this condition develops, the skin of a person will be rough and hard. The person will feel pain when stretching the affected area. In some cases, it can lead to the development of ulcers on the area.
Stiff Skin Syndrome Treatment
Stiff skin syndrome can be treated by restoring the blood supply to the affected area. This can be achieved by wearing cotton gloves when you are doing your daily activities. Also, it is important to keep the skin hydrated and moist to help in flushing out the excess waste your body produces.
Other Common Skin Conditions
Here are some of the other common skin conditions diabetics face:
1. Scleroedema – Scleroedema is a skin condition that occurs from the development of edema in the body. Mostly around the neck and upper back.
2. Scabies or pubic lice – This condition is caused when the body’s immune system is unable to attack and destroy the parasites.
3. Acanthosis nigricans – Most of the cases of this skin condition are seen on the back, chest and neck. It is characterized by dilated blood vessels that are dark and velvety-looking.
4. Vitiligo – This condition is characterized by white pigmentation loss of skin. It is caused by a lack of pigment in the hair and skin.
5. Corneal ulcer – This skin irritation occurs when the natural substances that protect the eye from infection is depleted or damaged.
How to Manage Diabetic Skin Conditions
To help manage your diabetic skin conditions, it is best to practice the following:
i. Maintain a healthy diet
Your diet plays an important role in your health. Eating the right kind of food will not only help prevent diabetes but it will also help you manage its complications. The foods you eat should be filling and provide sufficient nutrients to your body. Make sure that your diet is not lacking in fiber as it can help to purge toxins from your skin. Also, eat healthy fats like Omega-3 fatty acids and Omega-6 fatty acids.
ii. Manage your stress level
Managing your stress is one of the best ways to help combat diabetes. It is a stressful condition that can trigger or aggravate the skin conditions you have. One way you can manage your stress level is by exercising regularly. Exercise is an effective way to manage stress because it helps you to destress and relieve your body of excess toxins.
iii. Take care when showering or bathing
Avoid taking too hot of a bath or shower. The water will increase your skin’s temperature and it may cause the blood vessels to dilate and expand. Taking a hot shower can also dry out the skin causing it to become dry and brittle.
iv. Use moisturizers
Moisturizers help keep your skin moist, soft and supple. Apply moisturizer on your skin as soon as you get out of the bath or shower. This will help to prevent your skin from getting irritated and cracked.
Diabetes takes a toll on the body. It cannot only make you sick but it can also make you look old and unattractive. The condition can cause a variety of skin problems like the ones we discussed above. The good news is, managing your diabetes will also help you manage your skin. Follow the above guidelines and you will surely feel better about yourself.