Diabetes Information

The Connection Between Carbs and High Blood Sugar
Carbs and High Blood Sugar
High blood sugar can be a serious problem, and not just for those with diabetes. Eating too much of the wrong type of carbs can affect your blood sugar levels, whether you’re diabetic or not. Learn how the two are connected, and how you can make simple dietary and lifestyle changes to help keep your blood sugar in check.
High Blood Sugar and the Connection to Carbohydrates
Understanding the link between carbohydrates and high blood sugar is crucial for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
Here, we will delve into the brief explanation of high blood sugar and its effects, emphasizing the importance of comprehending the connection between carbs and elevated blood sugar levels.
High Blood Sugar: A Brief Explanation:
When we consume food, especially those rich in carbohydrates, our bodies break down these complex sugars into glucose, the primary source of energy for our cells. As glucose enters the bloodstream, our pancreas releases the hormone insulin, which enables glucose to enter the cells and provide them with energy.
However, in individuals with diabetes, a disruption occurs in this balance, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Effects of High Blood Sugar
- Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels can cause excessive thirst, leading individuals to consume more fluids and subsequently urinate more frequently. This occurrence is due to the kidneys working harder to eliminate the excess glucose from the body through urine.
- Fatigue and Lack of Energy: When cells are unable to efficiently absorb glucose due to insufficient insulin or insulin resistance, the body is deprived of its main energy source. Consequently, this can lead to constant fatigue, decreased productivity, and an overall lack of energy.
- Blurred Vision and Slow Healing: Prolonged periods of elevated blood sugar levels can affect various parts of the body, including the eyes. Blurred vision may occur due to the swelling of the lens caused by changes in fluid balance. Additionally, high blood sugar impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds, increasing the risk of infections and delaying the healing process.
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease: Persistently high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and lead to the development of cardiovascular conditions. Over time, the excess glucose in the bloodstream can cause inflammation and atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart-related complications.
Understanding the Connection: Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar:
- Carbohydrates: The Primary Culprit
Carbohydrates play a significant role in raising blood sugar levels as they are broken down into glucose during digestion. It is essential to distinguish between different types of carbohydrates, such as simple carbohydrates found in sugary foods and refined grains, and complex carbohydrates present in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables.
- Counting Carbohydrates for Blood Sugar Control
Carbohydrate counting is a valuable strategy for individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. By monitoring and balancing their carbohydrate intake throughout the day, individuals can optimize their insulin dosage and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Understanding Carbohydrates
Here, we will delve into the fascinating world of carbohydrates – the essential nutrients that fuel our bodies and provide us with the energy we need to go about our day. We will explore the definition and types of carbohydrates, understand their role as a primary source of energy, and uncover the impact they have on our blood sugar levels. So, let’s begin our journey of understanding carbohydrates!
Definition and Types of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients, alongside proteins and fats, that are vital for maintaining a healthy and balanced diet. They are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and they can be classified into two main types: simple and complex carbohydrates.
Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, consist of one or two sugar molecules and are easier for the body to break down and absorb. They are commonly found in fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and refined sugars. Examples of simple carbohydrates include glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
On the other hand, complex carbohydrates are made up of longer chains of sugar molecules, making them more complex for the body to digest. They are found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables like potatoes. Complex carbohydrates provide a slower and more sustained release of energy compared to simple carbohydrates.
Role of Carbohydrates as a Primary Source of Energy
Carbohydrates play a vital role as the primary source of energy for our bodies. When we consume carbohydrates, our digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which is then transported through the bloodstream to cells throughout the body. Our body’s cells use glucose as fuel to perform various functions, including physical activity, brain function, and everyday tasks.
Additionally, carbohydrates provide quick energy. Simple carbohydrates, due to their shorter chains of sugar molecules, are rapidly absorbed by the body, leading to a quick burst of energy. This is particularly beneficial during intense physical activities or when immediate energy is needed.
Impact of Carbohydrates on Blood Sugar Levels
One crucial aspect of understanding carbohydrates is their impact on blood sugar levels. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which enters our bloodstream. As a result, the level of glucose in our blood rises.
For individuals with diabetes or those concerned about blood sugar management, monitoring carbohydrate intake becomes essential. Simple carbohydrates, due to their ease of digestion, can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, provide a slower and steadier release of glucose, promoting more stable blood sugar levels.
It is essential to strike a balance when consuming carbohydrates, especially for individuals with diabetes, to ensure proper blood sugar control. Understanding the types and effects of carbohydrates can aid in making informed dietary choices and managing overall health.
How Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbohydrates are a crucial source of energy for our bodies. They are found in various foods like grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. When carbohydrates are consumed, they undergo a digestion process in our bodies, ultimately affecting our blood sugar levels. Understanding how carbohydrates impact blood sugar is vital for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
- Digestion Process of Carbohydrates in the Body
The digestion of carbohydrates begins in our mouths, where enzymes break down complex carbohydrates into smaller molecules. As we chew and swallow, these carbohydrates pass through our digestive system and into our stomachs. Here, the stomach acid further breaks them down.
Next, the carbohydrates enter the small intestine, where they are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and galactose. These sugars are then absorbed into the bloodstream, causing a rise in blood sugar levels.
- Conversion of Carbohydrates to Glucose
Glucose, the primary sugar molecule derived from carbohydrates, plays a vital role in keeping our bodies functioning optimally. Once carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, it is transported via the bloodstream to our cells, providing them with the energy they need.
However, it is crucial to note that not all carbohydrates are equal. Different types of carbohydrates, such as complex and simple carbohydrates, affect our blood sugar levels differently.
Simple carbohydrates, found in foods like soda, candy, and sugary sweets, are rapidly converted into glucose, causing a sharp increase in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, are digested more slowly, leading to a gradual and steady release of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Release of Insulin to Regulate Blood Sugar Levels
To maintain stable blood sugar levels, our bodies rely on insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. When blood sugar levels rise after consuming carbohydrates, the pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream.
Insulin acts as a key that unlocks the cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy. It signals to the cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream, consequently lowering blood sugar levels. This intricate process helps prevent blood sugar levels from reaching dangerously high levels.
However, in individuals with diabetes, the production or effectiveness of insulin is impaired. This can result in high blood sugar levels because the cells are unable to effectively utilize glucose.
Consequently, people with diabetes need to manage their carbohydrate intake, medication, and lifestyle choices to regulate their blood sugar levels effectively.
The Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a measurement that ranks carbohydrates based on their effect on blood sugar levels. It provides valuable insights into how different foods can affect our bodies and is a valuable tool for managing blood sugar levels and overall health.
- Definition and Significance of the Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index is a numerical scale that measures how quickly and how much a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels compared to pure glucose, which has a GI value of 100. The GI scale ranges from to 100, with higher values indicating a faster and larger rise in blood sugar levels. This index is particularly relevant for individuals with diabetes, as it helps them make informed food choices that can aid in managing their condition.
The significance of the glycemic index lies in understanding how different carbohydrates affect our bodies. Foods with a high GI value are rapidly digested and absorbed, causing a sharp increase in blood sugar levels.
On the other hand, low-GI foods are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual and more sustained rise in blood sugar levels. By incorporating low-GI foods into our diets, we can promote stable blood sugar levels, increase satiety, and potentially reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
- Explanation of Low-GI and High-GI Foods
Low-GI foods are those that have a GI value of 55 or less. These foods are usually rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, which slow down digestion and absorption, leading to a gentle and steady increase in blood sugar levels.
Examples of low-GI foods include whole grains like quinoa and oatmeal, legumes such as lentils and chickpeas, most fruits and vegetables, and nuts and seeds. Incorporating these foods into our meals can provide sustained energy, promote weight management, and support overall well-being.
On the other hand, high-GI foods are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. These foods have a GI value of 70 or higher and are often low in fiber and nutrients. Examples of high-GI foods include sugary snacks and beverages, white bread and rice, potatoes, and processed breakfast cereals.
Consuming too many high-GI foods can result in blood sugar fluctuations, increased hunger, and a higher risk of chronic diseases. However, it’s important to note that not all high-GI foods are unhealthy, as some nutritious fruits and vegetables can have a high GI value due to their natural sugars.
- Influence of GI on Blood Sugar Levels
The glycemic index plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. When we consume high-GI foods, our blood sugar levels rise rapidly, triggering the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin helps transport glucose from the blood into the cells for energy or storage. However, this sudden surge in blood sugar followed by a rapid drop can leave us feeling tired, hungry, and craving more high-GI foods.
In contrast, low-GI foods promote a slower and more steady increase in blood sugar levels, resulting in a gradual release of insulin. This helps maintain stable energy levels, keeps us feeling fuller for longer, and reduces the likelihood of overeating or experiencing intense sugar cravings. For individuals with diabetes, understanding the GI of various foods can assist in managing insulin levels and achieving better glycemic control.
The Impact of Carbohydrate Consumption on High Blood Sugar
Now, it is time to explore how excessive carbohydrate intake can lead to blood sugar spikes, the effects of refined and processed carbohydrates on blood sugar, and the crucial role of portion control in managing blood sugar levels.
Excessive Carbohydrate Intake and Blood Sugar Spikes
- Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar: Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is a primary source of energy for our bodies. When we consume excessive amounts of carbohydrates, our blood sugar levels can soar, leading to a condition known as hyperglycemia.
- Glycemic Index: Different carbohydrates have varying effects on blood sugar levels. High glycemic index foods, such as white bread and sugary drinks, cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, while low glycemic index foods, like whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, result in a slower rise in blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Resistance: Chronically high blood sugar levels due to excessive carbohydrate consumption can contribute to insulin resistance. This condition makes it difficult for the body to properly regulate blood sugar, leading to a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Effects of Refined and Processed Carbohydrates on Blood Sugar
- Definition of Refined and Processed Carbohydrates: Refined and processed carbohydrates refer to foods that have been stripped of their natural fiber and nutrients during processing. These include white bread, pasta, sugary cereals, and processed snacks.
- Rapid Blood Sugar Spikes: Refined and processed carbohydrates are quickly broken down into glucose, causing a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This sudden surge is followed by a sharp drop, leaving individuals feeling fatigued and hungry, which can lead to overeating.
- Lack of Satiety: Foods high in refined carbohydrates often lack fiber and protein, which are essential for feeling full and satisfied. As a result, individuals may consume larger portions, leading to continued blood sugar spikes and weight gain.
Role of Portion Control in Managing Blood Sugar Levels
- Understanding Portion Sizes: Portion control involves being mindful of the quantity of food we consume. It is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. It allows for a more balanced and controlled intake of carbohydrates, preventing blood sugar spikes.
- Balancing Macronutrients: By managing portion sizes, we can ensure that our meals consist of a proper balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This helps slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to more stable blood sugar levels.
- The Plate Method: A useful tool for portion control is the plate method. This involves dividing your plate into sections for specific food groups, such as dedicating half the plate to non-starchy vegetables, a quarter to lean protein, and a quarter to whole grains or starchy vegetables.
Managing High Blood Sugar through Carbohydrate Choices
High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, is a common concern for individuals living with diabetes or anyone seeking to maintain optimal blood sugar levels. One effective way to manage this condition is by making mindful carbohydrate choices. In this chapter, we will explore the importance of selecting complex carbohydrates over simple ones, incorporating fiber-rich foods, and finding the right balance with proteins and fats to minimize blood sugar spikes.
- Opting for Complex Carbohydrates over Simple Carbohydrates
When it comes to managing blood sugar levels, the type of carbohydrates we consume plays a crucial role. Complex carbohydrates are a healthier choice compared to simple carbohydrates, as they are digested and absorbed more slowly by the body. This slow breakdown reduces the sudden increase in blood glucose levels.
The list of complex carbohydrates includes nutrient-rich whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread. Unlike refined grains, which have been stripped of most of their nutritional value, whole grains offer essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. By replacing white bread, white rice, and processed cereals with their whole grain counterparts, you can provide your body with a steady release of energy and better blood sugar regulation.
- Incorporating Fiber-Rich Foods to Slow Down Carbohydrate Digestion
Another effective way to manage high blood sugar is by incorporating fiber-rich foods into your daily diet. Dietary fiber is the indigestible part of plant-based foods that adds bulk to your meals, promoting feelings of fullness and aiding in digestion. More importantly, fiber helps slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Fruits and vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are excellent sources of dietary fiber. By including a variety of these foods in your meals, you not only enhance nutritional intake but also contribute to better blood sugar control. Aim for at least 25 to 30 grams of fiber per day, gradually increasing your intake to allow your body to adapt.
- Balancing Carbohydrate Intake with Proteins and Fats to Minimize Blood Sugar Spikes
While the focus of blood sugar management lies in carbohydrate choices, it’s crucial to strike a balance between carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Combining these macronutrients can help slow down digestion and minimize blood sugar spikes after meals.
Adding lean protein sources like poultry, fish, tofu, or beans to your meals helps regulate blood sugar levels. Protein takes longer to digest, preventing the rapid release of glucose into the bloodstream. Additionally, incorporating healthy fats from sources such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil can further slowdown digestion, providing a more sustained release of glucose.
By creating balanced meals that include a healthy mix of complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, you can effectively manage your blood sugar levels and maintain greater control over your health.
Monitoring Carbohydrate Intake for Better Blood Sugar Management
Here, we will discuss the importance of carbohydrate counting or tracking, the utilization of technology and tools to aid in carbohydrate monitoring, and the significance of consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance. By understanding these aspects, you can take control of your blood sugar levels and promote better overall health.
Importance of Carbohydrate Counting or Tracking
Carbohydrates are the main macronutrient that significantly affects blood sugar levels. Monitoring carbohydrate intake allows individuals to have better control over their blood sugar levels. Here’s why carbohydrate counting or tracking is crucial:
- Blood Sugar Management: By knowing the amount of carbohydrates consumed in each meal and snack, individuals can adjust their insulin doses or medications accordingly, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Individualized Approach: Different individuals may have different sensitivities to carbohydrates. Monitoring carbohydrate intake enables individuals to personalize their diet plans based on their unique needs, optimizing blood sugar management.
- Balanced Nutrition: Carbohydrate counting promotes a well-rounded and balanced diet. This approach emphasizes portion control and awareness of overall nutrient intake, ensuring that other essential nutrients, such as proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, are adequately included in meals.
Utilizing Technology and Tools to Aid in Carbohydrate Monitoring
With advancements in technology, various tools and applications have been developed to assist in carbohydrate monitoring. These technological aids offer convenience, accuracy, and real-time data, making blood sugar management easier for individuals. Here are some key tools and technologies:
- Carbohydrate Counting Apps: These smartphone applications allow users to track their carbohydrate intake by simply entering the food they consume. These apps often provide a database of foods and their corresponding carbohydrate content, simplifying the process of tracking and monitoring carbohydrate intake.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: CGM systems provide real-time blood sugar readings, helping individuals understand the impact of their carbohydrate intake on their blood sugar levels. By monitoring trends and patterns, individuals can make informed decisions about their food choices and insulin dosing.
- Insulin Pumps: Insulin pumps deliver a constant flow of insulin throughout the day, with the ability to customize insulin boluses based on carbohydrate intake. Some newer models even have built-in carbohydrate databases, allowing users to calculate and administer insulin doses more accurately.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional for Personalized Guidance
While technology and tools can greatly assist in carbohydrate monitoring, it is vital to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance. These professionals, including doctors, dietitians, and diabetes educators, can provide tailored advice and support based on an individual’s specific needs. Here’s why consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial:
- Individualized Recommendations: Healthcare professionals consider various factors such as age, weight, physical activity level, and overall health status to provide personalized recommendations regarding carbohydrate intake. This ensures that individuals receive the most appropriate guidance for their specific circumstances.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adjustments: Healthcare professionals can help individuals set goals and regularly monitor their progress. They can make adjustments to the carbohydrate intake plan as needed, considering changes in health or lifestyle that may impact blood sugar management.
- Education and Support: Diabetes management encompasses more than just monitoring carbohydrate intake. Healthcare professionals offer essential education on food choices, portion sizes, reading nutrition labels, and other aspects crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. They also provide the necessary support, answering questions and addressing concerns individuals may have along their diabetes journey.
Conclusion
High blood sugar is a problem that can have serious health implications. Eating too many of the wrong kinds of carbs can make it harder to manage your blood sugar, so it’s important to be aware of the connection between carbs and high blood sugar. Making small changes like eating more whole grains, eating smaller portions, reducing sugar intake and getting active can help you stay healthy and keep your blood sugar levels in check.
FAQs about the Connection Between Carbs and High Blood Sugar
Can all carbohydrates cause high blood sugar?
- While all carbohydrates can affect blood sugar levels, some have a greater impact than others. Refined carbs, processed foods, and sugary beverages tend to cause a more rapid and significant increase in blood sugar compared to whole foods that contain natural sugars and fiber.
Is it necessary to avoid carbohydrates completely to maintain normal blood sugar levels?
- It is not necessary to eliminate carbohydrates entirely from your diet. However, individuals with high blood sugar or diabetes should be mindful of their carbohydrate intake and make healthier choices by opting for complex carbs, fiber-rich foods, and controlling portion sizes.
Can low-carb diets help manage high blood sugar?
- Low-carb diets, such as the ketogenic or Atkins diet, have shown positive effects in managing high blood sugar. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the body relies on alternative fuel sources, such as fats, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
What are some healthier carbohydrate options to help control blood sugar?
- Opt for whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread instead of refined grains. Include plenty of non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and cauliflower. Additionally, legumes like lentils and chickpeas are excellent sources of complex carbs and fiber.
Are there any specific carbs that can help stabilize blood sugar levels?
- Foods rich in fiber, such as oats, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, can help slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, resulting in a slower and more controlled release of glucose into the bloodstream. Incorporate these foods within a balanced diet to promote stable blood sugar levels.
Should I monitor my carbohydrate intake if I have prediabetes or diabetes?
- If you have prediabetes or diabetes, monitoring carbohydrate intake is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. It is recommended to work with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to determine a suitable carbohydrate intake based on individual needs and medication.
Can lifestyle factors besides carbohydrates impact high blood sugar levels?
- Yes, lifestyle factors like physical activity, stress levels, and the overall balance of your diet can have an impact on blood sugar levels. Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and a well-rounded diet can contribute to better blood sugar control alongside carbohydrate management.

Erythritol, a Common Sweetener, Linked to Potential Heart Attacks
Introduction
This article explores the latest study on erythritol, a low-calorie sweetener, and its potential benefits and drawbacks for cardiovascular health.
Unlike other sugar alcohols, such as sorbitol and xylitol, erythritol doesn’t cause digestive issues in most people because it is absorbed into the bloodstream before reaching the large intestine.
This property, along with its low calorie count, has made erythritol a popular alternative to sugar, especially among people with diabetes or those who are trying to lose weight.
However, there have been concerns about its effects on the heart. Some studies have suggested that erythritol may increase the risk of heart attacks.
In this article, we will explore the link between erythritol and heart attacks and determine whether this is a cause for concern.
How is Erythritol Produced?
Erythritol is produced by fermenting glucose with a yeast called Moniliella pollinis. The yeast converts the glucose into erythritol through a process called reduction, which removes oxygen from the glucose molecule.
It is also worth noting that some manufacturers may use a process called hydrogenation to produce erythritol, which can result in the production of small amounts of trans fats. Consumers should always check the ingredients of erythritol products to ensure that they are not consuming trans fats.
B. Explanation of the link between Erythritol and heart attack
Common Uses of Erythritol
Some products that commonly contain erythritol include:
- Sugar-Free Gum – Erythritol is commonly used in sugar-free gum as a sweetener that doesn’t negatively impact dental health.
- Baked Goods – Erythritol can be used in baked goods as a sugar substitute without affecting texture or taste.
- Desserts – Erythritol can be used in a wide range of desserts such as ice creams and puddings as a low-calorie alternative to sugar.
Erythritol has gained popularity as a low-calorie sweetener due to its ability to provide sweetness without adding calories or negatively affecting dental health or blood sugar levels. It has 70% of the sweetness of sugar but only 6% of the calories.
Erythritol and Heart Attacks: What’s the Link?
There have been concerns that erythritol may increase the risk of heart attacks. One study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that rats fed high doses of erythritol had an increased risk of heart attacks.
The researchers suggested that erythritol may increase levels of a harmful molecule called fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP). FBP can cause inflammation and damage to the blood vessels, which can increase the risk of heart attacks.
Another study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food found that erythritol may have negative effects on cholesterol levels. The study found that rats fed a high-fat diet supplemented with erythritol had higher levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and lower levels of HDL (good) cholesterol compared to the control group.
However, it is important to note that these studies were conducted on rats and not humans. Further research is needed to determine the effects of erythritol on the human heart.
Is Erythritol Safe?
The FDA has deemed erythritol to be safe for consumption. It has been given the status of Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS), which means that it is a safe food additive that does not require pre-market approval from the FDA.
Numerous studies conducted on humans have found that erythritol is safe for consumption. It does not have any known side effects, and it is not metabolized by the body in the same way as sugar, which means that it does not raise blood sugar levels.
How to Use Erythritol Safely and Effectively
If you choose to use erythritol as a sugar substitute, it’s essential to do so responsibly. Here are some tips to help you use erythritol safely and effectively:
- Start slowly: If you’ve never consumed erythritol before, start with small amounts and gradually increase to see how your body reacts.
- Choose high-quality products: Look for erythritol products that are free of additives and other unhealthy ingredients.
- Consider your overall diet: While erythritol may be a healthier alternative to sugar, it’s still important to maintain a balanced diet that includes plenty of whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Consult your healthcare provider: If you have any health concerns or take medications that may interact with erythritol, talk to your healthcare provider before using it as a sugar substitute.
Alternatives to Erythritol
Luckily, there are a variety of alternatives to erythritol that can be used in its place.
1. Stevia
- Stevia is a natural sweetener that comes from the leaves of the stevia plant. It is calorie-free and does not raise blood sugar levels, making it a great alternative to erythritol for people with diabetes or those looking to cut calories. Stevia can be used in a variety of ways, including in baking and as a sweetener for drinks.
2. Xylitol
- Xylitol is a sugar alcohol that is commonly used as a sweetener. It is similar in taste and texture to sugar, but has fewer calories and is less likely to cause digestive issues. Xylitol is also believed to have dental benefits, as it can help prevent tooth decay. However, it is important to note that xylitol can be toxic to dogs, so it should be kept away from pets.
3. Allulose
- Allulose is a relatively new low-calorie sweetener that is gaining popularity. It is similar in taste and texture to sugar, but has significantly fewer calories and does not raise blood sugar levels. Allulose can be used in baking and cooking, but its low melting point makes it unsuitable for some applications.
4. Monk Fruit
- Monk fruit is a natural sweetener that comes from the monk fruit plant. It is calorie-free and does not raise blood sugar levels, making it a great alternative to erythritol for people with diabetes or those looking to cut calories. Monk fruit extract is commonly used in packaged foods and drinks, but it can also be bought as a sweetener for home use.
Tips for Reducing Intake of Erythritol
1. Read Labels Carefully
One of the easiest ways to reduce your intake of erythritol is to carefully read the labels of the foods and drinks you consume. Many products contain erythritol, even those that are not marketed as low-sugar or low-calorie options. By reading the ingredient list, you can identify which products to avoid or limit.
2. Cook from Scratch
Another way to reduce the amount of erythritol you consume is to cook from scratch. Many pre-packaged foods and snacks contain erythritol, but when you cook your own meals, you have control over the ingredients you use. You can choose to use natural sweeteners, like honey or maple syrup, instead of erythritol.
3. Choose Foods Low in Erythritol
When shopping for food, choose products that contain little to no erythritol. Opt for fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains. These foods are naturally low in erythritol and can provide the essential vitamins and minerals that your body needs.
4. Limit Intake of Sugar-Free Products
Sugar-free products are a great alternative for those looking to reduce their sugar intake, but they often contain erythritol as a substitute. To reduce your intake of erythritol, try limiting your consumption of sugar-free products or finding alternatives that do not contain the sugar substitute.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s clear that the link between erythritol and heart attacks requires more research to fully understand its impact. However, by using erythritol safely and effectively, as well as exploring alternatives and reducing intake when necessary, we can still enjoy the benefits of this sugar substitute without any negative health consequences. So let’s continue to educate ourselves on this topic and make informed decisions to keep our hearts healthy and happy!
FAQ
Does erythritol raise blood sugar levels?
- No, erythritol does not raise blood sugar levels. Unlike sugar, erythritol is a sugar alcohol that is not metabolized by the body and does not affect insulin levels.
Can erythritol cause digestive issues?
- Erythritol can cause digestive issues in some people, especially when consumed in large amounts. However, studies have shown that erythritol is generally well-tolerated and less likely to cause digestive issues than other sugar alcohols.
Does erythritol have any calories?
- Erythritol has very few calories, with only 0.2 calories per gram compared to sugar’s 4 calories per gram.
Can erythritol be used in baking?
- Yes, erythritol can be used in baking as a substitute for sugar. However, it is important to note that erythritol does not have the same properties as sugar and may not work as well in some recipes.
Is erythritol safe for pets?
- Erythritol can be toxic to pets, especially dogs, and should not be consumed by them.
How does erythritol compare to other artificial sweeteners?
- Erythritol is generally considered to be a safer and healthier alternative to other artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame and saccharin, which have been linked to various health concerns.

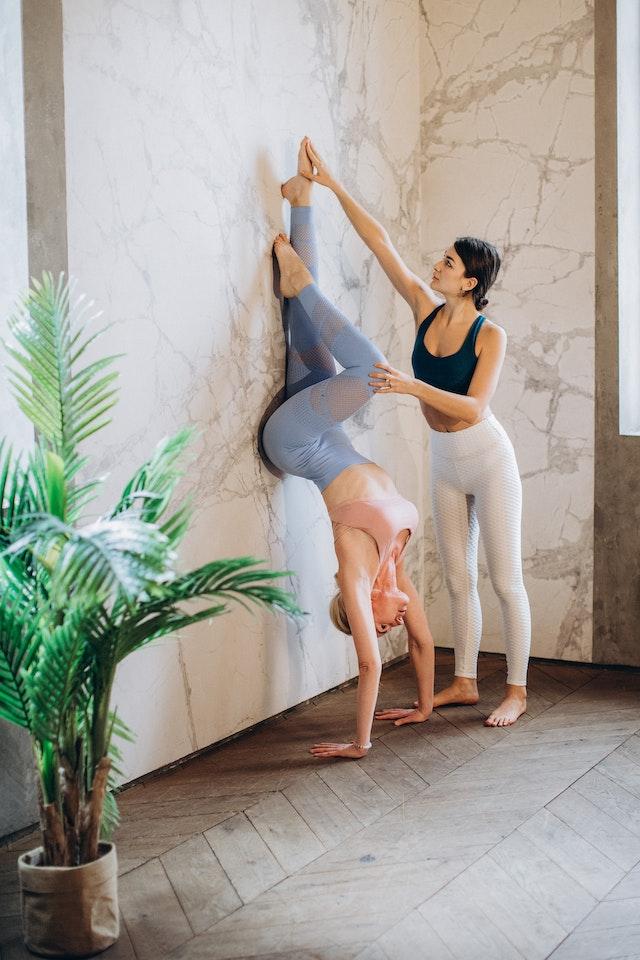
Is Yoga Good for Diabetes
Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It develops when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use the produced insulin effectively. This results in high levels of glucose in the blood, leading to a range of health complications.
Though there is no cure for diabetes, it is possible to manage its symptoms and improve overall health using various lifestyle changes, including exercise and diet. In recent years, yoga has become an increasingly popular activity among individuals with diabetes. But is yoga good for diabetes? Let’s explore the potential benefits of yoga for people with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes
To understand how yoga can benefit people with diabetes, it’s essential to first understand how the condition works. As mentioned before, diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood. The two types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2, with the latter being the more common form.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys the cells that produce insulin, leading to a complete deficiency of insulin in the body. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections to keep their blood sugar levels under control.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, occurs when the body stops responding to insulin effectively, leading to high levels of glucose in the blood. This type of diabetes is primarily caused by poor lifestyle choices such as a sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy eating habits, and obesity.
How Yoga can Benefit People with Diabetes
A growing body of research has shown that yoga can be an effective tool for managing diabetes symptoms. Here are some ways yoga can benefit people with diabetes:
Reducing Stress
- Stress is a significant risk factor for diabetes complications, and high levels of stress can lead to unstable blood sugar levels. Yoga, with its emphasis on breath control, meditation, and relaxation, can help reduce stress levels in the body. Regular yoga practice can help people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
- Yoga can help improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to use the insulin it produces. A study published in the Journal of Yoga and Physical Therapy found that regular yoga practice can help reduce blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. This effect is likely due to the combination of relaxation, pranayama (breathing exercises), and asanas (yoga postures) that help improve insulin sensitivity.
Lowering Blood Pressure
- High blood pressure is a common complication of diabetes and a significant risk factor for heart disease. Yoga has been shown to help lower blood pressure in people with diabetes, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Improving Overall Fitness
- Yoga is a form of exercise that can help improve overall fitness levels, including flexibility, strength, and balance. This can be especially beneficial for people with diabetes, who may be at an increased risk of falls and fractures due to neuropathy and poor blood sugar control.
Best Yoga Poses for Diabetes Management
Here are some of the best yoga poses for managing diabetes symptoms:
Tadasana (Mountain Pose):
- This pose is excellent for overall posture correction and improving breathing patterns, which can help reduce stress levels in the body.
Vrikshasana (Tree Pose):
- This pose helps improve balance and concentration while stretching the entire body, including the legs, arms, and spine.
Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose):
- The cobra pose stretches and strengthens the back muscles, improving posture and reducing back pain, which can be a common complication of diabetes.
Dhanurasana (Bow Pose):
- The bow pose stretches the entire body, improving flexibility and strengthening the upper back and spine.
Savasana (Corpse Pose):
- This pose is excellent for relaxation and reducing stress levels in the body. It can also help improve sleep quality, which is important for diabetes management.
Conclusion
Though there is no cure for diabetes, the condition can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise. Yoga can be a useful tool for people with diabetes to manage their symptoms and improve overall health. Whether you are new to yoga or a seasoned practitioner, incorporating yoga into your diabetes management plan can have significant health benefits.
FAQ
How does Yoga help to lower blood sugar levels?
- Yoga helps to lower blood sugar levels in several ways. Firstly, it reduces stress, which can cause blood sugar levels to spike.
- Secondly, it improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more efficiently.
- Finally, it promotes weight loss and improves overall fitness, which can help to control blood sugar levels over the long term.
How long will it take for me to see results from practicing Yoga for diabetes management?
- The time it takes to see results varies depending on a number of factors, including how regularly you practice Yoga, the intensity of your practice, and your overall health. Most people begin to see improvements in blood sugar levels within a few weeks of starting a regular Yoga practice.
Is Yoga safe for people with diabetes?
- Yes, Yoga is generally safe for people with diabetes. However, it is important to speak with your doctor before beginning any new exercise program, especially if you have other health conditions that may be affected by exercise.
Can Yoga cure diabetes?
- No, Yoga cannot cure diabetes. However, it can be an effective tool for managing diabetes symptoms and improving overall health.
What type of Yoga is best for diabetes management?
- There are many different types of Yoga, and all can be beneficial for diabetes management. However, some types, such as Hatha Yoga, may be particularly helpful due to their focus on relaxation and stress reduction.
Do I need to be flexible in order to practice Yoga?
- No, you do not need to be flexible in order to practice Yoga. Yoga is designed to be accessible to people of all fitness levels and abilities.
How much time do I need to devote to practicing Yoga for diabetes management?
- Experts recommend practicing Yoga for at least 30 minutes per day, at least 5 days per week, in order to see significant improvements in blood sugar levels and other diabetes symptoms.
Can Yoga be used in conjunction with other diabetes treatments, such as medication?
- Yes, Yoga can be used in conjunction with other diabetes treatments, including medication. However, it is important to speak with your doctor before making any changes to your medication regimen.
What are some other benefits of practicing Yoga for diabetes management?
- In addition to lowering blood sugar levels, practicing Yoga can help to improve overall health and fitness, reduce stress and anxiety, improve sleep quality, and promote a sense of well-being.
Where can I find Yoga classes or online resources for managing diabetes?
- There are many yoga studios and fitness centers that offer Yoga classes for people with diabetes. Additionally, there are many online resources, including videos and instructional materials, that can be used to practice Yoga at home. It may be helpful to speak with a certified Yoga instructor who has experience working with people with diabetes to help you find the best resources for your needs.

Is Pine Needle Tea Good for Diabetics
Is Pine Needle Tea Good for Diabetics
Pine needle tea is a kind of herbal tea that has been used for centuries because of its various health benefits, including its positive effects on diabetes.
We’ll go over some of the reasons why it’s so important that you know about pine needle tea and how it may help you.
Pine needle infusion has a mild, earthy taste and scent and may be prepared using a hot water infusion of fresh pine needles.
Depending on the kind of pine tree utilized, some claim that the flavor resembles that of orange juice.
Pine needle tea is often made from the needles of lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta), ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa), or white pine (Pinus albicaulis).
If you’re dealing with a young pine tree that hasn’t produced any cones or buds yet, you should utilize the tips of the needles (the green part).
These immature needles are richer in vitamin C than their more mature counterparts.
Needles have a limited shelf life and may lose part of their effectiveness after several uses.
Choose just the innermost needles at their point of union with the stem if you’re working with an older tree. Needles that have turned brown or are otherwise wilted should be left out of your collection.
You may buy dried pine needle tea from health food shops or online, or you can pick the needles by hand in the winter when they are most effective.
Pine needles’ health benefits stem mostly from their high vitamin and mineral content.
It has phytonutrients, which aid in detoxification and the elimination of free radicals.
Pine needle has been used as a remedy in alternative medicine for hundreds of years.
The Native Americans utilized tea to treat the common cold, flu, and sore throats, but it also had additional health advantages.
Pine Needle Tea Has Health Benefits
There are Plenty of Antioxidants.
There are several antioxidants, including vitamin C and beta-carotene, in pine needles.
In addition, they include chemicals like shikimic acid and manganese that help reduce inflammation.
These chemicals are helpful in warding off oxidative stress and cell damage caused by free radicals.
In the winter, a cup of pine needle tea is just what you need to warm yourself.
This herbal tea is beneficial for your health in many ways, including its capacity to kill cancer cells and increase blood flow.
Aids in Reducing Glucose Levels and Fat Storage.
Pine tea is beneficial for people with diabetes and other chronic conditions because it lowers blood sugar levels and prevents weight gain by lowering insulin resistance.
Enhances the Performance of the Immune System.
Heparin, an anti-inflammatory substance found in pine needles, may assist the body’s immune system naturally fight infections.
Vitamin C, von, and zinc are just a few immune-boosting vitamins and minerals found in pine needles.
According to the research, pneumonia rates are lower in locations with pine forests than those without.
Pine Needle Tea Has Been Shown to Reduce Blood Pressure.
If high blood pressure or hypertension is not controlled, it may lead to cardiovascular disease.
Pine needles reduce blood pressure through increasing blood flow and decreasing inflammation.
Its anti-inflammatory characteristics also aid in reducing cholesterol by halting the formation of plaque on arterial walls.
The Use of Pine Needle Tea May Improve Digestion
Pine needle tannins have been studied for their potential to alleviate the symptoms of gastritis, bloating, and diarrhea (stomach inflammation).
These tannins’ antiseptic qualities aid in the prevention of gastrointestinal tract bacterial infections.
Super-Rich in Vitamin A
One of the best natural sources of vitamin A is pine needles.
Pine needles have a much greater concentration of vitamin A than any other commercially available herbal tea, with 1,500 IU (150% DV) in only one cup.
Vitamin A is essential for normal eyesight, skin, and immune system function.
In addition to aiding in hormone regulation, bone health promotion, inflammation prevention, and white blood cell activity enhancement, zinc has been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of viral infections, including the common cold and the flu.
Reduces the Appearance of Scars and Acne
Acne and other skin problems may be alleviated by using pine needles to boost the immune system and fight off infections.
There are anti-inflammatory compounds called tannies in pine needles.
If you suffer from eczema or psoriasis, two inflammatory skin illnesses that may worsen when your body is under stress, this may be of particular use to you.
Protection Against Microbial Infection
Pine needle has antiviral and antibacterial properties, making them a useful treatment for cold and flu symptoms, including sore throats, runny noses, body pains, headaches, fever, and more.
It’s also good for you since it stimulates the creation of white blood cells, making you more resistant to whatever illness may come your way.
Aids in the Treatment of Bronchitis and Pneumonia
Pine tea’s antibacterial characteristics aid in the recovery from respiratory infections, including bronchitis and pneumonia, and they also help relieve congestion in the sinuses and lungs.
It’s high in vitamin C, which helps the body resist infections by increasing the formation of white blood cells.
Promotes a Hearty Circulatory System
Vitamin C, which is included in pine needles, is beneficial to cardiovascular health for a number of reasons, including its effects on cholesterol levels, inflammation, and blood clotting.
Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant to protect the body from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Anyone concerned about preventing cardiovascular disease and stroke should consider this option.
Ingesting Pine Tea May Help Ease Anxiety and Stress
Pine needles may calm people and animals by producing a calming effect similar to chamomile tea.
Those with diseases including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADD), depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) might benefit from this (PTSD).
Reduces Arthritis and Joint Pain
By lowering overall body inflammation, the tannins in pine needles may help alleviate joint pain and arthritic symptoms.
The tannins may also ease muscle spasms and joint stiffness.
Has Diuretic Properties
Medication, known as a diuretic, aids the kidneys in excreting excess water.
Persons suffering from edema or hypertension can benefit from this.
A Pine needle is a natural diuretic that can help the body get rid of excess fluid and reduce swelling.
Lessen the Pain of Menstruation
Vitamin C, ascorbic acid, can be found in pine needles.
Cramps during menstruation can be alleviated, and anemia from excessive menstrual blood loss can be avoided with vitamin C.
Dysmenorrhea sufferers may find relief from its role in wound healing and infection prevention (painful menstruation).
Recipe for Pine Needle Tea
Produces 3 Cups
Ingredients
- Half a cup of Eastern white pine needles, trimmed to 1/2-inch lengths (by chopping or cutting).
- Three cups of water
Instructions
- Fill a stainless steel pot all the way with water and bring it to a boil.
- Sprinkle some pine needles on top. When needles are added to boiling water, the temperature drops below the boiling point.
- Take the tea off the heat and let it steep for 15 to 20 minutes if you prefer a gentler flavor.
- If you want your tea to have more flavor, simmer it (don’t boil) for 20 minutes. The next day, uncover and let stand at room temperature or proceed to the next step and serve.
- Remove the pine needles, sweeten them to taste, and enjoy either hot or cold tea.
Notes
You shouldn’t boil the pine needles if you want to keep the vitamin C content high and stop the bitter terpenes from being released. This tea’s vitamin C content is only good for a short time, so consume it quickly.
Pine needle tea is available on Amazon if not available locally.
FAQ
Is it safe to drink pine needle tea every day?
- Pine needle tea is safe to consume daily, however, excessive use should be avoided. Start with a half cup if you’re trying it for the first time. If you’ve acclimated well to it and aren’t experiencing any negative effects, you can take it once or twice a day.
What does pine needle tea taste like?
- Flavor-wise, pine needle tea is quite mild and refreshing. Pine needles may also have a citrusy flavor, however, this depends on the specific kind.
How healthy is pine needle tea?
- Its high vitamin C content (five times that of lemons) may help with anything from sluggish circulation and exhaustion to varicose veins and heart disease. Pine needle tea’s high vitamin C content also makes it effective in warding off disease and infection.
What is the active ingredient in pine needle tea?
- A-terpineol accounts for 30.2 percent, linalool for 24.4 percent, limonene for 17.01 percent, and anethole for 14.5 percent. Caryophyllene (3.14%) and eugenol (2.14%) are the main components. The essential oil from pine needles has been shown to have powerful antioxidant properties, as measured by its ability to quench free radicals, prevent lipid peroxidation, and increase reducing power.
How many calories are in pine needle tea?
- Pine Needle Tea, it turns out, has little calorie content, which is great news for people trying to reduce their caloric consumption. Around two calories may be expected from the typical serving size.
Are pine needles healthy for the liver?
- Pinene is only one of the numerous phenolic chemicals found in pine needles. In this way, PNE might influence liver regeneration by mitigating the oxidative stress brought on by this process.
Is pine needle tea inflammatory?
- Antioxidants found in abundance in pine needle tea help prevent cancer, heart disease, and premature aging by neutralizing free radicals.
Does pine needle tea have magnesium?
- Pine needles have many health advantages; you may enjoy them in a delicious tea. Vitamins A, B, C, and D are abundant in pine needles. Moreover, they are rich in calcium, iron, and magnesium minerals.
Is pine needle tea a diuretic?
- Tea produced from pine needles has been shown to positively affect urinary health due to its diuretic qualities, just like herbal diuretics. Nutritional elements in pine needles prevent depletion from fluid loss.
Is there caffeine in pine tea?
- Yet Pine Needles Tea is not a caffeinated tea. It is completely free of it, making it a good option for those trying to limit their use.
Can I drink pine needle tea at night?
- Melatonin, which is found in pine needle tea, is a proven sleep aid. Reduce your stress levels, feel calmer, and get a good night’s sleep with its aid. Pinus radiata needles, when steeped in hot water and ingested, have characteristics that assist in reducing stress by calming the mind and body.
Is it Harmful to Drink Pine Needle Tea?
- Pine needle tea is typically safe, although it should not be eaten during pregnancy or when breastfeeding due to the risk of miscarriage.

Do You Have Cloudy Urine?
If your pee is not a typical, clear, light-yellow hue and instead appears milky or murky, you have cloudy urine. Although murky urine is typically not harmful, it may be an indication of a medical concern if it occurs frequently and repeatedly.
What is cloudy urine?
When your urine is milky in color and not clear, it is said to have cloudy urine. Cloudy urine is usually not harmful, but it can be a sign of a medical disease if it occurs frequently and repeatedly.
What does cloudy urine look like?
The color of typical urine is a translucent light yellow. As opposed to the typical straw yellow color, the color of cloudy urine ranges from foggy white to light yellow.
What causes cloudy urine?
The presence of alkaline is the most frequent reason for cloudy urine. Water, salts, and waste products from the kidneys make up urine; the ratio of these elements determines whether the urine is alkaline or acidic (pH). pH values for normal urine range from 4.5 to 8 in terms of acidity to alkalinity.
Pee that measures 8 pH or higher is alkaline, whereas urine that measures 5 pH or lower is considered acidic (basic). Urine that is murky is due to high alkalinity.
The following are additional potential reasons for cloudy urine:
- Dehydration.
- Kidney leakage (chyluria).
- Infection.
- High fruit and vegetable diet.
- Vaginal discharge.
What if I have cloudy urine during pregnancy?
Frequent urination is typical throughout pregnancy. As a result, you could occasionally notice that the color of your urine changes. Pregnancy-related reasons for cloudy urine include:
- Vaginal discharge.
- Dehydration (from morning sickness). Infection.
- Preeclampsia.
Visit your healthcare practitioner for a more thorough evaluation if you frequently have cloudy or discolored urine, or if you develop any symptoms like a headache, blurred vision, abdominal pain, or swelling.
What foods cause cloudy urine?
Some foods might increase your level of alkalinity, which can result in hazy urine. You are more likely to have greater levels of alkalinity, which can result in cloudy urine if you consume a diet high in fruits and vegetables and low in meats, grains, and cheeses (low-PRAL).
Urine changes to look for
Your urine’s qualities can vary from day to day based on a number of factors, but in general, healthy urine is light yellow and has a faint odor.
What diseases/disorders have cloudy urine as a side effect?
Cloudy urine is a symptom of a number of illnesses or conditions, including the following:
- Diabetes.
- Chyluria.
- Infection (urinary tract infection,).
- Preeclampsia.
- Kidney disease or kidney stones.
Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic, progressive condition that causes a lengthy range of symptoms, including nerve damage, eye issues, and frequent urination. It develops when your body is unable to balance the amount of sugar in your blood. Urine that is hazy can also result from it.
The color and scent of your blood alter when you have a lot of sugar and protein in it. Urine that is cloudy and has a sweet scent is a typical sign of type 2 diabetes.
Dehydration
When you do not drink enough, your pee may become hazy. Urine becomes more concentrated when there is a fluid deficit. The hue will also darken.
The solution to this issue is to increase your daily water intake. Your urine will be clear and light yellow after you have had enough fluids.
Urinary tract infection
Bacteria that enter your bladder, kidneys, or urethra can cause a urinary tract infection (UTI). Urine leaks from the location. You will have the following signs in addition to hazy urine:
- The burning or agony when urinating
- An increased urge to use the restroom pee leaks
- Odorous or bloody urine
- Lower abdominal pain
Most likely, your doctor would advise taking antibiotics to get rid of the infection. To ensure that all of the bacteria are killed, take all of the medications that have been prescribed.
Kidney Stones
The minerals and salts in your urine cause crystals called kidney stones to grow in your kidneys. Urine can become backed up in your bladder or another area of your urinary tract if there are large stones present. Sometimes they can result in really painful pain. Your lower back, side, or even when you urinate, could pain.
You run the risk of having blood or murky urine. Moreover, it could smell bad or have a red, pink, or brown appearance.
You can also experience the following symptoms:
• Fever and chills
• vomit and feel sick
In your urine, some kidney stones may naturally dissolve. Large stones that cannot be broken up by urination can be divided up by doctors using a noninvasive method. Stone removal surgery is occasionally required.
Does cloudy urine mean that I have a sexually transmitted disease (STD) or a sexually transmitted infection (STI)?
Urine that is cloudy is a symptom of some STDs and STLs. Although cloudy urine is not the only sign of many STDs or STls, it may help your doctor make a diagnosis. Cloudy urine is a sign of a number of ailments or infections, including
• Chlamydia.
• Gonorrhea.
• Vaginitis.
How is cloudy urine treated?
The following steps can be taken to treat hazy urine:
• Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated.
• Taking vitamin C to lower alkaline levels.
• Using antibiotics to treat any infections.
• Eating a healthy diet.
How can I prevent cloudy urine?
By leading a healthy lifestyle that includes drinking plenty of water and eating a diet that is balanced, you can avoid having hazy urine. You can also go see your doctor to get infections treated right away before they become more dangerous to your health.
FAQs
Is foamy urine the same as cloudy urine?
Urination occurs quickly, which results in air pockets forming in the urine and giving it a frothy quality, which is the source of foamy urine. In contrast to the typical, light-yellow tone, cloudy urine is not clear and appears to have a milky hue.
You should get evaluated by your doctor if you notice that your urine is continuously frothy as this could be an indication of kidney issues.
Is cloudy urine serious?
An issue in your urinary tract could be the cause of hazy urine. It can be a sign of a major medical issue even though it normally doesn’t suggest a medical emergency. Dehydration is one factor that might contribute to cloudy urine.
Is cloudy urine smelly?
The smell of urine can alter, although it often is not harmful and only lasts a short while. Your diet and any vitamins or minerals you are taking can alter the smell of your urine. For instance, vitamin B-6 pills and asparagus both leave a noticeable odor in the urine.
Keeping hydrated can help prevent occasional hazy urine as well as a strong odor. Contact your healthcare physician if the smell of your urine lasts more than a few days.
Can urine be cloudy without infection?
Can urine be cloudy without an infection? Other than diseases, urine can become hazy for a variety of reasons. Cloudy urine can be brought on by dehydration, diabetes, diet, kidney stones, and more.
What does protein in urine look like?
Urine that is foamy or bubbly. Your hands, feet, tummy, and face swelling (edema). urinating more frequently. breathing difficulty.
When should I see my healthcare provider for cloudy urine?
Urine that is occasionally cloudy is typical. Get in touch with your doctor if you have persistently hazy urine that doesn’t clear up in a few days.
How Many Grams of Sugar Spikes Insulin?
Blood sugar spikes happen when your blood sugar increases after eating and suddenly drops.
They may result in short-term hunger and drowsiness. Type 2 diabetes can develop over time if your body is unable to adequately control blood sugar levels.
Your blood sugar will increase by roughly 5 mg/di after ingesting 1 gram of pure glucose, while this amount may change according to the person’s weight, diabetes condition, and present blood sugar level.
A growing number of people are developing diabetes. In actuality, 25% of the 29 million Americans who have diabetes are completely unaware of their condition.
Your blood arteries may stiffen and narrow as a result of blood sugar surges, which increases your risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
Go low-carb
Blood sugar levels are raised by carbohydrate-containing foods.
Carbs are converted into simple sugars when you ingest them. Following that, these sugars get into circulation.
When your blood sugar levels increase, your pancreas secretes the hormone insulin, which instructs your cells to take up sugar from the blood. You have a dip in blood sugar as a result of this.
A low-carb diet has been linked to lower blood sugar levels, according to numerous research.
Besides helping with weight loss, which can lower blood sugar surges, low-carb diets also have this additional advantage. You can cut back on your carbohydrate intake in a variety of ways, including by keeping track of them.
Eat fewer refined carbs
Sugars or refined grains are examples of refined carbohydrates, also referred to as processed carbohydrates.
Table sugar, white bread, white rice, soda, candy, breakfast cereals, and desserts are a few prominent sources of refined carbohydrates.
Nearly all of the nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and fiber have been removed from refined carbohydrates.
Because they are metabolized by the body so easily and fast, refined carbohydrates are considered to have a high glycemic index. Blood sugar levels increase as a result of this.
High-glycemic-index foods may cause a surge in blood sugar followed by a subsequent dip in blood sugar, which can increase appetite, cause overeating, and result in weight gain.
Different carbohydrates have different glycemic indexes. It depends on a lot of factors, including ripeness, what else you eat, and how the carbohydrates are prepared or cooked.
The majority of fruits, non-starchy vegetables, and legumes, as well as whole-grain foods, have a lower glycemic index than other foods.
Reduce your sugar intake
The daily added sugar intake for an American is 22 teaspoons or 88 grams. Around 350 calories are contained in that.
While some of it is added as table sugar, the majority of it originates from prepared and processed foods like candy, cookies, and sodas.
Sugars like sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup that have been added to foods are not necessary for your nutrition. As a result, they are only worthless calories.
These simple sugars are very quickly broken down by our body, which leads to a very immediate rise in blood sugar. Replace sugar with sugar replacements as a compromise rather than completely giving it up.
Keep a healthy weight
Currently, it is estimated that two out of every three persons in the US are overweight or obese.
Obesity can make it more challenging for your body to use insulin and regulate blood sugar levels. This may result in blood sugar increases and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
There is a ton of evidence that connects obesity to insulin resistance and the onset of type 2 diabetes, while the exact mechanisms by which it occurs are still unclear.
On the other side, it has been demonstrated that losing weight enhances blood sugar regulation.
Exercise more
By enhancing your cells’ sensitivity to the hormone insulin, exercise helps prevent blood sugar increases.
Blood sugar levels are lowered by exercise because it causes muscle cells to absorb sugar from the circulation.
Exercise of any intensity has been shown to lessen blood sugar rise, including vigorous exercise.
Blood sugar regulation may differ depending on whether you exercise on an empty or full stomach.
As a double whammy to counteract blood sugar rises, increasing activity also offers the added benefit of aiding in weight loss.
Eat more fiber
The components of plant foods that your body cannot digest makeup fiber. Soluble fiber and insoluble fiber are the two main categories. Particularly soluble fiber can aid in reducing blood sugar peaks.
It disintegrates in water to create a gel-like material that aids in reducing the rate at which carbohydrates are absorbed in the gut. Instead of a spike, this causes the blood sugar to rise and fall gradually.
Additionally, fiber can help you feel full, which can help you eat less and have less of an appetite. Good sources of soluble fiber include:
• Nuts
• Legumes
• Some fruits, such as strawberries, raspberries, and blueberries
• Many vegetables
Drink more water
Lack of water intake might cause blood sugar to increase.
Your body creates the hormone vasopressin when you are dehydrated. As a result, your kidneys are encouraged to retain fluid, and the body is prevented from excreting extra sugar in your urine.
More sugar is also released into the blood by your liver as a result of it.
It is debatable how much water is ideal to consume. Basically, it depends on the person.
You should always drink as soon as you feel thirsty, and you should drink more water in hot weather and while exercising.
Drink water instead of sugary drinks or sodas because they will cause blood sugar to increase.
Introduce some vinegar into your diet
Many health advantages have been discovered for vinegar, especially apple cider vinegar.
Weight loss, lowered cholesterol, antimicrobial effects, and blood sugar regulation have all been related to it.
The glycemic index of a food can be lowered by adding vinegar, which can aid in preventing blood sugar increases. Pickled meals considerably lower the meal’s glycemic index, according to a Japanese study, which found this to be true.
Get enough chromium and magnesium
Chromium and magnesium have both been shown in studies to be useful in reducing blood sugar peaks.
• Chromium
You require trace levels of the mineral chromium.
It is believed to improve the way that insulin works. Encouraging the cells to take up sugar from the blood may help prevent blood sugar increases.
Here are the suggested dietary allowances for chromium. Broccoli, egg yolks, shrimp, tomatoes, and Brazil nuts are examples of nutrient-dense foods.
• Magnesium
The element magnesium has also been connected to the regulation of blood sugar.
On this page, you can find the suggested daily intakes for magnesium. Almonds, avocados, cashews, peanuts, and spinach are all rich food sources.
Add some spice to your life
For countless years, alternative medicine practitioners have utilized fenugreek and cinnamon. The management of blood sugar has been connected to both of them.
• Cinnamon
There is conflicting scientific data supporting the use of cinnamon in blood sugar management.
Cinnamon has been demonstrated to improve insulin sensitivity and lessen blood sugar increases after a carb-based diet in healthy individuals.
There are two types of cinnamon:
- Cassia: Can be produced by a number of different Cinnamomum tree species. This is the variety that is most frequently found in supermarkets.
- Ceylon: Obtained exclusively from a tree called Cinnamomum Verum. Although it costs more, it might have more antioxidants.
Coumarin, a compound found in cassia cinnamon, has the potential to be dangerous.
The acceptable daily intake of coumarin has been defined by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) at 0.045 mg per pound of body weight (0.1 mg/kg). For a 165-pound (75 kg) person, this is equivalent to around half a teaspoon (1 gram) of Cassia cinnamon.
• Fenugreek
The seeds of fenugreek are rich in soluble fiber, which is one of its qualities.
As a result, the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates are slowed, assisting in preventing blood sugar increases. However, it seems that more than simply the seeds may help to lower blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar peaks may be lessened with fenugreek. Although it can be added to food, some individuals choose to take it as a supplement because of its strong flavor.
• Berberine
There are numerous plants from which the chemical berberine can be derived.
For thousands of years, it has been utilized in traditional Chinese medicine. Its applications include lowering cholesterol, promoting weight loss, and managing blood sugar.
Berberine improves insulin sensitivity by decreasing the amount of sugar the liver produces. Even some type 2 diabetes medications have been proven to be as ineffective as it is.
Despite the fact that berberine seems to be rather safe, if you have any health issues or are currently on any medications, talk to your doctor before using it.
Consider these lifestyle factors
You should also take into account these lifestyle factors that can alter blood sugar if you truly want to lessen your blood sugar spikes.
• Stress
Stress can have a detrimental impact on your health in a number of ways, including by creating headaches, elevated blood pressure, and anxiety.
Additionally, it has been demonstrated to have an impact on blood sugar. Your body releases specific hormones as your stress level rises. The result is a release of sugar-based stored energy for the fight-or-flight response into your bloodstream.
Your blood sugar has been shown to benefit from actively treating stress. Yoga poses have been shown in a study of nursing students to lower stress levels, and blood sugar rises after meals.
• Sleep
Poor blood sugar regulation has been linked to both insufficient and excessive sleep. Your blood sugar levels might be impacted by even one or two bad nights.
Both amount and quality matter when it comes to sleeping. In terms of managing blood sugar, a study indicated that the deepest stage of sleep (NREM) was crucial.
• Alcohol
A lot of added sugar is frequently found in alcoholic beverages. This is especially true for cocktails and mixed drinks, which can have up to 30 grams of sugar per serving.
Similar to how adding sugar in meals causes blood sugar rises, so does the sugar in alcoholic beverages. The majority of alcoholic beverages are likewise very, very low in nutrients. They are, in fact, empty calories, similar to added sugar.
The effectiveness of insulin can also be lowered over time by heavy drinking, which results in high blood sugar and eventually leads to type 2 diabetes.
The bottom line
You may prevent blood sugar rises by making simple dietary changes like following a low-carb, high-fiber diet and staying away from added sugars and processed grains.
Beyond just assisting in blood sugar regulation, frequent exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and drinking lots of water can all be beneficial to your health.
However, before making any dietary changes, talk to your doctor if you have any medical issues or are taking any medications.
For the majority of people, adopting these straightforward dietary and lifestyle modifications is a fantastic strategy to reduce your chance of developing type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
FAQ
How much sugar can cause insulin spikes?
When your blood sugar levels rise above 250 mg/dl, you often start to experience the symptoms of hyperglycemia. The longer it goes untreated, the worse the symptoms may get. Frequent urine is one sign of a blood sugar increase.
How much does it take to spike insulin?
Thirty-five grams of casein, however, are sufficient, according to the study, to cause an insulin surge the morning following an overnight fast. Furthermore, this protein-induced insulin surge happens extremely soon after protein consumption and typically peaks 15 minutes after ingestion.
How many g of sugar is OK per day?
The American Heart Association (AHA) advises a tougher added-sugar restriction of no more than 150 calories (or approximately 9 teaspoons or 36 grams of sugar) per day for most men and no more than 100 calories (or about 6 teaspoons or 24 grams) per day for the majority of adult women.
How much sugar spike is normal?
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) states that a blood sugar level under 180 mg/dl, 1 to 2 hours after a meal, is a general target. Experts disagree on what the exact figure should be. Discuss your goals with your doctor, and don’t change your medication without first consulting them.
How high is too high for a blood sugar spike?
When your blood glucose level is 200 mg/dl or greater, it occurs. If you forget to take your diabetic medication, consume too much, or do not exercise enough, hyperglycemia may result. High blood sugar can occasionally be caused by medications you take for other health issues.

Bee Pollen for Diabetes
With its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial characteristics, bee pollen is frequently touted as a useful dietary supplement. In addition, there are numerous other health benefits that are claimed for it, including that it lowers allergies, increases athletic performance, balances hormones, and prevents cancer.
Because it contains nutrients that can benefit people with diabetes and associated complications, bee pollen is referred to as nature’s wonder food.
Diabetes develops when the amount of insulin produced is insufficient, causing the bloodstream to hold onto the glucose that should have been used by the cells as an energy source. Complications related to diabetes might also have an impact on the body’s other organs.
Fortunately, bee pollen can assist those who are managing their diabetes and associated complications by:
Strengthening the immune system
- The body is protected from stress brought on by diabetes by the high antioxidant content of bee pollen. Blood sugar levels that are too high can harm key organs by putting them under stress. Bee pollen may be able to reduce those damages and enhance its performance.
Increasing energy
- Because they do not consume enough calories to burn as energy, diabetics experience fatigue frequently. Athletes use bee pollen, which is rich in protein and amino acids, to boost their energy reserves.
Hasten wound healing
- Diabetes patients are aware of the risk of infection as a complication of their condition. A surplus of sugar in their blood prevents their open wounds from healing quickly. Infection and even necrosis are risk factors that are increased by open wounds. Vitamins A, C, and E, which can speed up wound healing and stop infection, are included in bee pollen.
Manage weight
- Obesity and diabetes are frequently related. Due to the components in bee pollen that boost metabolism and aid in fat burning, it can aid in the management of diabetes and obesity.
Increase the overall health and well-being
- In addition to these nutrients, bee pollen is also rich in minerals, enzymes, coenzymes, the B complex, and a host of other substances. Diabetes might make a person more susceptible to developing other ailments. Through the provision of the nutrients required by the body to fight off viruses and germs, bee pollen can improve general health and wellness.
If a person can combine their diabetes with a healthy and active lifestyle, they may be able to control their condition. If used in conjunction with a healthy diet and exercise, bee pollen would be very beneficial. Bee pollen can be consumed straight or as a supplement for greater convenience.
If they are created of good quality, bee pollen supplements are strong and beneficial for diabetes. Some supplements are inexpensive because they contain fillers and preservatives that are harmful to the body.
One of the world’s ideal foods is the pollen that has accumulated in beehives. Regarding nutrition, it possesses every single essential component. In fact, if you were abandoned on a remote island with just bee pollen for food, you might be able to survive on it alone—provided, of course, that you also had access to clean water.
Pollen is more protein-rich than meat pound for pound. Furthermore, it’s stuffed full of vitamins and nutrients that were previously known to be beneficial for diabetes. The B complex vitamins, such as Thiamine, are all present in pollen as an illustration (Vitamin B1). Already, we can see the main benefits of pollen emerge since Thiamine is frequently employed in the treatment of diabetes.
Nicotinic acid, like vitamin B1, is widely used to treat diabetes, and pollen is a very good source of this substance. The fact that it gives you a ton of important nutrients while being extremely low in calories is the benefit that stands out the most. Less than 36 calories are included in an ounce of pollen. Bee pollen will also be a very powerful assist in weight loss because of the low-calorie count and the enormous amount of minerals it offers.
In addition to improving metabolic rate, it also aids in reducing food cravings. Sportsmen have used it for a very long time since it also increases energy levels.
Given that diabetes is frequently brought on by being overweight and/or leading a sedentary lifestyle, appetite suppression, an elevated metabolism, and increased energy are the ideal trifecta for diabetes sufferers.
In conclusion, bee pollen is undoubtedly beneficial for treating diabetes, but it’s important to remember to only buy pollen from reliable sources and to ask the two questions I’ve listed above before placing your order.
FAQ
Is bee pollen high in sugar?
Consequently, bee-collected pollen has a high carbohydrate content, with up to 40% of its weight being made up of sugars.
Does bee pollen help with sugar cravings?
Bee pollen is also a rich source of fat-burning amino acids, which might help you resist the urge for sugar throughout the day. It promotes good digestion by using enzymes to target the foods that are sitting in your stomach and break them down more quickly.
Does bee pollen reduce cholesterol?
Bees gather pollen from flowers to utilize as a source of food, and this pollen is known as bee pollen. It has been used to reduce cholesterol and weight because of its high protein content.
When is the best time to take bee pollen?
Anytime during the day or night is safe to take it. Just be aware that some people have a sudden burst of energy after taking the chemical, so it would be advisable to take it earlier in the day rather than later at night. It can also be added to a variety of foods, including cereal, applesauce, yogurt, smoothies, and more.
How quickly does bee pollen work?
Some claim that taking it would cure your allergies within a month, while others assert that if you want to experience any relief, you must begin taking it six weeks prior to allergy season.
How much bee pollen should you take daily?
Start with 1/4 teaspoon and work your way up to 2 teaspoons every day, according to proponents of alternative medicine, while keeping an eye out for any adverse responses that may cause itching, swelling, shortness of breath, dizziness, or other extreme whole-body reactions.
Can I take bee pollen on an empty stomach?
The worries I have heard regarding taking it with vitamins or pharmaceuticals are generally baseless because it is not a drug. Bee pollen is actually available for consumption at any time of day or night.
Is bee pollen a Superfood?
Bee pollen is a superfood since it is a tonic ingredient with high bioactivity. This is due to the fact that it includes every nutrient required to support human existence and comprises more than 96 distinct nutrients in total.
Does bee pollen detox your body?
Pollen can help maintain the youthful and radiant appearance of your skin because it is an excellent source of several vitamins and minerals. It increases the flow of blood to all skin cells, aids in body detoxification, minimizes the appearance of wrinkles, and hastens the healing process.
Who should not take bee pollen?
Check with your doctor before beginning any supplements because they may possibly interact with some medications. Additionally, due to safety concerns, it would be advisable to stay away if you have allergies, are pregnant, nursing, or are less than 1 year old.
The Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Despite having names that sound similar, type 1 and type 2 diabetes are two separate illnesses with distinctive causes.
Type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are fundamentally distinct from one another since type 1 is thought to be brought on by an autoimmune response and manifests in infancy.
Long-term lifestyle variables like inactivity and obesity are linked to the development of type 2 diabetes, which occurs over a number of years. The diagnosis is typically made in adults.
However, family history may be important. Type 1 diabetes risk factors are not completely understood.
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The immune system of the body defends against outside intruders, such as dangerous germs and viruses.
• It is thought that an autoimmune response is what causes type 1 diabetes. When a person has type 1 diabetes, their immune system misidentifies healthy cells from their body as foreign invaders.
• The insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas are attacked by and destroyed by the immune system. The body is unable to manufacture insulin if these beta cells are gone.
Why the immune system occasionally targets the body’s cells remains a mystery to researchers. It might be influenced by genetic and environmental elements, such as virus exposure.
There is a continuous investigation into autoimmune illnesses. Type 1 diabetes is not brought on by diet or way of life.
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
- Insulin resistance is a complication of type 2 diabetes. Although the body continues to manufacture insulin, it is unable to utilize it efficiently.
- Although there are a number of lifestyle factors, such as being sedentary and being overweight, that may be involved. Researchers do not yet fully understand why some people develop insulin resistance while others do not.
- Additional genetic and environmental factors might also be important. Your pancreas will attempt to make up for this by generating more insulin if you acquire type 2 diabetes. Glucose builds up in your bloodstream as a result of your body’s inability to utilize insulin properly.
How Does Diabetes Affect the Body?
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the two most common varieties.
• Each kind of diabetes is a chronic illness that interferes with your body’s ability to control blood sugar or glucose levels. Your body’s cells run on glucose for fuel, but glucose needs a key to get into your cells. That key lies in insulin.
• Insulin production is absent in those with type 1 diabetes. It is comparable to being locked out.
• In the later stages of the disease, type 2 diabetics frequently produce insufficient insulin and do not respond to insulin as well as they should. It’s comparable to having a key that is broken.
• Chronically high blood sugar levels are a risk for both types of diabetes. Diabetes problems are now more likely as a result.
What Are the Risk Factors for Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes risk factors are less understood than type 2 diabetes risk factors.
Some known risk factors are:
- Family history: A person is more likely to develop type 1 diabetes if they have a parent or sibling who has the disease.
- Age: Although type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, children and teenagers are the age group where it most frequently does.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
Type 2 diabetes is a possibility for you if you:
• Possess prediabetes or have just raised blood sugar
• Have a weight problem or are obese
• Excessive belly fat
• Are not active three times a week or more
• Are older than 45
• Own a history of gestational diabetes, or diabetes while pregnant, and have given birth to a child that weighed greater than 9 pounds.
• Are Black, Hispanic or Latino, American Indian, or Alaska Native people more likely to experience health inequalities because of structural injustices?
• Possess a type 2 diabetic member in close family
• Afflicted with polycystic ovary syndrome
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetes?
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes both have symptoms that might develop if not treated, including:
• Frequent urination
• Feeling very thirsty and drinking a lot.
• Feeling quite hungry.
• Feeling extremely worn out.
• Having vision haze
• Not having your cuts or sores heal completely.
• Extremely dry skin
• Being sick more frequently than usual
• Mood swings, impatience, and accidental weight loss are among the symptoms that type 1 and type 2 diabetics may face.
• Diabetes and tingling in the hands and feet. Diabetes of any kind, including type 1 and type 2, can cause tingling and numbness in the hands and feet. According to the American Diabetes Association, type 1 diabetes patients’ chance of experiencing tingling and numbness is greatly decreased by good glucose control (ADA).
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes show in completely different ways, although sharing many of the same symptoms.
Many types 2 diabetics do not have symptoms for many years, and when they do, they often progress slowly and gradually.
When type 2 diabetes first develops, some people do not even have any symptoms and do not know they have it until serious consequences. Typically, over the course of several weeks, type 1 diabetes symptoms appear suddenly. This kind, formerly known as juvenile diabetes, typically appears in childhood or adolescence. Later in life, type 1 diabetes is, however, a possibility.
How Are Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Treated?
Right now, type 1 diabetes has no known cure. Insulin must be regularly given, and blood sugar levels must be tested often in those with type 1 diabetes because they cannot make any.
A few people inject themselves multiple times a day into soft tissue like the stomach, arm, or buttocks. Pumps for insulin are used by others. The body receives insulin through a tiny tube from insulin pumps in a consistent dosage.
Due to the rapid ups and downs in blood sugar levels, blood sugar testing is a crucial component of managing type 1 diabetes.
However, many patients require further assistance. Type 2 diabetes can be controlled and even prevented with diet and exercise. Medications that improve the way your body uses insulin may be prescribed by your doctor if lifestyle changes are ineffective.
A crucial component of managing type 2 diabetes is regularly checking your blood sugar. You cannot determine whether you are achieving your target levels without it.
Blood sugar checks may be advised more frequently or on an as-needed basis by your doctor. Your physician might suggest insulin injections if your blood sugar levels are high.
Can Diabetes Be Prevented?
It is impossible to prevent type 1 diabetes. With certain lifestyle modifications, such as keeping a reasonable weight, you may be able to reduce your chance of getting type 2 diabetes.
Working with your doctor to create a healthy weight-loss plan, increasing your exercise levels, eating a balanced diet, and consuming fewer sugary or highly processed foods are all ways to lose weight if you are overweight.
Careful monitoring can restore your blood sugar levels to normal and stop the onset of serious problems even if you are unable to prevent the disease.
FAQ
Is type 2 diabetes better or worse?
Many times, type 2 diabetes is less severe than type 1. However, it still has the potential to have severe health consequences, particularly in the sensitive blood vessels of your kidneys, nerves, and eyes. A stroke and heart disease are also become more likely by type 2.
Can type 2 diabetes go away?
Type 2 diabetes has no known treatment options. However, it might be feasible to reverse the disease to the point where you no longer require medicine to manage it, and your body is not adversely affected by having blood sugar levels that are too high.
Can walking cure diabetes?
Walking can help lower blood glucose levels and thus improve diabetes control, according to research studies.
Is fasting good for diabetes?
Fasting routines have been shown to be effective in reducing the signs and symptoms of diabetes and addressing some of its underlying causes, according to preliminary studies. However, not everyone should engage in the practice, and many dieticians and medical professionals continue to provide warnings about potential harm to metabolic and blood sugar health.
How do you reset your pancreas?
US researchers claim that by following a certain fasting diet, the pancreas might be encouraged to rebuild itself. In animal studies, diabetes symptoms were cured by restoring the organ’s ability to manage blood sugar levels. According to the study, which was published in the journal Cell, a diet “reboots” the body.