Diabetes and Weight
What Role Does Exercise Play in Reversing Pre-diabetes?
Pre-diabetes is a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Unfortunately, pre-diabetes can progress to type 2 diabetes if lifestyle changes are not made. While diet and medication are commonly used to manage pre-diabetes, the role of exercise in reversing the condition is often overlooked.
Understanding Pre-Diabetes
Pre-diabetes is a condition where a person’s blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as Type 2 diabetes. It is a significant health issue as it can lead to the development of Type 2 diabetes and its associated complications. In this chapter, we will discuss what pre-diabetes is, what causes it, and how it can be diagnosed and managed.
What is Pre-Diabetes?
Pre-diabetes is a common condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 84 million adults in the United States have pre-diabetes. This condition is often referred to as impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance.
What Causes Pre-Diabetes?
Pre-diabetes occurs when the body is unable to use insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone that moves sugar from the blood into the cells of the body, where it is used for energy. When the body is unable to use insulin efficiently, it leads to high blood sugar levels.
Some of the risk factors for pre-diabetes include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being over the age of 45, and having high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels. In addition, physical inactivity, poor diet, and smoking can also increase the risk of developing pre-diabetes.
Diagnosis and Management of Pre-Diabetes
Pre-diabetes can be diagnosed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels after a person has fasted for at least eight hours. The two most common tests used to diagnose pre-diabetes are the A1C test and the fasting plasma glucose test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months, while the fasting plasma glucose test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
Once diagnosed, the goal of managing pre-diabetes is to prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes. This can be achieved through lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, following a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and quitting smoking. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels.
The Dangers of Progression to Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that can cause a host of serious health problems, including heart disease, kidney disease, blindness, and limb amputations.
- If left untreated, pre-diabetes can progress to type 2 diabetes in just a few years. In fact, around 15-30% of individuals with pre-diabetes develop type 2 diabetes within five years.
- Once diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes and/or medication may be necessary to manage the condition, and this can be both physically and financially taxing.
The Benefits of Prevention
- By preventing pre-diabetes from progressing to type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes, you can help reduce your risk of developing the associated health problems.
- Prevention can also mean avoiding the need for medication and other treatments associated with type 2 diabetes.
- The good news is that lifestyle changes, including healthy eating, regular physical activity, and weight loss, can significantly reduce the risk of progression to type 2 diabetes.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
- Early diagnosis of pre-diabetes is essential for prevention. Simple blood tests can detect pre-diabetes, and individuals who are diagnosed can take action to prevent progression to type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment for pre-diabetes may include lifestyle changes like those mentioned above, as well as medication in some cases.
- Diabetes educators and other healthcare professionals can help individuals with pre-diabetes make the necessary lifestyle changes and provide support for ongoing prevention efforts.
How Exercise Works in Reversing Pre-Diabetes:
1. Boosts insulin sensitivity: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps to regulate blood sugar levels. In pre-diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, and as a result, it is unable to use it effectively. Exercise helps to increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin, making it easier for the cells to use glucose for energy.
2. Reduces fat deposits: Excess body fat, especially around the waist, is a risk factor for pre-diabetes. Exercise helps to burn calories and reduce body fat. As a result, this reduces the risk of pre-diabetes and helps to reverse it.
3. Promotes weight loss: Exercise helps to burn calories, which promotes weight loss. This is crucial in reversing pre-diabetes because losing just 5-10% of your body weight can significantly improve blood sugar levels.
4. Strengthens the heart: Pre-diabetes, just like diabetes, can damage many organs, including the heart. Exercise helps to make the heart stronger and more efficient, which reduces the risk of heart diseases.
5. Improves energy levels: Exercise helps to improve overall fitness and energy levels, which makes it easier to perform daily activities.
Designing Your Exercise Plan
When designing an exercise plan, it is essential to take into account several factors such as age, fitness level, and medical history. These factors will determine the intensity, duration, and frequency of your exercise program.
Types of Exercise for Pre-diabetes
There are three main types of exercise that you should include in your exercise plan: aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Aerobic exercise such as brisk walking, cycling, and swimming helps to improve cardiovascular fitness and manage blood sugar levels. Strength training, on the other hand, helps to build muscle and boost metabolism. Flexibility exercises such as yoga and stretching help to improve range of motion and reduce the risk of injury.
How Much Exercise is Enough?
The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread over three to five days. In addition, resistance training should be done at least twice a week, with at least one set of 10-15 repetitions per exercise. It is also essential to avoid prolonged periods of sitting and to get up and move around every 30 minutes.
Getting Started with Exercise
If you are new to exercise, it is essential to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program. Consider working with a certified personal trainer who has experience working with people with pre-diabetes. Remember that exercise should be enjoyable and sustainable, so choose activities that you enjoy and fit into your lifestyle.
Conclusion
Pre-diabetes is a condition that can be reversed through lifestyle changes, including regular exercise. Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, promote weight loss, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By incorporating exercise into your daily routine, you can take control of your health and prevent the progression of pre-diabetes.
FAQ
Can a blood sugar supplement reverse pre-diabetes?
- While blood sugar supplements cannot cure pre-diabetes, they can help in controlling blood sugar levels and prevent the condition from progressing to type 2 diabetes.
How much exercise is needed to reverse pre-diabetes?
- Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week to help manage blood sugar levels and reverse pre-diabetes.
Should I consult my healthcare provider before starting an exercise program?
- It is always recommended to consult a healthcare provider before starting any exercise program, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
How long does it take to see the results of lifestyle changes such as exercise and diet in controlling blood sugar levels?
- The results of lifestyle changes may vary for each individual. However, incorporating regular exercise and a healthy diet can help lower blood sugar levels and improve overall health. It is important to stay consistent and monitor your progress with your healthcare provider.

Can You Lose Weight with Metformin?
Diabetes is one of the conditions that affect most people globally. Luckily, there is medication for this condition.
The most common diabetes medication that can also improve diabetes management, according to research, is Metformin. According to research, it has been found that certain people might lose weight by using Metformin.
If you have type 2 diabetes, one of the first treatment options considered to help you manage glucose levels in your body is Metformin. There is research that suggests that Metformin may likely lead to a modest weight reduction despite it being not a weight loss drug.
Metformin and Weight Loss
People with diabetes were treated with Metformin, and they lost up to 8 kgs (around 18 lbs.) of their weight due to calorie intake, according to a small, 24-week study that was conducted in 1998.
Additionally, it was found that after using Metformin, over 4,000 people with type 2 diabetes experienced up to 2.5 kilograms (around 5.3 lbs.) weight loss for over four years when a much larger trial took place.
You are likely to lose a low amount of weight when using Metformin weight loss medication. Further, it was found that around 29% of people lost 5% or more of their body weight, and only 8% lost approximately 10% after using Metformin for weight loss.
There are various ways that using Metformin weight loss medication might have an impact on your weight. Reducing your appetite is one of the ways that Metformin for weight loss medication works.
Hormones such as Leptin and insulin have a significant role to play in your appetite. Using Metformin increases your body’s sensitivity to these hormones. Leptin is essential to your appetite since it is responsible for letting your body know when it is full and stop eating.
When your body increases its sensitivity to this hormone, you may feel less hungry.
Further, the hormone responsible for suppressing appetite is known as GLP-1. Using Metformin may increase the secretion of this hormone in your body which then suppresses your appetite and then leads to you losing weight in the process.
Semaglutide (Wegovy), a GLP-1 receptor agonist drug that precisely targets this hormone, has received FDA approval to treat both obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Reducing the amount of visceral fat in your liver and muscle tissue is another way of metformin weight loss. The abdominal cavity, which houses your liver, stomach, and intestines, among other internal organs, is where visceral fat is deposited.
It can also accumulate in muscles, including the muscle in your heart. Because visceral fat is linked to a higher risk of a number of healthy illnesses like heart disease, it is seen as being more harmful than subcutaneous fat.
Side Effects of Metformin
Generally, Metformin is considered safe. However, there are certain side effects that come along when using this medication.
Some of the common side effects include vomiting, nausea and diarrhea. You can eat less food if you are experiencing unpleasant side effects. Consuming less food is a modest way of weight loss.
Off-bale use of Metformin for weight loss
The FDA has not approved the use of Metformin as a stand-alone therapy for weight reduction. This is because the weight loss effects of Metformin are inconsistent.
However, if doctors believe Metformin could be helpful, they may still prescribe it off-label. There are prediabetes patients with a high risk for metabolic complications, and off-label metformin use is more common.
Best ways to lose weight
Although it significantly lowers blood glucose, the generic drug metformin is not a weight loss aid. Despite this, maintaining a healthy weight is still crucial to managing your diabetes and lowering your risk of complications while also enhancing your general health and wellbeing.
FAQ about Metformin and Weight loss
1. Why does Metformin make you lose weight?
Metformin works by lowering the amount of visceral fat in your liver and muscle tissue to reduce your weight. Several of your body organs, such as the liver, stomach and intestines, are found in the abdominal cavity, where visceral fat is stored. It can also accumulate in muscles, including the muscle in your heart.
2. Can you lose belly fat with Metformin?
Despite Metformin having a beneficial effect on lipids, it has no clinically significant effect in reducing visceral fat mass. This trail gives credibility to the emerging data that Metformin is not a weight loss medicine.
3. How quickly do you lose weight on Metformin?
Metformin is not a quick fix despite studies showing that it may help with weight loss. When using Metformin, you will lose weight gradually, with the results starting to show after a year or two according to one-long-term sturdy. The amount of weight lost while using Metformin varies from one person to another.

4. How do I know Metformin is working?
Your blood sugar levels will not reduce instantly when using Metformin. However, after taking Metformin, the effects can be noticeable within 48 hours. You will have clear signs that Metformin after using it for 4 to 5 days.
5. Does Metformin speed up metabolism?
The decline in fasting RQ suggests that fat was the primary energy source used during this time. Animal studies demonstrated that the administration of Metformin resulted in a decrease in body fat independent of its anorexigenic effects, which is consistent with energy metabolism results.
6. How long can you stay on Metformin?
Some patients with prediabetes are recommended to use Metformin by the American Diabetes Association. You will be on Metformin for the long term if it is prescribed for you.
Unless you experience changes that require you to stop using it or complications to your health, the long-term duration could take even decades.
7. Can a non-diabetic take Metformin to lose weight?
There is mounting evidence that Metformin may help obese non-diabetic people lose weight (6,33). According to a systematic review, orlistat and Metformin both effectively lower the BMI of overweight or obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
8. Does Metformin make you poop?
It is not clear which mechanism metformin uses in lowering blood sugar concentration. However, it was found that Metformin promotes the excretion of sugar into the stool according to the bioimaging study on humans.
9. Does coffee affect Metformin?
Coffee contains caffeine. Metformin works by reducing how fast how your body breaks down caffeine. Therefore, caffeine in coffee might have increased effects and side effects when you take it with Metformin.
10. Should you drink a lot of water when taking Metformin?
In order to help reduce stomach or bowel side effects that may occur during the first few weeks of treatment, it is recommended that you take Metformin with water. It would be best if you drank a full glass of water while swallowing the tablet or extended-release tablet.
11. Is Metformin best taken at night or in the morning?
It is best to take Metformin at bedtime instead of supper time if you are taking it as Glucophage retard to improve diabetes control by reducing morning hyperglycemia.
12. Do I need to check blood sugar while taking Metformin?
When taking oral medications like Glucophage (Metformin), home testing is not typically necessary. Every three to six months, doctors generally request a blood test called a hemoglobin A1C test in place of testing.
13. How long does 500mg of Metformin last?
After taking Metformin (Glucophage), it will stay in your system for up to 96.8 hours or around four days. The half-life elimination of Metformin is around 17.6 hours.
14. What is the most common side effect of Metformin?
There are side effects that you may experience when using Metformin for the first time. Some of the side effects that you may have are nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. With time, these side effects disappear. You can take Metformin with a meal to reduce the side effects.

Do Diabetes Medications Cause Weight Gain?
Diabetes Medications – In the USA alone, a little over 10% of all people have some form of diabetes. For those who don’t know enough about diabetes, the long and short of it is that this occurs when your body can’t produce enough insulin.
When the body is short on insulin the body’s blood glucose (blood sugar) can rise to levels that are unsafe for the body. Out of the many people who suffer from diabetes, there are quite a few who have Type 2 diabetes.
Despite the serious nature of diabetes, there are many ways to treat this condition. One thing that people with diabetes do need to understand is that their lifestyle needs to change.
But there are also medications and even a few remedies that do work when it comes to keeping one’s glucose levels stabilized. One of the main concerns for anyone however is finding the right treatment, since there are plenty of medications that can have serious side effects.
Some medications can affect a person’s weight, which is not intended but can be a negative side effect. Not all diabetes medications will affect a person’s weight, as the body chemistry of each person is different and needs to be taken into account. This article has been written to discuss the different medications used for diabetes and how they can affect those who need them.
Why do some diabetes medications cause weight gain?
The average diabetes medications tend to cause fluctuations in weight by affecting how sugar is processed and used within the body.
Typically, insulin will help the body turn sugars that are derived from food into energy that will help to fuel the body. Insulin makes it possible for sugar to break down in your body so that it can be utilized efficiently. This process can help to lower your blood sugar.
When there’s too much sugar in your blood, the insulin in your system sends a signal to the liver to convert the sugar into fat. Over time, this added fat can cause increased weight gain.
When people use insulin as a medication to balance out their system, it will act like natural insulin. This is necessary to help avoid the process of sugar being turned into fat continually.
The side effect of some medications is that they will signal your body to produce even more insulin, which can lead to weight gain. On the flip side, some medications will aid in getting rid of excess sugar in the body. Less sugar means less material to turn into fat. The result, in this case, is that weight loss could occur instead.
Is weight gain or weight loss more common with diabetes medication?
To be honest, neither gain nor loss is common with diabetes medications. There are several types of medications available, and sometimes it becomes a process to figure out what will work the best for each individual.
Every medication is designed to work a bit differently to lower blood sugar levels. The risk of weight gain or loss depends heavily on the medication and what it’s meant to do.
The unfortunate aspect of weight gain is that it can and does discourage some people from discontinuing their usage. When this happens, the risk of complications begins to rise. It’s important to keep your healthcare provider informed when taking any medication, as they can recommend something else if you experience any side effects.
How long do you need to take diabetes medication before weight changes can be noticed?
Changes can occur in the first few months. Some people taking diabetes medication have reported weight gain in the first 6 months. This side effect does vary from person to person and can depend heavily on the amount of exercise a person engages in, as well as their diet.
Which diabetes medications are known to cause weight gain?
Four groups of medication have been seen to cause weight gain. The feature that all of them share is that they affect the insulin levels in the body.
Insulin:
As one of the most common medications for diabetes, this works by stimulating the pancreas to produce a greater amount of insulin.
Sulfonylureas:
This type of medication also leads to weight gain as more sugars are turned into fat. The primary medications that are known to increase weight gain include: Amaryl, Glucotrol, and Glyburide
Thiazolidinediones:
These are another common group of medications that can affect weight gain. These medications tend to lower blood sugar by making the body more sensitive to insulin. Two FDA-approved substances are Actos and Avandia.
Meglitinides:
This group of medications also force the pancreas to produce more insulin. Weight gain on these medications has been noted as being up 7 lbs. in the first 3 months of usage. The two available forms of this medication are Starlix and Repaglinide.
Which diabetes medications cause weight loss?
Four medications can cause weight loss when taken. Much like those that cause weight gain, they work differently with each person that takes them.
GLP-1 agonists:
This is a group of medications that have been seeing a rise in popularity when it comes to helping diabetes and causing weight loss. On top of telling the pancreas to produce insulin, these medications can make a person feel full between meals.
Studies have shown that people using these medications have lost up to 13 lbs. There are several medications able to be used at this time, such as Trulicity, Byetta, Victoza, and Ozempic to name a few.
SGLT-2 Inhibitors:
Some people have noted weight loss after about 6 weeks while taking these medications, which include Invokana, Farxiga, and Jardiance to name a few.
Metformin:
The particular medication doesn’t always promote weight loss, but it does tend to make the body more sensitive to natural insulin. The results can take up to a year to notice if weight loss does occur.
Pramlintide:
This is a form of amylin that is made in a lab and is used to slow down food movement through the stomach. It can cause weight loss of anywhere from 4 to 7 lbs. depending on the individual.
Several medications have little to no effect on a person’s weight such as DPP-4, Nesina, Tradjenta, Onglyza, and Januvia to name a few. The trick with weight gain or loss when it comes to diabetes is how often a person exercises and what their diet is like.
The Bottom Line
Diabetes medications are needed for those whose bodies are having trouble producing insulin at normal levels. But some medications can cause weight gain or loss as a side effect. What it comes down to is how healthy of a lifestyle an individual has, since the different effects medications can cause will be determined in part by the habits of the person taking the medication.

What Are Common Diabetic Symptoms?
Diabetes affects up to 10% of the American population, according to the CDC. It is on the rise, with at least 1.5 million cases diagnosed yearly. Sadly, 1 in every 5 people is unaware they have the disease in the United States. Below shall be discussed the different diabetic symptoms.
The Negative Effects of High Blood Sugar Levels to the Body
The eyes
Diabetes increases your chances of experiencing dangerous vision problems that could lead to blindness. Some of these issues include:
- Glaucoma: Damages the nerve connecting your eye to the brain, leading to serious vision problems.
- Cataracts: The lens of your eye gets affected and becomes cloudy
- Retinopathy: The retina at the back of your eye changes.
The heart
Your heart’s nerves and blood vessels are at risk of damage after experiencing high blood sugar for a prolonged period. This increases the risk of heart diseases, including heart failure, stroke, and heart attacks.
The risk increases even more when you suffer from high cholesterol levels.
The kidneys
Diabetes affects the functioning of your kidney’s blood vessels. After a while, they may even stop working, leading to kidney failure.
The feet
With high blood sugar, blood flow to your feet is negatively affected. This leads to nerve damage which can cause sores, scrapes, and cuts not to heal in good time. With nerve damage, your feet may get injured without your knowledge leading to infections.
Sometimes, the infections get worse, and one may need an amputation.
The nerves
High blood sugar causes diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage). The side effects include pain, numbness, and tingling sensations, primarily in your feet.
The skin
Your skin becomes weak when you have diabetes. Scaly patches, yeast infections, and itching are some issues you may experience on your skin.
Erectile dysfunction
Since high blood sugar affects blood flow and nerves in the body, it can get complicated for a man to maintain an erection. Men with diabetes may experience a hard sex life.
Is it Possible for You to Tell if You Have Diabetes?
Well, yes and no, depending on the type you have. Warning signs for type 2 diabetes are quite subtle and can go undetected until one starts experiencing long-term effects. For type 1 diabetes, on the other hand, the signs appear in less than a month and are much more aggressive.
Early symptoms are a result of higher than normal glucose levels.
Diabetes Warning Signs / Diabetic Symptoms
Early signs of diabetes are quite similar for both type 1 and type 2, and they include:
1. Feeling thirsty constantly and peeing more often than usual – Diabetic Symptoms
Normally, humans pee up to 7 times a day. However, with diabetes, the frequency increases. Our bodies reabsorb glucose from the kidneys, but high blood sugar makes it hard for the necessary amount to be reabsorbed.
This leads to the production of more urine, which requires fluid from your body. As a result, you pee more often than usual, and because of passing that large amount of liquid, you get thirsty more often than average.
Interestingly the more liquids you intake, the more you pee.
2. Blurred vision – Diabetic Symptoms
The lenses of your eyes may swell up due to changes in body fluid levels when you have diabetes. This leads to poor vision because the shapes of your eyes change.
3. Hunger and fatigue – Diabetic Symptoms
For energy, the body converts the food you eat into glucose. However, you need insulin to absorb the converted glucose into your body cells. With diabetes, your body may become insulin resistant or produce it in fewer quantities.
This leads to fatigue and feeling hungry more than usual.
4. Itchy skin and dry mouth – Diabetic Symptoms
With diabetes, you lose so much fluid from your body through urination. The body needs this fluid to keep your skin and mouth hydrated. Without it, your skin becomes itchy while your mouth experiences dryness.
Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms
- Frequent nausea and vomiting
Our bodies burn fat and produce ketones. When you have type 1 diabetes, the ketone levels produced are higher than expected, and they can lead to a dangerous condition known as diabetic ketoacidosis.
High ketone levels make you feel sick in the stomach, causing you to vomit and feel nausea more often than normal.
- Unexpected weight loss
Since the body fails to absorb as much glucose as needed, it burns fats and muscles for energy. This will cause you to lose weight rapidly without even changing your diet. Taking foods high in trans fatty acids is advised to boost your health.
Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
Type two diabetes symptoms take some time to show. These symptoms occur due to high glucose levels in your body for a prolonged period, and they include:
- Numbness or pain in your legs and feet
These may occur due to nerve damage caused by the disease.
- Persistent yeast infection in different parts of the body
Men and women with type 2 diabetes experience yeast infections in parts of the body where it is warm, and the skin folds under the breasts, between the toes and fingers, and around the sex organs.
This is because yeast feeds on glucose, and these areas have plenty of glucose.
- Sores and cuts begin to heal slowly
High blood sugar levels affect blood flow and also cause nerve damage. Because of these, your sores and cuts start to heal slower than before.
What are Gestational Diabetic Symptoms?
When pregnant, you may experience no signs of high blood sugar levels. However, you may notice that you urinate more frequently and get thirsty often.
How to Tell you are Experiencing Diabetes Complications
Warning signs of type 2 diabetes include:
- Impaired vision
- Erectile dysfunction
- Cuts and sores heal slower
- Itchiness, especially around the sex organs
- Recurring yeast infections
- Your skin may appear darker or velvety around the neck, groin, and armpits. This condition is known as acanthosis nigricans
- You may begin to gain weight
What is Hypoglycemia?
Also known as low blood sugar, hypoglycemia occurs when your glucose and sugar levels in the blood are too low to produce energy. Some signs include:
- Trembling
- Nervousness
- Confusion
- Impatience and crankiness
- Dizziness
- Frequent hunger
- Always feeling sleepy
- Recurring fatigue
- Feeling cold, clammy, or sweating more than usual
- Numbness or tingling sensations around your cheeks, tongue, and lips
With hypoglycemia, you may notice these few changes in your body:
- Problems with body coordination
- Repeated seizures
- Your skin gets pale
- A faster heartbeat rate
- Recurring headaches
- Blurred vision
- Unusual nightmares and crying in your sleep
What is Hyperglycemia?
The medical term for hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) is hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS). This condition has many warning signs, including those we have listed for diabetes, and they are:
- Frequent urination
- Persistent hunger
- Feeling thirsty frequently
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Sugar in the urine
- Blurred vision
- Tingling sensations or numbness in the feet
- Skin and vaginal infections
- Unexpected weight loss
- Slow-healing cuts and sores
- Blood glucose levels that are over 180 mg/dl
Hyperglycemia is a severe condition in either type of diabetes (more common in type 2) which can lead to diabetic coma and sometimes death. When your blood sugar levels skyrocket, you end up more dehydrated, and symptoms include:
- Persistent thirst
- Dry mouth
- Blood sugar levels above 600 mg/dl
- Confusion and insomnia
- Recurring fever of over 101 F
- Dry skin that stays warm with no sweat
- Hallucinations
- Eventual vision loss
- One side of your body becomes weak
What can You do Lower your Risk of Diabetes?
Adopting a good lifestyle and feeding habits is a sure way to reduce your risk of getting diabetes. Make these few things a part of your routine:
Maintain strict blood sugar control
To avoid diabetes, try your best to maintain your blood sugar levels within these ranges:
Before meals: 70-130 mg/dl
2 hours after meals: below 180 mg/dl
AIC or glycated hemoglobin level at 7%
Keep an eye on your blood pressure and cholesterol levels
Aside from diabetes, you may develop more severe health issues when your cholesterol and blood pressure rise above normal such as heart diseases. Try your best to maintain your cholesterol at or below 200 and your blood pressure below 140/190.
If it becomes a problem, your doctor can prescribe medication to help maintain these levels.
Go for checkups regularly
Your doctor can examine your blood and urine and perform other tests to detect any issues your body may be experiencing. These visits are vital because many diabetes complications have no obvious warning signs.
Avoid smoking
Inhalation of smoke raises your blood pressure and negatively affects your body’s blood flow. There are treatments available that can help you quit smoking.
Look for any cuts, bruises, ingrown toenails, redness, or swelling. Ensure you dry your feet after washing and apply some lotion to avoid cracked heels and dry skin. Protect your feet by wearing shoes outside and at the beach, and you can add socks during the cold weather.
Keep your eyes protected
Go for eye checkups at least once a year. This way, you will catch any issues early enough before they worsen.
Examine your feet every day
Before taking a bath, ensure the water is not too hot not to burn your feet, and always keep your toenails short and clean.
Keep your skin healthy
On areas where your skin rubs together, such as your armpits, apply talcum for protection. Avoid hot baths and showers or dry soaps and bath gels. Always keep your skin moisturized with hand and body lotion.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is advised that you get tested for diabetes, especially if you have other conditions that might put you at risk or are above the age of 45. This will help you mitigate the side effects such as nerve damage.
Visit or call a doctor if you experience the following:
- Nausea and vomiting frequently
- Urinating a lot
- Consistent stomach aches
- You begin to breathe deeper and faster than normal
- Your breath smells sweet (like nail polish remover). This is due to high ketone levels in your body.)

Controlling Diabetes with Diet
Controlling Diabetes with Diet – With a healthy diet and with regular exercise, diabetes can be controlled in a way that it won’t get any worse. Maintaining normal blood sugar levels can lessen the risk of having severe diabetes.
Controlling Diabetes with Diet, how? Here are a few general things you need to balance to have and maintain normal blood glucose levels:
- Taking prescribed medication for Diabetes
- Eating the right kind of food
- Doing regular exercise or any physical activity
Being able to manage these three basic things will definitely help achieve the optimal blood glucose levels.
What are Carbohydrates?
What is the role or what is the purpose of carbohydrates? Well, carbohydrates are the main source of energy for our body. About half of our daily calorie intake should have carbohydrates to have enough energy to get through the day.
What different food that are carbohydrates? These following carbohydrates break down into sugar in our blood:
- Bread
- Grains
- Starchy Veggies
- Fruits
- Dairy Products
- Sweets
Once the carbohydrates are broken down to sugar, the sugar gets stored and is as energy for the body. The presence of insulin is important in transporting the sugar to reach its designated storage area. Having too little insulin in the body will result in having high blood sugar levels. Controlling diabetes with diet is one of many ways to help reduce the risk of having severe diabetes.
Counting Carbohydrates? How does it work? Controlling Diabetes with Diet
Carb-counting (Carbohydrate counting) is the method of literally counting the amount of carbohydrates from the food or drinks you consume. Controlling diabetes with diet would include controlling how much carbohydrates you put in your body by distributing the amount evenly over your meals.
How do you know the amount of carbohydrates in your food or drink?
It is most probably listed on food labels at the back of the food packaging or it can be easily searched from the internet. It is better to read the labels including the serving size.
An example is 1 slice of toasted bread, with 1 teaspoon of peanutbutter, half of a regular sized banana, and 1 cup of regular milk is equivalent to three (3) carbohydrate servings or forty-five (45g) grams of carbs. (1 serving = 15 grams of carbohydrates)
Though google may provide a general idea of the amount of carbs in the food / drink you eat, having a registered dietitian by your side is definitely a bonus. A dietitian will help you with controlling diabetes with diet.
Are there Good and Bad carbohydrates?
The better carbs are those with a higher amount of fiber in them. Several research shows that getting right amounts of fiber regularly is beneficial for our health.
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate wherein fiber-rich foods will generally have more nutrients for the body. That explains why fiber is not in meat, fat and not even in dairy products. The following are examples of carbs with fiber are the following:
- Whole grain bread
- Whole grain cereals
- Whole grain pasta
- Brown Rice
- Barley
- Beans and Lentils
Fruits are also a great source of fiber. It is suggested that some fruits be eaten with their skin on. However, don’t forget to wash them. Fresh fruits and vegetables will always be better than canned ones. Less processed would mean more fiber.

What does Regular Exercise mean?
Controlling diabetes with diet would not only mean the regulation of food intake but also the amount of physical activity you do daily. With regular exercise (which would mean any physical activity such as dancing, home workouts, walking, gardening, etc), the following benefits will be achieved:
- Insulin Sensitivity Increases
- Promotes Healthy Bones
- Promotes healthy weight
- Improves Sleep
- Help lower blood glucose levels
It is always best to check with your doctor!
Controlling Diabetes with Diet

5 Ways to Control Your Blood Sugar Levels

Type II diabetes is the common type of diabetes that a lot of people suffer from. It’s what is otherwise known as the Adult Onset Diabetes. This happens when your body fails to efficiently utilize insulin.
Diabetes basically means that your blood glucose levels are higher than the normal level. Since your body fails to react to insulin properly, the glucose from the food that you ate will not be synthesized into energy which is needed by the cells in your body and instead, it stays in your bloodstream causing a high glucose levels in the blood. Overtime, when this problem is not addressed, it can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular diseases, blindness, kidney failure, and problems with the nerves.
Ways to Avoid Blood Sugar Spikes and Dips
Although there are medicines that can help alleviate the symptoms, it’s always better to have a blood sugar support plan ready at hand. The best way to avoid the blood glucose spikes and dips is by changing your lifestyle. Here are 7 ways you can do to control your blood sugar:
1. Eat Nuts

Nuts are known to have healthy fats and have an effect on slowing down the body’s glucose absorption.
2. Exercise Regularly
Exercising has a lot of benefits – including regulation of blood sugar levels. Regular exercise helps you lose weight and is effective in increasing the body’s insulin sensitivity.
3. Include a Few Servings of Veggies on Your Diet
Vegetables such as broccoli, cucumber, and carrots contain less starch and are rich in fiber. These foods are a helpful blood sugar support while giving your body extra nutrients.
4. Manage Stress
When the body undergoes stress, the hormones that are released by the brain can cause blood sugar to rise. Research shows that a few minutes of meditation can help lower the blood’s sugar level.
5. Drink Lots of Water
Drinking lots of water can help in cleansing the body of excess sugar through urine. It’s also important to avoid drinks that are rich in sugar when you have a high blood glucose level.
Along with these tips on how to keep a normal blood sugar level, taking supplements such as Lally Naturals Blood Sugar Support can also help. Prevention is always better than cure so start taking baby steps to regulate your blood sugar level and avoid complications in the future.
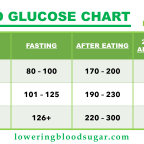
Blood Glucose Chart – Blood Sugar Levels for Adults
Blood Glucose Chart – Blood Sugar Levels for Adults
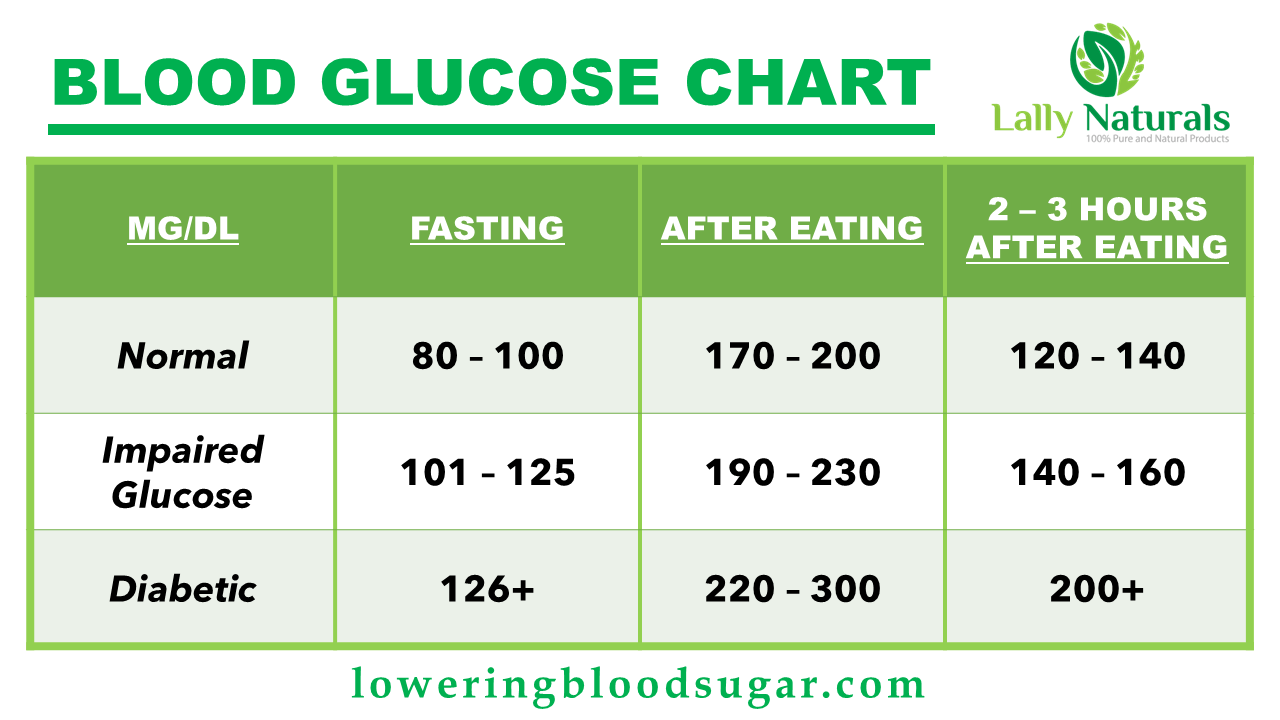
Blood Glucose Chart
Blood Sugar Levels for Adults With Diabetes
Be aware of changes in your body. There are common symptoms that cannot be ignored and would indicate that you have fluctuating blood sugar levels and should manage the same. Fatigue, sugar cravings, thirsty all the time, weight loss, mood swings, frequent infections, heavy breathing and trouble exercising are one of these signs that should not be taken for granted.
Manage your blood sugar with the help of natural blood sugar support supplements such as Lally Naturals Blood Sugar Support Supplements. Lally Naturals Blood Sugar Support utilizes the power of twenty (20) synergistic ingredients to provide one of the most comprehensive, potent blood sugar regulator & stabilizer products available today. It also effectively supports weight loss & cardiovascular health.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

Most Effective Tips to Avoid Blood Sugar Spikes
Diabetes Supplements – The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that as of today, there are an  estimated number of 30.1 million are suffering from diabetes and 84.1 million have prediabetes. Although the numbers remain steady, the United States still considers this disease to be a growing health problem. With the current statistics, there’s no denying that the need diabetes supplements are increasing.
estimated number of 30.1 million are suffering from diabetes and 84.1 million have prediabetes. Although the numbers remain steady, the United States still considers this disease to be a growing health problem. With the current statistics, there’s no denying that the need diabetes supplements are increasing.
Blood sugar spikes can happen when the blood sugar in the body rises then falls as fast after meals. As a result, the body cannot effectively utilize the sugar. Without intervention, these constant spikes could eventually lead to type II diabetes.
Most Effective Tips to Avoid Blood Sugar Spikes
There are, however, ways in which we can prevent blood sugar spikes from happening. Let’s look at some of them:
1. Switch to a Low Carb Diet
Carbohydrates are the number 1 culprit in increased blood sugar in the body. Studies have shown that a low carb diet can help a person lose weight and weight loss in turn, can help prevent blood sugar spikes.
2. Eat More Fruits and Veggies.
Fruits and vegetables can be a great alternative carbohydrate source. They are also rich in fiber which slows down carbohydrate break down thereby preventing blood sugar spikes.
 3. Cut off Sugar Intake
3. Cut off Sugar Intake
An average American consumes about 22 teaspoons of sugar every day. While some may be the normal table sugar, most of it comes from artificial sugar.
4. Consider Incorporating Spices in Your Diet
Cinnamon is known to be effective in regulating blood sugar levels by 3-5% which makes it an important ingredient in many diabetes supplements. It’s important to remember that although this is a good spice for diabetes, you must go easy on it.
Diabetes supplements are extremely important in stabilizing the blood sugar levels in the body. Manage your blood sugar with the help of natural blood sugar support supplements such as Lally Naturals Blood Sugar Support Supplements. Lally Naturals Blood Sugar Support utilizes the power of twenty (20) synergistic ingredients to provide one of the most comprehensive, potent blood sugar regulator & stabilizer products available today. It also effectively supports weight loss & cardiovascular health. Lally Naturals Blood Sugar Support is packed with vitamins and minerals needed by every person with diabetes. Along with exercise and proper diet, every diabetic person can expect blood sugar spikes to happen rarely.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

Blood Sugar Support to Balance Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar or glucose is the main source of energy that is obtained from the food we eat. Glucose is the main sugar in our body that  is carried to all cell through the blood stream. Our body regulates the level of blood sugar.
is carried to all cell through the blood stream. Our body regulates the level of blood sugar.
High Blood Sugar is manifested when you are losing weight, have blurred vision, very thirsty and tired and have frequent urination. When you have high blood sugar level, you may feel sick to your stomach, throw up or feel faint. It also causes you to lose fluid.
Low Blood Sugar is known as hypoglycemia. It is caused by too much insulin, delayed meal, missed meal, too much exercise or too much alcohol. It may also be a side effect from medicines taken for other health problems.
Other Ways for Blood Sugar Support & Maintaining Blood Sugar
Blood sugar support is needed to help balance blood sugar levels for the body to function properly.
– Eat a low-processed and anti-inflammatory diet
Balancing carbohydrates and sugar with protein and fats in your diet and getting it from whole and real food is one way of managing and treating and preventing diabetes. Consuming carbs and sugar with protein fiber and healthy fats can slow down the absorption into the bloodstream of sugar, aid in managing your appetite and helps in your digestion and metabolism. Healthy fats include virgin coconut oi, nuts and seeds and avocado. High-fiber foods include veggies, whole pieces of fruits and beans and grains.
Other foods and drinks that also can help stabilize blood sugar are green tea, cinnamon, apple cider vinegar, herbal tea, spices and fresh herbs.
– Use alternative carbs and sweeteners
To aid in maintaining blood sugar, avoid using refined flour and added sugars like cane sugar, beet sugar or beet juice. Use natural sweeteners like raw honey, dates, pure maple syrup or molasses in small portions daily. Whole grain flours should be used or coconut flour. Drink water, seltzer, herbal tea or black tea and coffee only. And coffee should be taken only up to two cups. Stay away from sweetened alcoholic drinks.
– Regular exercise
 Exercise can manage blood sugar. It helps lower blood sugar as the cells in your muscles take up more glucose for energy and tissue repair when you do short exercise while helps make cells more susceptible to insulin and helps prevent its resistance when doing long-term exercises. Exercises like cycling, running, swimming and lifting weights increases insulin sensitivity enabling your cells to better take up glucose during and after doing exercises.
Exercise can manage blood sugar. It helps lower blood sugar as the cells in your muscles take up more glucose for energy and tissue repair when you do short exercise while helps make cells more susceptible to insulin and helps prevent its resistance when doing long-term exercises. Exercises like cycling, running, swimming and lifting weights increases insulin sensitivity enabling your cells to better take up glucose during and after doing exercises.
– Manage stress
Stress raises release of cortisol, the stress hormone, and increases cravings for “comfort foods” and interrupts sleep. These factors cause high blood sugar level. Take time to de stress or try coping up with life struggles by doing the natural stress relievers like exercise, mediation and yoga. Spend more time outdoors, talk with friends and family or joining groups in your community are also helpful for diabetics and insulin resistant persons to manage stress and eventually lower down blood sugar.
– Get enough sleep
Lack of sleep can increase stress and appetite. These hormones like cortisol makes you hungry and crave for sugary snacks. Too little sleep, poor quality of sleep and sleeping at the wrong time impair secretion of insulin. In order to help balance blood sugar, try to get enough hours of sleep of between seven to nine hours and stick to it.
Be aware of changes in your body. There are common symptoms that cannot be ignored and would indicate that you have fluctuating blood sugar levels and should manage the same. Fatigue, sugar cravings, thirsty all the time, weight loss, mood swings, frequent infections, heavy breathing and trouble exercising are one of these signs that should not be taken for granted.
Manage your blood sugar with the help of natural blood sugar support supplements such as Lally Naturals Blood Sugar Support Supplements. Lally Naturals Blood Sugar Support utilizes the power of twenty (20) synergistic ingredients to provide one of the most comprehensive, potent blood sugar regulator & stabilizer products available today. It also effectively supports weight loss & cardiovascular health.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()